Balancing chemical equations
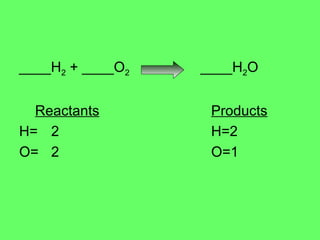
- 2. 1. Count the number of atoms on each side. ____H 2 + ____O 2 ____H 2 O 1 Reactants Products H= 2 H=2 O= 2 O=1 2. See that there are more O’s on the left than the right. Both sides need to have the same number of atoms. 3. Whatever number you put in front of a compound effects all element in the compound. 4. You cannot change the subscript in an equation. 5. If there are ( ) with a subscript the subscript effects all elements in the compound. (PO 4 ) 2 so P=2 O=8 6. If there is no subscript ex. O it is always a 1for ex O 1 .
- 3. ____H 2 + ____O 2 ____H 2 O Reactants Products H= 2 H=2 O= 2 O=1
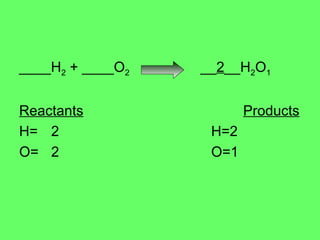
- 4. ____H 2 + ____O 2 __ 2 __H 2 O 1 Reactants Products H= 2 H=2 O= 2 O=1
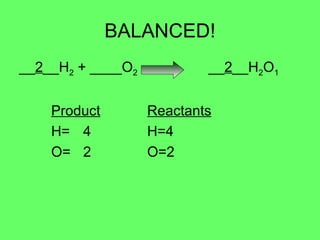
- 5. BALANCED! __ 2 __H 2 + ____O 2 __ 2 __H 2 O 1 Product Reactants H= 4 H=4 O= 2 O=2
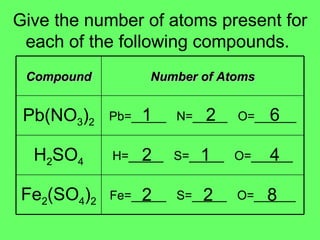
- 6. Give the number of atoms present for each of the following compounds. 1 2 6 2 1 4 2 2 8 Fe=_____ S=_____ O=______ Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 2 H=_____ S=_____ O=______ H 2 SO 4 Pb=_____ N=_____ O=______ Pb(NO 3 ) 2 Number of Atoms Compound
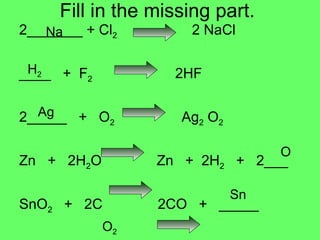
- 7. Fill in the missing part. 2_______ + Cl 2 2 NaCl ____ + F 2 2HF 2_____ + O 2 Ag 2 O 2 Zn + 2H 2 O Zn + 2H 2 + 2___ SnO 2 + 2C 2CO + _____ 2 NO + _______ 2NO 2 Na H 2 Ag O Sn O 2
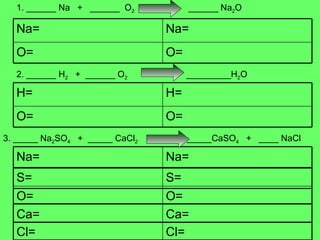
- 8. 1. ______ Na + ______ O 2 ______ Na 2 O 2. ______ H 2 + ______ O 2 _________H 2 O 3. _____ Na 2 SO 4 + _____ CaCl 2 _____CaSO 4 + ____ NaCl O= O= Na= Na= O= O= H= H= Ca= Ca= O= O= Cl= Cl= S= S= Na= Na=
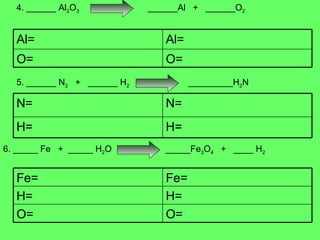
- 9. 4. ______ Al 2 O 3 ______Al + ______O 2 5. ______ N 2 + ______ H 2 _________H 2 N 6. _____ Fe + _____ H 2 O _____Fe 3 O 4 + ____ H 2 O= O= Al= Al= H= H= N= N= O= H= Fe= O= H= Fe=
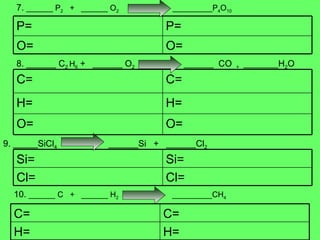
- 10. 7. ______ P 2 + ______ O 2 _________P 4 O 10 8. ______ C 2 H 6 + ______ O 2 ______ CO + _______H 2 O 9. _____SiCl 4 ______Si + ______Cl 2 10. ______ C + ______ H 2 _________CH 4 O= O= P= P= H= H= O= O= C= C= Cl= Cl= Si= Si= H= H= C= C=
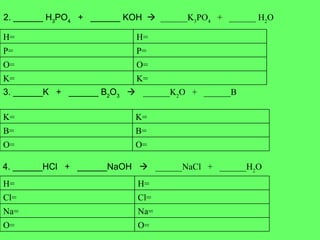
- 11. 2. ______ H 3 PO 4 + ______ KOH ïƒ ______K 3 PO 4 + ______ H 2 O 3. ______K + ______ B 2 O 3 ïƒ ______K 2 O + ______B 4. ______HCl + ______NaOH ïƒ ______NaCl + ______H 2 O K= K= O= O= P= P= H= H= O= O= B= B= K= K= O= O= Na= Na= Cl= Cl= H= H=
- 12. 5. ______Na + ______NaNO 3 ïƒ ______Na 2 O + ______N 2 6. ______ C + ______S 8 ïƒ ______CS 2 7. ______Na + ______O 2 ïƒ ______Na 2 O 2 8. ______N 2 + ______O 2 ïƒ ______N 2 O 2 O= O= N= N= Na= Na= S= S= C= C= O= O= Na= Na= O= O= N= N=
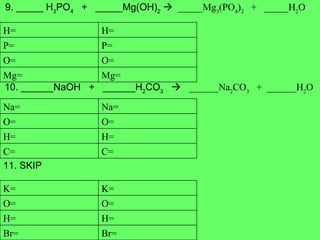
- 13. 9. _____ H 3 PO 4 + _____Mg(OH) 2 ïƒ _____Mg 3 (PO 4 ) 2 + _____H 2 O 10. ______NaOH + ______H 2 CO 3 ïƒ ______Na 2 CO 3 + ______H 2 O 11. SKIP Mg= Mg= O= O= P= P= H= H= C= C= H= H= O= O= Na= Na= Br= Br= H= H= O= O= K= K=
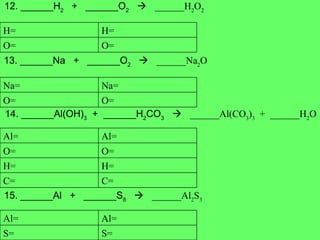
- 14. 12. ______H 2 + ______O 2 ïƒ ______H 2 O 2 13. ______Na + ______O 2 ïƒ ______Na 2 O 14. ______Al(OH) 3 + ______H 2 CO 3 ïƒ ______Al(CO 3 ) 3 + ______H 2 O 15. ______Al + ______S 8 ïƒ ______Al 2 S 3 O= O= H= H= O= O= Na= Na= C= C= H= H= O= O= Al= Al= S= S= Al= Al=
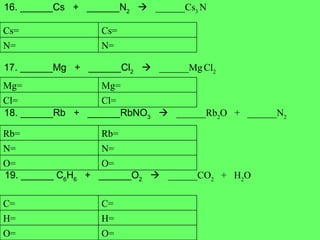
- 15. 16. ______Cs + ______N 2 ïƒ ______Cs 3 N 17. ______Mg + ______Cl 2 ïƒ ______Mg Cl 2 18. ______Rb + ______RbNO 3 ïƒ ______Rb 2 O + ______N 2 19. ______ C 6 H 6 + ______O 2 ïƒ ______CO 2 + H 2 O N= N= Cs= Cs= Cl= Cl= Mg= Mg= O= O= N= N= Rb= Rb= O= O= H= H= C= C=
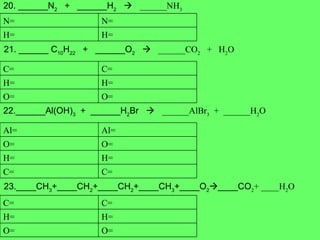
- 16. 20. ______N 2 + ______H 2 ïƒ ______NH 3 21. ______ C 10 H 22 + ______O 2 ïƒ ______CO 2 + H 2 O 22.______Al(OH) 3 + ______H 2 Br ïƒ ______AlBr 3 + ______H 2 O 23.____CH 3 +____CH 2 +____CH 2 +____CH 3 +____O 2 ïƒ ____CO 2 + ____H 2 O H= H= N= N= O= O= H= H= C= C= C= C= H= H= O= O= Al= Al= O= O= H= H= C= C=
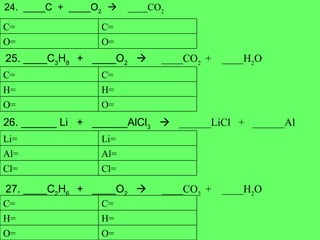
- 17. 24. ____C + ____O 2 ïƒ ____CO 2 25. ____C 3 H 8 + ____O 2 ïƒ ____CO 2 + ____H 2 O 26. ______ Li + ______AlCl 3 ïƒ ______LiCl + ______Al 27. ____C 2 H 6 + ____O 2 ïƒ ____CO 2 + ____H 2 O O= O= C= C= O= O= H= H= C= C= Cl= Cl= Al= Al= Li= Li= O= O= H= H= C= C=
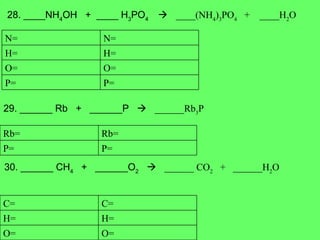
- 18. 28. ____NH 4 OH + ____ H 3 PO 4 ïƒ ____(NH 4 ) 3 PO 4 + ____H 2 O 29. ______ Rb + ______P ïƒ ______Rb 3 P 30. ______ CH 4 + ______O 2 ïƒ ______ CO 2 + ______H 2 O P= P= O= O= H= H= N= N= P= P= Rb= Rb= O= O= H= H= C= C=
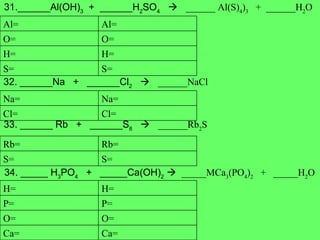
- 19. 31.______Al(OH) 3 + ______H 2 SO 4 ïƒ ______ Al(S) 4 ) 3 + ______H 2 O 32. ______Na + ______Cl 2 ïƒ ______NaCl 33. ______ Rb + ______S 8 ïƒ ______Rb 2 S 34. _____ H 3 PO 4 + _____Ca(OH) 2 ïƒ _____MCa 3 (PO 4 ) 2 + _____H 2 O S= S= H= H= O= O= Al= Al= Cl= Cl= Na= Na= S= S= Rb= Rb= Ca= Ca= O= O= P= P= H= H=
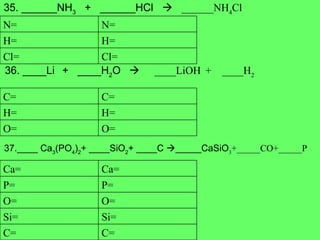
- 20. 35 . ______NH 3 + ______HCl ïƒ ______NH 4 Cl 36. ____Li + ____H 2 O ïƒ ____LiOH + ____H 2 37.____ Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 + ____SiO 2 + ____C ïƒ _____CaSiO 3 +_____CO+_____P Cl= Cl= H= H= N= N= O= O= H= H= C= C= C= C= Si= Si= O= O= P= P= Ca= Ca=
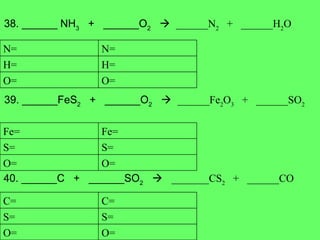
- 21. 38. ______ NH 3 + ______O 2 ïƒ ______N 2 + ______H 2 O 39. ______FeS 2 + ______O 2 ïƒ ______Fe 2 O 3 + ______SO 2 40. ______C + ______SO 2 ïƒ _______CS 2 + ______CO O= O= H= H= N= N= O= O= S= S= Fe= Fe= O= O= S= S= C= C=
- 22. 6 Types of Chemical Reactions
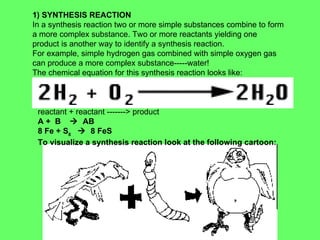
- 23. 1) SYNTHESIS REACTION In a synthesis reaction two or more simple substances combine to form a more complex substance. Two or more reactants yielding one product is another way to identify a synthesis reaction. For example, simple hydrogen gas combined with simple oxygen gas can produce a more complex substance-----water! The chemical equation for this synthesis reaction looks like: reactant + reactant -------> product A + B ïƒ AB 8 Fe + S 8 ïƒ 8 FeS To visualize a synthesis reaction look at the following cartoon:
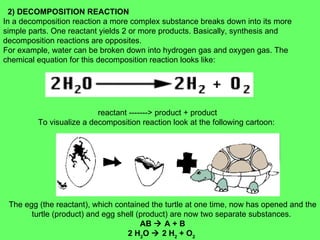
- 24.  2) DECOMPOSITION REACTION In a decomposition reaction a more complex substance breaks down into its more simple parts. One reactant yields 2 or more products. Basically, synthesis and decomposition reactions are opposites. For example, water can be broken down into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The chemical equation for this decomposition reaction looks like: reactant -------> product + product To visualize a decomposition reaction look at the following cartoon: The egg (the reactant), which contained the turtle at one time, now has opened and the turtle (product) and egg shell (product) are now two separate substances. AB ïƒ A + B 2 H 2 O ïƒ 2 H 2 + O 2
- 25. 3) SINGLE REPLACEMENT (DISPLACEMENT) REACTION In a single replacement reaction a single uncombined element replaces another in a compound. Two reactants yield two products. For example when zinc combines with hydrochloric acid, the zinc replaces hydrogen. The chemical equation for this single replacement reaction looks like: reactant + reactant ---------> product + product To visualize a single replacement reaction look at the following cartoon: Notice, the guy in the orange shirt steals the date of the other guy. So, a part of one of the reactants trades places and is in a different place among the products. A + BC ïƒ AC + B Mg + 2 H 2 O ïƒ Mg(OH) 2 + H 2
- 26. 4) DOUBLE REPLACEMENT (DISPLACEMENT) REACTION In a double replacement reaction parts of two compounds switch places to form two new compounds. Two reactants yield two products. For example when silver nitrate combines with sodium chloride, two new compounds--silver chloride and sodium nitrate are formed because the sodium and silver switched places. The chemical equation for this double replacement reaction looks like: reactant + reactant ---------> product + product To visualize a double replacement reaction look at the following cartoon: AB + CD ---> AD + CB Pb(NO 3 ) 2 + 2 KI ---> PbI 2 + 2 KNO 3
- 27. Both of these reactions are special DOUBLE REPLACEMENT (DISPLACEMENT) REACTION. 5) Acid-base : This is a special kind of double displacement reaction that takes place when an acid and base react with each other. Generally, the product of this reaction is some ionic salt and water: HBr + NaOH ---> NaBr + H2O 6) Combustion : A combustion reaction is when oxygen combines with another compound to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. C10H8 + 12 O2 ---> 10 CO2 + 4 H2O
- 28. Six Types of Chemical Reaction Worksheet Balance the following reactions and indicate which of the six types of chemical reaction are being represented:
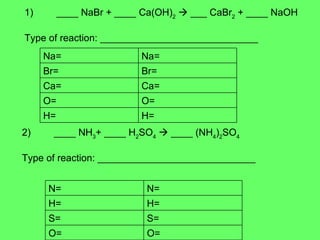
- 29. 1) ____ NaBr + ____ Ca(OH) 2 ïƒ ___ CaBr 2 + ____ NaOH Type of reaction: _____________________________ 2) ____ NH 3 + ____ H 2 SO 4 ïƒ ____ (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 Type of reaction: _____________________________ H= H= O= O= Ca= Ca= Br= Br= Na= Na= O= O= S= S= H= H= N= N=
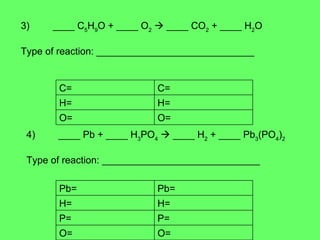
- 30. 3) ____ C 5 H 9 O + ____ O 2 ïƒ ____ CO 2 + ____ H 2 O Type of reaction: _____________________________ 4) ____ Pb + ____ H 3 PO 4 ïƒ ____ H 2 + ____ Pb 3 (PO 4 ) 2 Type of reaction: _____________________________ O= O= H= H= C= C= O= O= P= P= H= H= Pb= Pb=
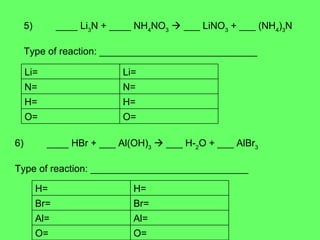
- 31. 5) ____ Li 3 N + ____ NH 4 NO 3 ïƒ ___ LiNO 3 + ___ (NH 4 ) 3 N Type of reaction: _____________________________ 6) ____ HBr + ___ Al(OH) 3 ïƒ ___ H 2 O + ___ AlBr 3 Type of reaction: _____________________________ O= O= H= H= N= N= Li= Li= O= O= Al= Al= Br= Br= H= H=
- 32. 7) What’s the main difference between a double displacement reaction and an acid-base reaction? Acid-base reactions form water.
- 33. 8) Combustion reactions always result in the formation of water. What other types of chemical reaction may result in the formation of water? Write examples of these reactions on the opposite side of this paper. Acid-base: HCl + NaOH ïƒ H2O + NaCl Synthesis: 2 H2 + O2 ïƒ 2 H2O Decomposition: NH4OH ïƒ NH3 + H2O Single displacement: H2 + 2 NaOH ïƒ 2 Na + 2 H2O (not common)