Bao cao trang bi dien
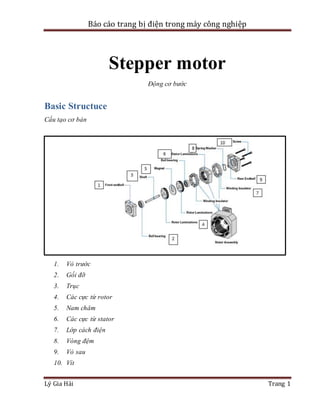
- 1. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 1 Stepper motor Động cơ bước Basic Structuce Cấu tạo cơ bản 1. Vỏ trước 2. Gối đỡ 3. Trục 4. Các cực từ rotor 5. Nam châm 6. Các cực từ stator 7. Lớp cách điện 8. Vòng đệm 9. Vỏ sau 10. Vít
- 2. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 2 Working Principle Nguyên tắc hoạt động Stepper motor is a brushless DC motor that rotates in steps. This is very useful because it can be precisely positioned without any feedback sensor, which represents an open-loop controller. The stepper motor consists of a rotor that is generally a permanent magnet and it is surrounded by the windings of the stator. As we activate the windings step by step in a particular order and let a current flow through them they will magnetize the stator and make electromagnetic poles respectively that will cause propulsion to the motor. So that’ the basic working principle of the stepper motors. Động cơ bước là một động cơ DC không chổi than quay theo các bước. Điều này rất hữu ích vì nó có thể được định vị chính xác mà không cần bất kỳ cảm biến phản hồi nào, động cơ bước đại diện cho bộ điều khiển vòng hở. Động cơ bước bao gồm một rôto thường là một nam châm vĩnh cửu và nó được bao quanh bởi các cuộn dây của stato. Khi chúng ta kích hoạt các cuộn dây từng bước theo một thứ tự cụ thể và để dòng điện chạy qua chúng, chúng sẽ từ hóa stato và tạo ra các cực điện từ tương ứng gây ra lực đẩy cho động cơ. Và đây là Nguyên tắc hoạt động cơ bản của các động cơ bước. Driving Modes Các chế độ vận hành There are several different ways of driving the stepper motor. The first one is the Wave Drive or Single-Coil Excitation. In this mode we active just one coil at a time which means that for this example of motor with 4 coils, the rotor will make full cycle in 4 steps. Có nhiều cách khác nhau để điều khiển động cơ bước. Đầu tiên là điều khiển sóng kích thích hoặc một cuộn dây kích thích. Trong chế độ này, chúng ta chỉ kích hoạt một cuộn dây tại một thời điểm, điều đó có nghĩa là với ví dụ này về động cơ có 4 cuộn dây, rôto sẽ thực hiện chu kỳ đầy đủ trong 4 bước.
- 3. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 3 Next is the Full step drive mode which provides much higher torque output because we always have 2 active coils at a given time. However this doesn’t improve the resolution of the stepper and again the rotor will make a full cycle in 4 steps. Tiếp theo là chế độ hoạt động toàn bước cho công suất mô-men xoắn cao hơn nhiều vì chúng ta luôn có 2 cuộn dây hoạt động tại một thời điểm nhất định. Tuy nhiên, điều này không cải thiện độ phân giải của bước và một lần nữa rôto sẽ thực hiện một chu kỳ đầy đủ trong 4 bước. The stepper motor uses a four-step switching sequence, which is called a full-step switching sequence. Figure shows a switching diagram and a table that indicates the sequence for the four switches used to control the stepper motor. The diagram shows four switches with four separate amplifiers. The diagram for the motor shows the same four windings that were discussed in the theory of operation the previous section. Each of the windings is tapped at one end and they are connected through a resistor to the negative terminal of the power supply. Động cơ bước sử dụng trình tự chuyển đổi bốn bước, được gọi là trình tự chuyển đổi toàn bước. Hình hiển thị sơ đồ chuyển mạch và bảng biểu thị trình tự cho bốn công tắc được sử dụng để điều khiển động cơ bước. Sơ đồ cho thấy bốn công tắc với bốn bộ khuếch đại riêng biệt. Sơ đồ cho động cơ cho thấy bốn cuộn dây tương tự đã được thảo luận trong lý thuyết vận hành phần trước. Mỗi cuộn dây được gõ ở một đầu và chúng được kết nối thông qua một điện trở đến cực âm của nguồn điện.
- 4. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 4 For increasing the resolution of the stepper we use the Half Step Drive mode. This mode is actually a combination of the previous two modes. Để tăng độ phân giải của bước, chúng ta sử dụng chế độ nửa bước. Chế độ này thực sự là sự kết hợp của hai chế độ trước đó. Here we have one active coil followed by 2 active coils and then again one active coil followed by 2 active coils and so on. So with this mode we get double the resolution with the same construction. Now the rotor will make full cycle in 8 steps. Ở đây chúng ta có một cuộn dây hoạt động theo sau là 2 cuộn dây hoạt động và sau đó một cuộn dây hoạt động tiếp theo là 2 cuộn dây hoạt động, v.v. Vì vậy, với chế độ này, chúng ta có được gấp đôi độ phân giải với cùng một cấu trúc. Bây giờ các cánh quạt sẽ thực hiện đầy đủ chu kỳ trong 8 bước. The switching diagram for the half-step sequence is shown in Fig. The main feature of this switching sequence is that you can double the resolution of the stepper motor by causing the rotor to move half the distance it does when the full-step switching sequence is used. This means that a 200-step motor, which has a resolution of 1.8°, will have a resolution of 400 steps and 0.9°. The half-step switching sequence requires a special stepper motor controller, but it can be used with a standard hybrid motor. The way the controller gets the motor to reach the half-step is to energize both phases at the same time with equal current. Sơ đồ chuyển mạch cho chuỗi nửa bước được hiển thị trong hình . Tính năng chính của chuỗi chuyển đổi này là bạn có thể tăng gấp đôi độ phân giải của động cơ bước bằng cách làm cho rôto di chuyển một nửa khoảng cách khi trình tự chuyển đổi toàn bước được
- 5. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 5 sử dụng. Điều này có nghĩa là một động cơ 200 bước, có độ phân giải 1,8 °, sẽ có độ phân giải 400 bước và 0,9 °. Trình tự chuyển đổi nửa bước đòi hỏi một bộ điều khiển động cơ bước đặc biệt, nhưng nó có thể được sử dụng với một động cơ lai tiêu chuẩn. Cách bộ điều khiển đưa động cơ đạt được nửa bước là cung cấp năng lượng cho cả hai pha cùng một lúc với dòng điện bằng nhau. However the most common method of controlling stepper motors nowadays is the Microstepping. In this mode we provide variable controlled current to the coils in form of sin wave. This will provide smooth motion of the rotor, decrease the stress of the parts and increase the accuracy of the stepper motor. Tuy nhiên, phương pháp phổ biến nhất để điều khiển động cơ bước hiện nay là Vi bước. Trong chế độ này, chúng ta cung cấp dòng điều khiển biến đổi cho các cuộn dây dưới dạng sóng sin. Điều này sẽ cung cấp chuyển động trơn tru của rôto, giảm ứng suất của các bộ phận và tăng độ chính xác của động cơ bước. Another way of increasing the resolution of the stepper motor is by increasing the numbers of the poles of the rotor and the numbers of the pole of the stator. Một cách khác để tăng độ phân giải của động cơ bước là tăng số cực của rôto và số cực của stato. The full-step and half-step motors tend to be slightly jerky in their operation as the motor moves from step to step. The amount of resolution is also limited by the number of physical poles that the rotor can have. The amount of resolution (number of steps) can be increased by manipulating the current that the controller sends to the motor during each step. The current can be adjusted so that it looks similar to a sine wave. Các động cơ toàn bước và nửa bước có xu hướng hơi giật khi vận hành khi động cơ chuyển từ bước này sang bước khác. Lượng phân giải cũng bị giới hạn bởi số cực vật lý
- 6. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 6 mà rôto có thể có. Số lượng độ phân giải (số bước) có thể được tăng lên bằng cách thao tác dòng điện mà bộ điều khiển gửi đến động cơ trong mỗi bước. Dòng điện có thể được điều chỉnh để nó trông giống như sóng hình sin. The voltage sent to the motor is now a sine wave. The motor for this type of application is generally a permanent magnet brushless DC motor. When the sine wave is sent to the motor at 60 Hz, it will cause the motor shaft to rotate at 72 rpm. The motor windings will require a capacitor to be wired in series for this type of application. Điện áp gửi đến động cơ bây giờ là một sóng hình sin. Động cơ cho loại ứng dụng này thường là động cơ DC không chổi than nam châm vĩnh cửu. Khi sóng hình sin được gửi đến động cơ ở tần số 60 Hz, nó sẽ khiến trục động cơ quay với tốc độ 72 vòng / phút. Các cuộn dây động cơ sẽ yêu cầu một tụ điện được nối tiếp cho loại thiết bị này. Stepper Motor Types by Construction Phân loại động cơ bước bằng cấu tạo By construction there are 3 different types of stepper motors: permanent magnet stepper, variable reluctance stepper and hybrid synchronous stepper motor. Bằng cấu tạo có 3 loại động cơ bước khác nhau: động cơ bước nam châm vĩnh cửu, động cơ bước biến trở từ và động cơ bước đồng bộ lai.
- 7. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 7 1/The Permanent Magnet stepper has a permanent magnet rotor which is driven by the stators windings. They create opposite polarity poles compared to the poles of the rotor which propels the rotor. Động cơ bước nam châm vĩnh cửu có một rôto nam châm vĩnh cửu được điều khiển bởi các cuộn dây stato. Chúng tạo ra các cực phân cực ngược lại so với các cực của rôto đẩy rôto. The rotor and stator poles of a permanent magnet stepper are not teethed. Instead the rotor have alternative north and south poles parallel to the axis of the rotor shaft. Các rôto và cực stato của một bước nam châm vĩnh cửu không có răng. Thay vào đó, rôto có các cực bắc và nam thay thế song song với trục của trục rôto. 1. AA’ và BB’ là 2 pha 2. Vỏ động cơ 3. Các cuộn dây 4. Rotor nam châm vĩnh cửu When a stator is energized, it develops electromagnetic poles. The magnetic rotor aligns along the magnetic field of the stator. The other stator is then energized in the sequence so that the rotor moves and aligns itself to the new magnetic field. This way energizing the stators in a fixed sequence rotates the stepper motor by fixed angles. Khi stato được cấp năng lượng, nó sẽ tạo thành các cực điện từ. Rôto từ tính thẳng hàng dọc theo từ trường của stato. Stator khác sau đó được cấp năng lượng theo trình tự để rôto di chuyển và tự sắp xếp theo từ trường mới. Cách này tạo năng lượng cho các stator theo một trình tự cố định làm quay động cơ bước theo các góc cố định.
- 8. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 8 1. Cực bắc 2. Cực nam The resolution of a permanent magnet stepper can be increased by increasing number of poles in the rotor or increasing the number of phases. Độ phân giải của động cơ bước bước nam châm vĩnh cửu có thể được tăng lên bằng cách tăng số cực trong rôto hoặc tăng số lượng pha. 2/The next type, the Variable Reluctant stepper motor uses a non-magnetizes soft iron rotor.The rotor has teeth that are offset from the stator and as we active the windings in aparticular order the rotor moves respectively so that it has minimum gab between the stator and the teeth of the rotor Loại tiếp theo, động cơ bước biến trở từ sử dụng một rôto sắt mềm không từ hóa. Rôto có răng được bù từ stato và khi chúng ta kích hoạt các cuộn dây theo thứ tự cách nhau, rôto di chuyển tương ứng để nó có đầu nối tối thiểu giữa stato và răng của rôto The variable reluctance stepper has a toothed non-magnetic soft iron rotor. When the stator coil is energized the rotor moves to have a minimum gap between the stator and its teeth. Động cơ bước biến trở từ có một rôto sắt mềm không từ tính có răng. Khi cuộn dây stato được cấp năng lượng, rôto di chuyển để có một khoảng cách tối thiểu giữa stato và răng của nó.
- 9. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 9 1. AA’ và BB’ là 2 pha 2. Lõi sắt non rotor 3. Vỏ motor 4. Các cuộn dây The variable reluctance stepper has a toothed non-magnetic soft iron rotor. When the stator coil is energized the rotor moves to have a minimum gap between the stator and its teeth. Động cơ bước biến trở từ có rôto sắt mềm không từ tính có răng. Khi cuộn dây stato được cấp năng lượng, rôto di chuyển để có một khoảng cách tối thiểu giữa stato và răng của nó. The teeth of the rotor are designed so that when they are aligned with one stator they get misaligned with the next stator. Now when the next stator is energized, the rotor moves to align its teeth with the next stator. This way energizing stators in a fixed sequence completes the rotation of the step motor. Răng của rôto được thiết kế sao cho khi chúng thẳng hàng với một stato, chúng sẽ bị lệch với stato tiếp theo. Bây giờ khi stato tiếp theo được cấp năng lượng, rôto di chuyển để căn chỉnh răng của nó với stato tiếp theo. Cách này cung cấp năng lượng cho các stator trong một chuỗi cố định hoàn thành việc quay động cơ bước.
- 10. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 10 The resolution of a variable reluctance stepper can be increased by increasing the number of teeth in the rotor and by increasing the number of phases. Độ phân giải của động cơ bước biến trở từ có thể được tăng lên bằng cách tăng số lượng răng trong rôto và bằng cách tăng số lượng pha. 3/The Hybrid Synchronous motor is combinations of the previous two steppers. It has permanent magnet toothed rotor and also a toothed stator. The rotor has two sections, which are opposite in polarity and their teeth are offset as shown here Động cơ đồng bộ lai là sự kết hợp của hai loại trước đó. Nó có rôto răng vĩnh cửu và cũng là một stato có răng. Rôto có hai phần, đối diện nhau ở hai cực và răng của chúng được bù trừ như thể hiện như hình This is a front view of a commonly used hybrid stepper motor which has 8 poles on the stator that are activated by 2 windings, A and B. So if we activate the winding A, we will magnetize 4 poles of which two of them will have South polarity and two of them North polarity. Đây là hình ảnh phía trước của động cơ bước lai thường được sử dụng có 8 cực trên stato được kích hoạt bởi 2 cuộn
- 11. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 11 dây A và B. Vì vậy, nếu chúng ta kích hoạt cuộn dây A, chúng ta sẽ từ hóa 4 cực trong đó hai cực sẽ có Nam cực và hai trong số chúng là Bắc cực. We can see that in such a way the rotors teeth are aligned with the teeth of poles A and unaligned with the teeth of the poles B. That means that in the next step when we turn off the A poles and activate the B poles, the rotor will move counter clock wise and its teeth will align with the teeth of the B poles. Chúng ta có thể thấy rằng theo cách như vậy, các răng của rôto được xếp thẳng hàng với răng của cực A và không khớp với răng của các cực B. Điều đó có nghĩa là trong bước tiếp theo khi chúng ta tắt cực A và kích hoạt các cực B, Rôto sẽ di chuyển ngược chiều kim đồng hồ và răng của nó sẽ thẳng hàng với răng của các cực B. If we keep activating the poles in a particular order the rotor will move continuously. Here we can also use different driving modes like the wave drive, full step drive, half step drive and microstepping for even further increasing the resolution of the stepper motor. Nếu chúng ta tiếp tục kích hoạt các cực theo một thứ tự cụ thể, rôto sẽ di chuyển liên tục. Ở đây, chúng ta cũng có thể sử dụng các chế độ điều khiển khác nhau như điều khiển sóng, điều khiển toàn bước, điều khiển nửa bước và vi bước để tăng thêm độ phân giải của động cơ bước.
- 12. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 12 How to select stepper motors Chọn động cơ bước như thế nào First, define the motion profile. This includes such parameters as required positioning time and acceleration/deceleration time. Related factors include the required positioning increments as well as the application’s necessary accuracy and resolution. Đầu tiên, xác định hồ sơ chuyển động. Điều này bao gồm các tham số như thời gian định vị cần thiết và thời gian tăng tốc / giảm tốc. Các yếu tố liên quan bao gồm các mức tăng định vị cần thiết cũng như độ chính xác và độ phân giải cần thiết của ứng dụng. Second, calculate the speed, load inertia, acceleration torque, and load torque requirements with a safety factor. The acceleration torque calculation sometimes tends to be omitted. However, it is a critical factor to consider Thứ hai, tính toán tốc độ, quán tính tải, mô men gia tốc và yêu cầu mô men tải với hệ số an toàn. Việc tính toán mô men gia tốc đôi khi có xu hướng bị bỏ qua. Tuy nhiên, đây là một yếu tố quan trọng để xem xét Third, select a motor based on the torque and speed requirements by referring to the motor’s torque-speed curve. Unlike other motors, stepper motors are not rated in wattage. Motor windings can have different current ratings even with the same dimensional size, and the output torque and power varies depending on the winding and speed. Thứ ba, chọn một động cơ dựa trên các yêu cầu về mô-men xoắn và tốc độ bằng cách tham khảo đường cong tốc độ mô-men xoắn của mô-tơ. Không giống như các động cơ khác, động cơ bước không được đánh giá theo công suất. Cuộn dây động cơ có thể có các xếp hạng hiện tại khác nhau ngay cả với cùng kích thước, và mô-men xoắn đầu ra và công suất thay đổi tùy thuộc vào cuộn dây và tốc độ. Applications Ứng dụng Industrial Machines – Stepper motors are used in automotive gauges and machine tooling automated production equipments. Máy công nghiệp - Động cơ bước được sử dụng trong máy đo ô tô và máy công cụ thiết bị sản xuất tự động
- 13. Báo cáo trang bị điện trong máy công nghiệp Lý Gia Hải Trang 13 Security – new surveillance products for the security industry. Bảo mật - sản phẩm giám sát mới cho ngành an ninh. Medical – Stepper motors are used inside medical scanners, samplers, and also found inside digital dental photography, fluid pumps, respirators and blood analysis machinery. Y tế - Động cơ bước được sử dụng bên trong máy quét y tế, máy lấy mẫu và cũng được tìm thấy bên trong chụp ảnh nha khoa kỹ thuật số, bơm chất lỏng, mặt nạ phòng độc và máy phân tích máu. Consumer Electronics – Stepper motors in cameras for automatic digital camera focus and zoom functions. Điện tử tiêu dùng - Động cơ bước trong máy ảnh cho chức năng lấy nét và thu phóng camera kỹ thuật số tự động. Tài liệu tham khảo: https://howtomechatronics.com/how-it-works/electrical-engineering/stepper-motor/ https://www.moonsindustries.com/article/basic-structure-and-operating-principle-of- stepper-motor https://www.engineersgarage.com/articles/stepper-motors https://www.circuitspecialists.com/blog/stepper-motor-modes-of-operation-stepper- motor-controller-overview-and-information-regarding-multi-axis-motion-control/ http://www.ni.com/white-paper/14876/en/ https://www.motioncontroltips.com/key-tips-for-specifying-stepper-motors/ https://www.elprocus.com/stepper-motor-types-advantages-applications/