Basic electricity presentation module
- 1. Electricity - Comes from the ancient Greek word for amber - elektron. - Is a flow of electrons from an area high in electron excess to one lower electron content.
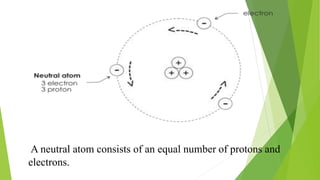
- 2. BASIC CONCEPTS IN ELECTRICITY ’üĄHow electricity is formed? When an element is divided continuously, the division will arrive to the smallest particles where it can no longer divide. This smallest particle of an element is called the atom.
- 3. A neutral atom consists of an equal number of protons and electrons.
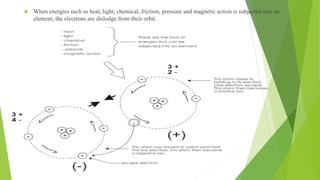
- 4. ’üĄ When energies such as heat, light, chemical, friction, pressure and magnetic action is subjected into an element, the electrons are dislodge from their orbit.
- 5. ’üĄ A positive ion will attract a negative ion. This ionic condition gives rise to static electricity.
- 6. KINDS OF ELECTRICITY A. Static Electricity -When two objects rubbed together, electrons are remove from surface atom, from one material to the other. A. Dynamic Electricity -this refers to electrons in motion. Moving electrons constitute electric current
- 7. Sources of Electricity ’üĄ Friction ’üĄ Rubbing the flexi glass with feather, will cause its electrons to escape and leave the flexi glass positively charged. When the flexi glass is placed near the paper, it will attract the electrons of the atoms of the paper.
- 8. Chemical Reaction ’üĄ dry cell ’üĄ The chemical reacting with metal a causes electrons from the atoms of metal A to escape. These electrons are caught by the atoms of metal B. Since A has lost its electrons, it becomes positively charged. Metal B which gains electrons becomes negatively charged. The formation of positive and negative charge at each end of a dry cell is also another form of static electricity.