Basic Introduction Biomedical.pptx
- 1. BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION SARAVANAN A ASSISTANT PROFESSOR EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING TIRUNELVELI ŌĆō 12. 1
- 2. ’ü▒ Instrumentation is the use of measuring instruments to monitor and control a process. It is the art and science of measurement and 2 process variables within a laboratory, or manufacturing control of production, area. INSTRUMENTATION
- 3. ’ü▒ Biomedical Instrumentation is the field of creating such instruments that help us to measure, record and transmit data to or from the body. 3 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION
- 4. ŌĆó Direct / Indirect ŌĆó Invasive / Noninvasive ŌĆó Contact / Remote ŌĆó Sense / Actuate ŌĆó Real-time / Static 4 TYPES OF BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION SYSTEM
- 5. There are many instruments used in biomedical such as: ’ü▒ X-Rays ’ü▒ Electrocardiography (ECG) ’ü▒ MRI ’ü▒ Ultrasound ’ü▒ CT Scan 5 INSTRUMENTS USED
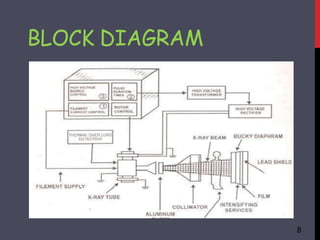
- 6. X-RAYS 6 ’ü▒The frequency of x-rays as approximately 1020 Hz and its wave length is approximately 0.01 to 10 nanometer. ’ü▒ It consist of high vacuum tube with a heater, cathode and anode, vacuum tube, a large DC voltage is used between cathode and anode of x-rays tube.
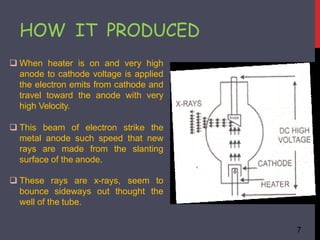
- 7. HOW IT PRODUCED 7 ’ü▒ When heater is on and very high anode to cathode voltage is applied the electron emits from cathode and travel toward the anode with very high Velocity. ’ü▒ This beam of electron strike the metal anode such speed that new rays are made from the slanting surface of the anode. ’ü▒ These rays are x-rays, seem to the bounce sideways out thought well of the tube.
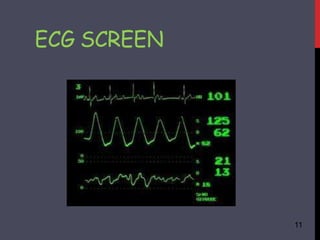
- 9. ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY 9 the polarization and depolarization of cardiac tissue and translates into a ’ü▒Electrocardiography is the recording of the electrical activity of the heart. ’ü▒ It picks up electrical impulses generated by waveform.
- 10. ’ü▒ It detects and amplifies the tiny electrical changes on the skin that are caused when the heart muscle depolarizes during each heartbeat. 10 heart muscle cell has a ’ü▒At rest, each negative charge, called the membrane potential, across its cell membrane. CONTŌĆ”
- 11. ECG SCREEN 11
- 13. ’ü▒ Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) makes use of the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. 13 ’ü▒ The hydrogen nuclei behave like compass needles that are partially aligned by a strong magnetic field in the scanner. ’ü▒ MRI does not involve radioactivity or ionising radiation. The frequencies used (typically 40-130 MHz) are in the normal radiofrequency range, and there are no adverse health effects.
- 14. Advantages: 14 ’ü▒MRI is particularly useful for the scanning and detection of abnormalities in soft tissue structures in the body ’ü▒ There is no involvement of any kind of radiations in the MRI. ’ü▒ MRI scan can provide information about the blood circulation throughout the body and blood vessels.
- 15. Disadvantages: 15 ’ü▒ MRI scan is done in an enclosed space, i.e. fearful of being in a closely enclosed surface, are facing problems with MRI to be done. ’ü▒ MRI scans involve really loud noises while processing because they involve a really high amount of electric current supply. ’ü▒ MRI scanners are usually expensive.
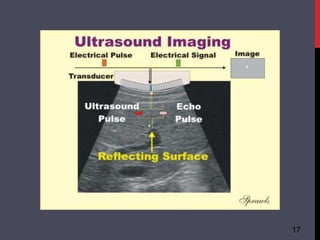
- 16. ULTRASOUND 16 ’ü▒Ultrasound is an oscillating sound pressure wave with a frequency greater than the upper limit of the human hearing range. ’ü▒The frequencies of ultrasound required for medical imaging are in the range 1 - 20 MHz. ’ü▒Ultrasound can be used for medical imaging, detection, measurement and cleaning.
- 17. 17
- 18. ADVANTAGE 18 ’ü▒ Usually non-invasive, safe and relatively painless ’ü▒ Uses no ionising radiation ’ü▒ Does not usually require injection of a contrast medium (dye) DISADVANTAGES ’ü▒ Quality and interpretation of the image highly depends on the skill of the person doing the scan. ’ü▒ Use of a special probe is required in some ultrasounds ’ü▒ Special preparations may be required before a procedure (e.g. fasting or a full bladder)
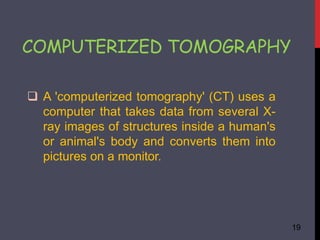
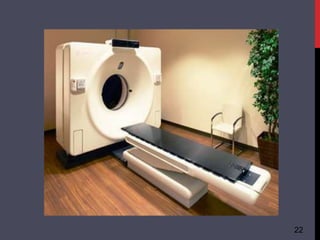
- 19. COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY 19 ’ü▒ A 'computerized tomography' (CT) uses a computer that takes data from several X- ray images of structures inside a human's or animal's body and converts them into pictures on a monitor.
- 20. WORKING 20 ’ü▒ A CT scanner emits a series of narrow beams through the human body as it moves through an arc. ’ü▒ Inside the CT scanner there is an X-ray detector which can see hundreds of different levels of density. It can see tissues inside a solid organ. This data is transmitted to a computer, which builds up a 3D cross-sectional picture of the part of the body and displays it on the screen.
- 21. ADVANTAGES ’ü▒Quick and painless ’ü▒Can help diagnose and guide treatment for a wider range of conditions than plain X-rays ’ü▒Can detect or exclude the presence of more serious problems DISADVANTAGES ’ü▒ Small increased risk of cancer in future from exposure to ionising radiation. ’ü▒ Uses higher doses of radiation, so the risks (while still small) are in general greater than other imaging types 21
- 22. 22