Basic Principles, Distance Measurement and Chain Surveying, Distance Measuring Methods-Taping
- 1. Engineering Surveying 1 Erbil Polytechnic University Technical Engineering College Civil Engineering Department 2022 - 2021 Practical Principle of Surveying Prepared by Assistant Lecturer Mr. Kamal Y. Abdullah Asst.Lecturer. Dilveen H. Omar At. Prof. Salar Khudhur Husseinss
- 2. Syllabus (Main Content) ŌĆó Basic Principles ŌĆó Distance Measurement and Chain Surveying ŌĆó Distance Measuring Methods-Taping 1-direct methods 2-Indirect method 2
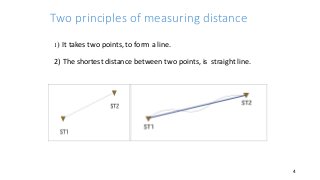
- 4. Two principles of measuring distance 1) It takes two points, to form a line. 2) The shortest distance between two points, is straight line. 4
- 5. Methods of Measuring Distance 5 1. Direct Methods of Measuring Distances 2. Indirect Methods of Measuring Distances
- 6. Indirect Methods of Measuring Distances 1-Theodolite instrument )Stadia(, 2-Tachometry 3-sub-tense method. The methods are Subtence bar, 4-Electronic distance mmeasurement (EDM) 5-Total Station, (TS) 6- G P S . 6
- 7. Electronic Distance Measurement (EDM) 7 accurately measure distance by measuring the time it takes a laser or other ray to travel from the EDM to a prism and back.
- 8. Electronic Distance Meters (EDM) 8
- 9. Surveying practical Length and distance measurement Observation & measurement Methods of measuring Length and distances 1-direct methods 2-Indirect method Direct methods) ) 1-pacing 2-measuring wheel 3-chain 4-tape 5-car odometer 9
- 10. Direct Methods of Measuring Distances ŌĆó Pacing ŌĆó Measuring distance by counting steps (paces). ŌĆó Distance is calculated by multiplying the number of paces by the individuals pace factor(usually every step one meter ). ŌĆó Advantages ŌĆó Simple ŌĆó Low tech ŌĆó No specialized equipment 10 ŌĆó Disadvantages ’üČ Topography affects accuracy ’üČ Requires practice to take a consistent pace. ’üČ Must be able to traverse the distance.. ŌĆó With practice, accuracy is about 2% of distance paced
- 11. Direct Methods of Measuring Distances ŌĆó Car Odometer ŌĆó measuring the distance passed over by any wheeled vehicle ŌĆó An instrument attached to the wheel of a vehicle, to measure the distance traversed. 11 Error 1% of distance
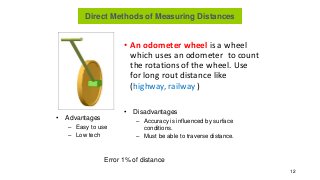
- 12. ŌĆó An odometer wheel is a wheel which uses an odometer to count the rotations of the wheel. Use for long rout distance like (highway, railway ) 12 ŌĆó Advantages ŌĆō Easy to use ŌĆō Low tech ŌĆó Disadvantages ŌĆō Accuracy is influenced by surface conditions. ŌĆō Must be able to traverse distance. Error 1% of distance Direct Methods of Measuring Distances
- 13. The Chain is an old tool used in Land Surveying to measure distance. Direct Methods of Measuring Distances Error 0.2% of distance 13
- 14. Measuring tape A tape measure or measuring tape is a flexible form of ruler. It consists of a tape of( cloth, plastic, fiber glass, or metal strip) with linear-measurement markings. 14
- 15. Distance Measuring Methods-Taping 15 ŌĆó Advantages ŌĆō High precision ŌĆō accuracy ŌĆō Can be used to measure horizontal distances. ŌĆó Disadvantages ŌĆō Multiple people ŌĆō Must have a clear, travelable route. ŌĆō High precision requires temperature and tension correction. Error 0.1% of distance. Tape
- 16. Type of Tape The following are the various types of tapes Cloth tape ŌĆó Shrinkage with water ŌĆó Flexible with tension ŌĆó Do not broken under load Metallic tape(Fiberglass) ŌĆó Less Shrinkage with water ŌĆó Less Flexible with tension ŌĆó Do not broken under load 16
- 17. Type of Tape 17 Invar Tapes: accurate tape made of steel (65%) & Nickel (35%) but they are very expensive Easy broken . Steel tape ŌĆó Easy broken ŌĆó High accuracy ŌĆó No effect by tension ŌĆó May caused injured skin
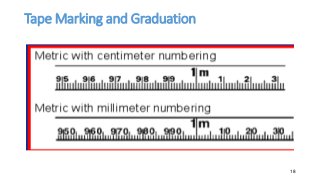
- 18. Tape Marking and Graduation 18
- 19. Tape Zero Point 19 Zero Point
- 20. Equipment for Taping ŌĆó Pins ŌĆó are used to mark tape lengths. ŌĆó Most taping pins are made of steel 20
- 21. Equipments for Taping ŌĆó Range Pole (Range Rod) ŌĆó are used in taping applications for sighting ŌĆó points, marking ground points and for lining up surveyors ŌĆó red and white to make them more easily seen. Each band. 21
- 22. Equipments for Taping ŌĆó Survey Pegs ŌĆó wooden (square or circular cross-section) & steel ŌĆó Use to mark point on the land 22
- 23. Equipments for Taping ŌĆó Plumb Bob ŌĆó are typically made of brass. Bobs are used to get a ŌĆó ŌĆ£plumbŌĆØ (straight) vertical line to a definite point, typically ŌĆó bobs should be used for higher or greater heights. 23
- 24. ŌĆó Level Ground ŌĆó Uniformly Sloping Ground ŌĆó Uneven Ground Processes in taping Surveying 24
- 25. 25
- 26. Level Ground 26 2-The distance greater than the tape length
- 27. 27
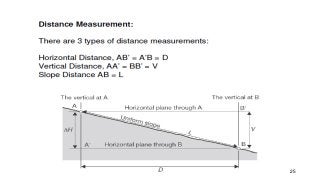
- 28. Slope distance 28 This requires measurement also of either the angle of inclination ╬▒ or the difference in elevation d.
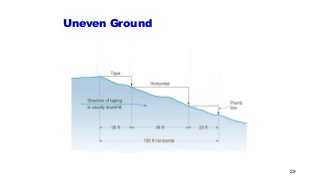
- 29. Uneven Ground 29
- 30. Uneven Ground ŌĆó To measure horizontal distance with a tape , a level and plumb bob must be used. The tape is held level, horizontal, and the measurement at the elevated end is transferred using a plumb bob. ŌĆó . 30
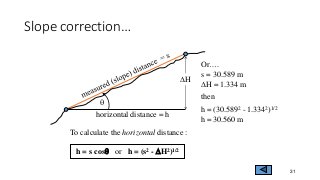
- 31. Slope correctionŌĆ” 31 For example : s = 30.589 m q = 2.5o DH = 1.334 m then h = 30.589 cos(2.5) h = 30.560 m To calculate the horizontal distance : h = s cosq or h = (s2 - DH2)1/2 q horizontal distance = h DH OrŌĆ”. s = 30.589 m DH = 1.334 m then h = (30.5892 - 1.3342)1/2 h = 30.560 m
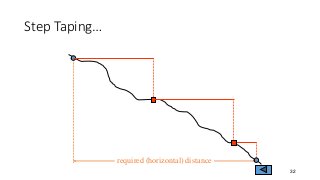
- 32. Step TapingŌĆ” 32 required (horizontal) distance
- 33. 33
- 34. Student Name : Report Number. : Report Name : Date : Mark : 34
- 35. Number 1- Report 2-Report Name( ) 3-Group Name 4- Apparatus 5-Object 6-Procedure 7-Sketch 8-Table 9- Calculation 10-Discussion 35
- 36. Report ( ) 1-Report Number ( 1 ) 2-Report name- Length and distance measurement .Perpendiculars off sets Erecting and Dropping . 3-Object A-B Are two fixed points to measure the horizontal distance between these two point A and B .To Erecting And Dropping lines for known point . 36
- 37. 4-Apparatus 1-Tape(1) 2-Pin(10) 3-Range Pole(5) 4-Optical Square ( 1) 5-Plumb bob . (1) 5 September 2021 37
- 38. 5-Procedure ŌĆó 1-Set two range poles vertically by means of plumb bob at points A and B ŌĆó 2-Ranging lines ŌĆō setting the range pole in the line by eye then using the optical prism. ŌĆó 6-Table- 38
- 39. ŌĆó 7-sketch by Scale: 8-Calculation : 5 September 2021 39
- 40. Tape) ) 1-Steel Tape 2-Pocket Steel Tape 3-Rolling Tape 4-Digital Measuring Tape 5-Invar Tape 6-Linen tape (cloth) 7-Fiberglass tape 40
- 41. Erecting and dropping perpendiculars (or offsets): ŌĆó A- Erecting perpendiculars ŌĆó 1-Pythagoras ŌĆó 2-Length of Tape 3- Erecting by optical square 41
- 42. Pythagoras Provided right-angle triangle (3-4-5) ratio to lay out XZ at 90 degrees to XY a twelve ŌĆō unit tape would have knots tied at unit positions 3 and 7 as shown in figure. One surveyor held the three ŌĆō unit knot at X the second surveyor held the seven ŌĆō unit knot at Y and the third surveyor holding both loose ends of the tape. Stretched the tape tightly resulting in the location of point Z. These early surveyors knew that multiplies 3:4:5 e.g (6:8:10), (30:40:50) would produce more accurate positioning. ŌĆó 42
- 43. 3-optical square 43 a small hand instrument used by surveyors for laying off a right angle by means of two mirrors set at an angle of 45 degrees
- 44. Dropping Perpendiculars 1-Radius . 2-Short length distance. 3-Dropping by optical square 44
- 45. Reference Plan and Geodetic Surveying by late David Clark Surveying By Frances H. Moffit Surveying And Leveling by T.P. Kanetkar Text Book Of Surveying by S. K. Hussain Engineering Surveying (6th Edition) by Schofield W. & Breach M. Surveying Principles and Application (6th Edition) by Barry F. Kavanagh. 45
- 46. Thank you all 46