basic radiation.pptx
- 1. Basic Radiation Physics Pradeep Kumar S Assistant Professor of Radiology Physics Govt. Royapettah Hospital, Chennai
- 7. âĒ The periodic table of elements lists the elements in ascending order of atomic number
- 9. 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.1 Basic definitions for atomic structure âĒ The constituent particles forming an atom are: âĒ Proton âĒ Neutron âĒ Electron Protons and neutrons are known as nucleons and form the nucleus. âĒ Atomic number Z Number of protons and number of electrons in an atom.
- 10. 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.1 Basic definitions for atomic structure âĒ Atomic mass number A Number of nucleons (Z+N) in an atom, where âĒ Z is the number of protons (atomic number) in an atom âĒ N is the number of neutrons in an atom.
- 11. ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE Basic definitions for atomic structure In nuclear physics the convention is to designate a nucleus X as where A is the atomic mass number Z is the atomic number For example: âĒ Cobalt-60 nucleus with Z = 27 protons and A = 33 neutrons is identified as . âĒ Radium-226 nucleus with 88 protons and 138 neutrons is identified as . Z A X 88 226 Ra 27 60 Co
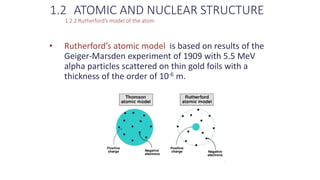
- 12. 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.2 Rutherfordâs model of the atom âĒ Rutherfordâs atomic model is based on results of the Geiger-Marsden experiment of 1909 with 5.5 MeV alpha particles scattered on thin gold foils with a thickness of the order of 10-6 m.
- 13. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.2 šÝšÝßĢ 2 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.2 Rutherfordâs model of the atom âĒ At the time of the Geiger-Marsden experiment Thomson atomic model was the prevailing atomic model. âĒ The model was based on an assumption that the positive and the negative (electron) charges of the atom were distributed uniformly over the atomic volume (âplum-pudding modelâ).
- 14. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.2 šÝšÝßĢ 4 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.2 Rutherfordâs model of the atom âĒ Ernest Rutherford concluded that the peculiar results of the Geiger-Marsden experiment did not support the Thomsonâs atomic model and proposed the currently accepted atomic model in which: âĒ Mass and positive charge of the atom are concentrated in the nucleus the size of which is of the order of 10-15 m. âĒ Negatively charged electrons revolve about the nucleus in a spherical cloud on the periphery of the Rutherford atom with a radius of the order of 10-10 m.
- 15. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.2 šÝšÝßĢ 5 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.2 Rutherfordâs model of the atom âĒ Based on his model and four additional assumptions, Rutherford derived the kinematics for the scattering of alpha particles on gold nuclei using basic principles of classical mechanics. âĒ The four assumptions are related to: âĒ Mass of the gold nucleus. âĒ Scattering of alpha particles. âĒ Penetration of the nucleus. âĒ Kinetic energy of the alpha particles.
- 16. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.2 šÝšÝßĢ 6 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.2 Rutherfordâs model of the atom âĒ The four assumptions are: âĒ Mass of the gold nucleus >> mass of the alpha particle. âĒ Scattering of alpha particles on atomic electrons is negligible. âĒ Alpha particle does not penetrate the nucleus, i.e., there are no nuclear reactions occurring. âĒ Alpha particles with kinetic energies of the order of a few MeV are non-relativistic and the simple classical relationship for the kinetic energy EK of the alpha particle is valid: ïĄïĩ ï― 2 K 2 m E
- 17. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.3 šÝšÝßĢ 1 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.3 Bohrâs model of the hydrogen atom âĒ Niels Bohr in 1913 combined Rutherfordâs concept of the nuclear atom with Planckâs idea of the quantized nature of the radiation process and developed an atomic model that successfully deals with one- electron structures, such as the hydrogen atom, singly ionized helium, etc. âĒ M nucleus with mass M âĒ me electron with mass me âĒ rn radius of electron orbit
- 18. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.3 šÝšÝßĢ 2 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.3 Bohrâs model of the hydrogen atom âĒ Bohrâs atomic model is based on four postulates: âĒ Postulate 1: Electrons revolve about the Rutherford nucleus in well-defined, allowed orbits (planetary-like motion). âĒ Postulate 2: While in orbit, the electron does not lose any energy despite being constantly accelerated (no energy loss while electron is in allowed orbit). âĒ Postulate 3: The angular momentum of the electron in an allowed orbit is quantized (quantization of angular momentum). âĒ Postulate 4: An atom emits radiation only when an electron makes a transition from one orbit to another (energy emission during orbital transitions).
- 19. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.3 šÝšÝßĢ 9 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.3 Bohrâs model of the hydrogen atom âĒ Energy levels En of orbital electron shells in a one-electron Bohr atom are: âĒ ER = Rydberg energy En ï― ïER Z n ïĐ ïŦ ïŠ ïđ ïŧ ïš 2 ï― ï13.6 eV Z n ïĐ ïŦ ïŠ ïđ ïŧ ïš 2
- 20. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.4 šÝšÝßĢ 4 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.4 Multi-electron atom Energy level diagram for multi-electron atom (lead) Shell (orbit) designations: n = 1 K shell (2 electrons) n = 2 L shell (8 electrons) n = 3 M shell (18 electrons) n = 4 N shell (32 electrons) âĶâĶ
- 21. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.5 šÝšÝßĢ 1 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.5 Nuclear structure âĒ Most of the atomic mass is concentrated in the atomic nucleus consisting of Z protons and A-Z neutrons where Z is the atomic number and A the atomic mass number (Rutherford-Bohr atomic model). âĒ Protons and neutrons are commonly called nucleons and are bound to the nucleus with the strong force.
- 22. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.5 šÝšÝßĢ 2 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.5 Nuclear structure âĒ In contrast to the electrostatic and gravitational forces that are inversely proportional to the square of the distance between two particles, the strong force between two particles is a very short range force, active only at distances of the order of a few femtometers. âĒ Radius r of the nucleus is estimated from: , where ro is the nuclear radius constant (1.4 fm). r ï― ro A 3
- 23. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.5 šÝšÝßĢ 3 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.5 Nuclear structure âĒ The sum of masses of the individual components of a nucleus that contains Z protons and (A-Z) neutrons is larger than the mass of the nucleus M. âĒ This difference in masses is called the mass defect (deficit) and its energy equivalent is called the total binding energy EB of the nucleus: ïm ïmc2 EB ï― Zmp c2 ïŦ (A ï Z)mn c2 ï Mc2
- 24. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.5 šÝšÝßĢ 4 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.5 Nuclear structure The binding energy per nucleon (EB/A) in a nucleus varies with the number of nucleons A and is of the order of 8 MeV per nucleon. EB A ï― Zmp c2 ïŦ (A ï Z)mn c2 ï Mc2 A Nucleus EB/A (MeV) 1.1 2.8 2.6 7.1 8.8 7.3 2 1H 3 1H 3 1He 4 1He 60 27Co 238 92U
- 25. Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students - 1.2.6 šÝšÝßĢ 1 1.2 ATOMIC AND NUCLEAR STRUCTURE 1.2.6 Nuclear reactions âĒ Nuclear reaction: Projectile (a) bombards target (A) which is transformed into nuclei (B) and (b). âĒ The most important physical quantities that are conserved in a nuclear reaction are: âĒ Charge âĒ Mass number âĒ Linear momentum âĒ Mass-energy A ïŦ a ï― B ïŦ b or A(a,b)B
- 26. RADIO NUCLIDES âĒ Nuclei having different number of protons, neutrons, or both are called nuclides. âĒ Unstable nuclides are called Radionuclides ,and atoms with unstable nuclei are called Radioisotopes.
- 27. Nuclear Terminology âĒ Nuclides with the same number of protons and different number of neutrons== Isotopes âĒ Nuclides with the same number of neutrons but different number of protons== Isotones âĒ Nuclides with the same number of nucleons == Isobars âĒ Identical nuclides with different energy states == Isomers
- 30. What is Radiation? âĒRadiation: Emission and propagation of energy in the form of waves or particles
- 31. Classification of radiation Radiation is classified into two main categories: âĒ Non-ionizing radiation (cannot ionize matter). âĒ Ionizing radiation (can ionize matter). âĒ Directly ionizing radiation (charged particles) electron, proton, alpha particle, heavy ion âĒ Indirectly ionizing radiation (neutral particles) photon (x ray, gamma ray), neutron
- 32. The process by which a neutral atom acquires a positive or negative charge Ionization electron is stripped from atom - - - - The neutral atom gains a + charge = an ion
- 33. âĒ Ionization: Removal of electrons âĒ Excitation: Shifting of an electron to a higher energy level
- 35. Binding Energy âĒ Energy required to remove an electron completely from an atom âĒ By convention, binding energies are negative with increasing magnitude for electrons in shells closer to the nucleus âĒ Binding energy of electrons in a particular orbit increases with the number of protons in the nucleus (i.e., atomic number, Z)