Basics- Income tax basic info.
- 1. Direct Tax BY CA BALA YADAV
- 2. TAX?
- 3. TAX Latin-Word-TAXO-Means-RATE ’üČFinancial Charge/other levy ’üČImposed upon a tax payer (tax payer may a individual or legal entity) ’üČBy the state or the functional equivalent of a state ’üČThat failure to pay or evasion of or resistance ’üČIs punishable by law. Our tax system is based on our "ability to pay." The more money we earn, the more taxes we pay. And the opposite is also true. If we earn a small income, we pay less taxes.
- 4. A means by which governments finance their expenditure by imposing charges on citizens and corporate entities. Governments use taxation to encourage or discourage certain economic decisions. For example, reduction in taxable personal (or household) income by the amount paid as interest on home mortgage loans results in greater construction activity, and generates more jobs.
- 5. TYPEs OF TAXES DIRECT TAXES ŌĆó A tax that is paid directly by an individual or organization to the imposing entity. ŌĆó e.g income tax, wealth tax etc. Burden of tax borne by the person himself. INDIRECT TAXES ŌĆó A tax that increases the price of a good so that consumers are actually paying the tax by paying more for the products. ŌĆó e.g excise duty, vat, sales tax, Service tax etc. Burden of tax shifted to another person
- 6. Income Tax Law The Income Tax Act, 1961 The Income Tax Rules, 1962 Circulars, Clarifications from CBDT Time to time Judicial Decision
- 7. INDIA territory of India as per Article 1 of the constitution territorial water, seabed & subsoil underlying continental shelf & EEZ Any other specified maritime zone & the air space above its territory and territorial waters
- 8. CY FY AYPY
- 9. AY-Assessment Year- Section 2 (9) of Income Tax Act, 1961 A year in which income of an assessee of the previous year/last year needed to be assessed. It is called as ŌĆ£tax yearŌĆØ in some of the countries. Assessment Year (AY) is a period of twelve months starting from April 1st and ending on March 31st. PY-Previous Year- Section 3 of Income Tax Act, 1961 A year in which income is earned to be taxed exactly in the immediately next/following assessment year. It is also known as ŌĆ£income yearŌĆØ in some of the countries.
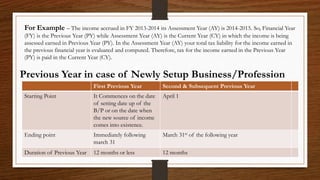
- 10. For Example ŌĆō The income accrued in FY 2013-2014 its Assessment Year (AY) is 2014-2015. So, Financial Year (FY) is the Previous Year (PY) while Assessment Year (AY) is the Current Year (CY) in which the income is being assessed earned in Previous Year (PY). In the Assessment Year (AY) your total tax liability for the income earned in the previous financial year is evaluated and computed. Therefore, tax for the income earned in the Previous Year (PY) is paid in the Current Year (CY). Previous Year in case of Newly Setup Business/Profession First Previous Year Second & Subsequent Previous Year Starting Point It Commences on the date of setting date up of the B/P or on the date when the new source of income comes into existence. April 1 Ending point Immediately following march 31 March 31st of the following year Duration of Previous Year 12 months or less 12 months
- 11. Income of the Previous Year is not Taxable in the immediate Assessment year i.e. Exceptions There are 5 cases in which income of previous year is not taxable in immediate assessment year. Means Income is Taxable in the Previous Year in which such Income is earned.
- 12. SHORT WAY ŌĆóSHIP ŌĆóLEAVES INDIA ŌĆóFOR SHORT DURATION ŌĆó TO TRANSFER PROPERTY OF ŌĆóDISCONTINUED BUSINESS
- 13. Subjectto conditions ŌĆó A non-resident who is carrying business and ŌĆó Earn income from carrying passenger/ livestock/ goods ŌĆó From airport of India. ŌĆó Master of ship is liable to fulfill all formalities. ŌĆó 7.5% of gross receipts (amount of fare/freight/charges) shall be deemed income. Shipping Business Of Non-Residents Section 172
- 14. Section 174 Income of a person leaving India either permanently or for a period of time
- 15. Section 174A Association of person or body of individual, formed or established for a particular event and purpose and likely to be dissolved in the same year in which the same was established.
- 16. Section 175 Person likely to transfer property to avoid tax
- 18. Some Important Terms & Definitions Under INCOME TAX ACT, 1961 ŌĆó Section 2(7) Section 2(8) ŌĆó Section 2(22) Section 2 (24) ŌĆó Section 2(25A) Section 2(26A) ŌĆó Section 2(26B) Section 2(29BA) Section 2(31)
- 19. PERSON u/s 2(31) INDIVIDUAL AOP/BOI ARTIFICIAL JURIDICIAL PERSON
- 20. A natural human being i.e. male, female, person of sound and unsound mind It also includes minor child. However income of minor child included in the income of a parent. AN INDIVIDUAL
- 21. ŌĆ£ ŌĆØ AS per Hindu Law, HUF means a family which consists of all the persons lineally descended from a common ancestors including their wives and unmarried daughters. HUF is not defined under tax laws. FIRM as defined under Indian Partnership Act, 1932 and shall includes LLPŌĆÖs. defined under Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- 22. AOP/BOI AOP ŌĆó As name suggest, two or more persons ŌĆó Join for a common purpose ŌĆó With a view to earn income. ŌĆó In AOP two or more persons joined hand in income producing activity only. ŌĆó Companies, Individual , firm , HUF can be a AOP Member. ŌĆó AOP have common design or will. BOI ŌĆó As name suggest, consist of individuals only for income earning activity. ŌĆó Companies , firm , HUF cannot be a member of BOI. ŌĆó BOI may or may not have such common design or will.
- 23. LOCAL AUTHORITY Artificial Judicial Persons ŌĆó It is the rest category for the purpose of income tax act. ŌĆó It includes entities which are not natural person and act as separate entity in the eyes of law. ŌĆó Artificial person with a juristic personality fall under this category. Panchayat Municipality Municipal Committee District Board Cantonment Board
- 24. Thank You