basics of computer ( B.K. school of maangement ).ppt
- 1. 1
- 2. 2
- 3. 3 Computer :- an electronic machine that can store, find and arrange information, calculate amounts and control other machines. COMPUTER Full Form: -Common Operating Machine Purposely used for Technological and Educational research. MEANING :- A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve, and process data.
- 4. 4 There are five basic components which include: ŌĆóInput Unit. ŌĆóOutput Unit. ŌĆóMemory Unit. ŌĆóControl Unit. ŌĆóArithmetical and Logical Unit.
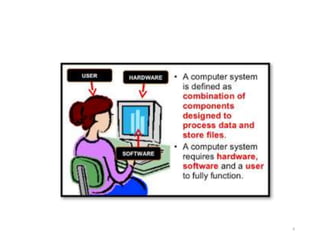
- 5. 5 The basic parts or components of a computer are as follows ŌłÆ ŌĆóInput Unit ŌłÆ Devices like keyboard and mouse that are used to input data and instructions to the computer are called input unit. ŌĆóOutput Unit ŌłÆ Devices like printer and visual display unit that are used to provide information to the user in desired format are called output unit. ŌĆóControl Unit ŌłÆ As the name suggests, this unit controls all the functions of the computer. All devices or parts of computer interact through thecontrol unit. ŌĆóArithmetic Logic Unit ŌłÆ This is the brain of the computer whereall arithmetic operations and logical operations take place. ŌĆóMemory ŌłÆ All input data, instructions and data interim to the processes are stored in the memory. Memory is of two types ŌĆō primary memory and secondary memory. Primary memory resides within the CPU whereas secondary memoryis external to it.
- 6. 6
- 7. 7 Hardware components :- 1. Input devices :- keyboard , mouse, scanner, camera, joystick, microphone. 2. Output devices :- monitors, printers, speakers, headphones, projectors. Software Components:- MS office , google chrome , windows, antivirus , VLC
- 8. 8 Characteristics of Computer:- To understand why computers are such an important part of our lives, let us look at some of its characteristics ŌłÆ ŌĆóSpeed ŌłÆ Typically, a computer can carry out 3-4 million instructions per second. ŌĆóAccuracy ŌłÆ Computers exhibit a very high degree of accuracy. Errors that may occur are usually due to inaccurate data, wrong instructions or bug in chips ŌĆō all human errors. ŌĆóReliability ŌłÆ Computers can carry out same type of work repeatedly without throwing up errors due to tiredness or boredom, which are very common among humans. ŌĆóVersatility ŌłÆ Computers can carry out a wide range of work from data entry and ticket booking to complex mathematical calculations and continuous astronomical observations. If you can input the necessary data with correct instructions, computer will do the processing. ŌĆóStorage Capacity ŌłÆ Computers can store a very large amount of data at a fraction of data is safe from normal wear and tear associated with paper.
- 9. 9 Advantages of Using Computer:- Now that we know the characteristics of computers, we can see the advantages that computers offerŌłÆ ŌĆóComputers can do the same task repetitively with same accuracy. ŌĆóComputers do not gettired orbored. ŌĆóComputers can take up routine tasks while releasing human resource for more intelligent functions.
- 10. 10 Disadvantages of Using Computer:- Despite so many advantages, computers have some disadvantages of their own ŌłÆ ŌĆóComputers have no intelligence; they follow the instructions blindly without considering the outcome. ŌĆóRegular electric supply is necessary to make computers work, which could provedifficult everywhere especially in developing nations
- 11. 11
- 12. In the early 1820s, it was designed by Charles Babbage who is known as "Father of Modern Computer". It was a mechanical computer which could perform simple calculations. It was a steam driven calculating machine designed to solve tables of numbers like logarithm tables. 12 History and Introduction of Computer
- 13. 13
- 14. The Five Generations of Computers 14
- 15. Generations of Computer ŌĆó The computer has evolved from a large-sized simple calculating machine to a smaller but much more powerful machine. ŌĆó The evolution of computer to the current state is defined in terms of the generations of computer. ŌĆó Each generation of computer is designed based on a new technological development, resulting in better, cheaper and smaller computers that are more powerful, faster and efficient than their predecessors. 15
- 16. Generations of Computer ŌĆó Currently, there are five generations of computer. In the following subsections, we will discuss the generations of computer in terms of the technology used by them (hardware and software), computing characteristics (speed, i.E., Number of instructions executed per second), physical appearance, and their applications. 16
- 18. First Generation Computers (1940-1956) ŌĆó The first computers used vacuum tubes(a sealed glass tube containing a near- vacuum which allows the free passage of electric current.) For circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. ŌĆó They were often enormous and taking up entire room. ŌĆó First generation computers relied on machine language. ŌĆó They were very expensive to operate and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, generated a lot of heat, which was often the cause of malfunctions(defect or breakdown). ŌĆó The univac and eniac computers are examples of first-generation computing devices. 18
- 19. First Generation Computers Advantages : ŌĆó It was only electronic device ŌĆó First device to hold memory Disadvantages : ŌĆó Too bulky i.e large in size ŌĆó Vacuum tubes burn frequently ŌĆó They were producing heat ŌĆó Maintenance problems 19
- 20. Second Generation Computers (1956-1963) ŌĆó Transistors replaced vacuum tubes and ushered in the second generation of computers. ŌĆó Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic. ŌĆó High-level programming languages were also being developed at this time, such as early versions of cobol and fortran. ŌĆó These were also the first computers that stored their instructions in their memory. 20
- 21. Second Generation Computers Advantages : ŌĆó Size reduced considerably ŌĆó The very fast ŌĆó Very much reliable Disadvantages : ŌĆó They over heated quickly ŌĆó Maintenance problems 21
- 23. Third Generation Computers (1964-1971) ŌĆó The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers. ŌĆó Transistors were miniaturized and placed on siliconchips, called semiconductors. ŌĆó Instead of punched cards and printouts, users interacted with third generation computers through keyboards and monitors and interfaced with an operating system. ŌĆó Allowed the device to run many different applications at one time. 23
- 24. Third generation computers Advantages : ŌĆó ICs are very small in size ŌĆó Improved performance ŌĆó Production cost cheap Disadvantages : ŌĆó ICs are sophisticated 24
- 26. Fourth Generation Computers (1971-present) ŌĆó The microprocessor brought the fourth generation of computers, as thousands of integrated circuits were built onto a single silicon chip. ŌĆó The intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, located all the components of the computer. ŌĆó From the central processing unit and memory to input/output controlsŌĆöon a single chip. ŌĆó . Fourth generation computers also saw the development of guis, the mouse and handheld devices. 26
- 28. 28
- 29. Fifth Generation Computers (present and beyond) ŌĆó Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence. ŌĆó Are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition. ŌĆó The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality. ŌĆó The goal of fifth-generation computing is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization. 29
- 31. 31
- 32. 32