Basics to Mining & Mineral Processing
- 1. Basics to Mining & Mineral Processing Presented By Rajesh Patnaik Sr. Sales Engineer ŌĆōEastern India
- 2. Mining: ŌĆó Mining is systematic extraction of ores or minerals from the ground.
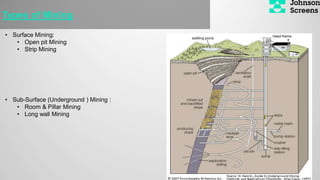
- 3. Types of Mining ŌĆó Surface Mining: ŌĆó Open pit Mining ŌĆó Strip Mining ŌĆó Sub-Surface (Underground ) Mining : ŌĆó Room & Pillar Mining ŌĆó Long wall Mining
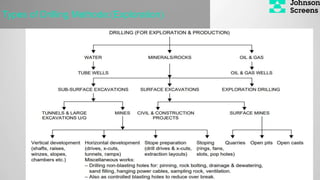
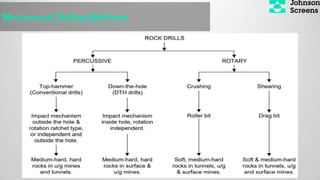
- 4. Types of Drilling Methode:(Exploration)
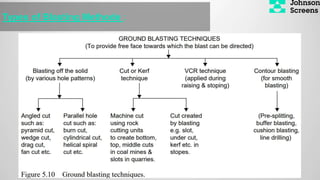
- 6. Types of Blasting Methode :
- 7. Fragmentation : ŌĆó Fragmentation is described as the size of individual piece of rock after blasting.
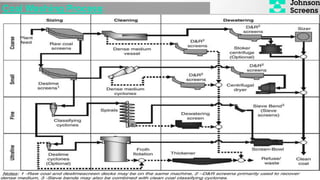
- 8. Sizing: Sizing is the process of separating a mixture of grains of different size into groups or grades whose characteristics is that the particles there in are necessary of same size, that have passed an aperture of certain dimension and failed to pass through some smaller aperture Sizing is the process of Production of a final product having a specific size. PURPOSES OF SIZING: 1. SIZING OR CLASSIFYING - to separate particles by size, usually to provide a downstream unit process with the particle size range suited to that unit operation; 2. SCALPING - to remove the coarsest size fractions in the feed material, usually so that they can be crushed or removed from the process; 3. GRADING- to prepare a number of products within specified size ranges. This is important in quarrying and iron ore, where the final product size is an important part of the specification; 4. MEDIA RECOVERY - for washing magnetic media from ore in dense medium circuits;
- 9. 5.DEWATERING- to drain free moisture from a wet sand slurry; 6.DE-SLIMING OR DE-DUSTING - to remove fine material, generally below 0.5 mm from a wet or dry feed . 7.TRASH REMOVAL - usually to remove wood fibers from a fine slurry stream. 8. To cut off the fine end from either feeds and thus save power and overgrinding
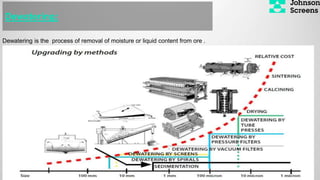
- 10. Dewatering is the process of removal of moisture or liquid content from ore . Dewatering:
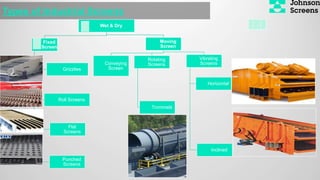
- 11. Types of Industrial Screens Wet & Dry Fixed Screen Grizzlies Roll Screens Flat Screens Punched Screens Moving Screen Conveying Screen Rotating Screens Trommels Vibrating Screens Horizontal Inclined
- 13. Coal Washing Equipments: ’é¦ Centrifuges: ’é¦ Uses centrifugal force to remove moisture content from fine and coarse coal to reduce overall weight as coal retains fluid longer than any other mineral. ’é¦ Basic Mechanism:
- 15. Iron Ore Processing : ŌĆó Use of Blast furnace is the major mode of Iron Making. ŌĆó It is an established fact that the amount of energy consumption and out put of a steel plant is directly propositional to the quality of the raw material particularly iron Input. ŌĆó Feed of raw iron can be any in any of the below form: ’é¦ Pig Iron ŌĆō Lumpy Iron Ore ’é¦ Base Mix/Agglomerates ( Mix of Sinter ,Pellets & Coke & Flux(Limestone & Dolomite). ’é¦ The general practice in the Indian stee industry is to consume high grade Iron ore >62% Fe. ’é¦ Iron Ore Beneficiation: Beneficiation is the process for improvement of Iron ore content and reduction of alumina & Silica. ’é¦ Iron ore Pelletization: Pelletizing is a process which involves mixing of very finely ground particles of ironore fines having a size which is less than200mesh(0.074 mm)with additives likebentoniteand then shaping them into near oval/spherical balls havingsize in therangeof 8mmto 16 mm in diameter by a pelletizer and hardening theballs by firing with a fuel.
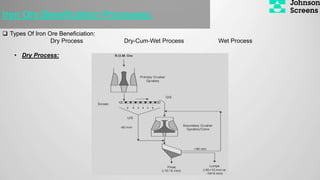
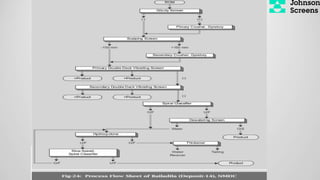
- 16. Iron Ore Beneficiation Processes: ’ü▒ Types Of Iron Ore Beneficiation: Dry Process Dry-Cum-Wet Process Wet Process ŌĆó Dry Process:
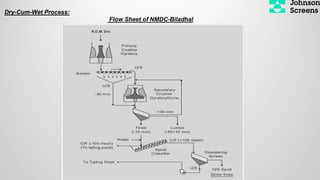
- 17. Dry-Cum-Wet Process: Flow Sheet of NMDC-Biladhal
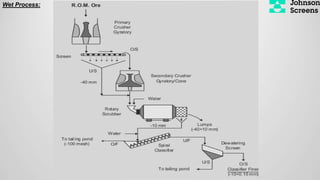
- 18. Wet Process:
- 20. Types of Iron Ore Washing : ŌĆó Gravity Concentration : ŌĆó Heavy Media Separation: ŌĆó Heavy Media Cyclone: ŌĆó Jigging: ŌĆó Spirals
- 21. WW Flat Panels & Polywedge: ŌĆó Coal washing plant during: ŌĆó Desliming. ŌĆó Fine separation. ŌĆó Corse washing. ŌĆó Iron Ore Beneficiation: ŌĆó Fine Separation. ŌĆó Dewatering Cycle. ŌĆó Steel Plant: ŌĆó Blast Furnace for Fines sizing. ŌĆó MRP (Metal Recovery Plant) for slag washing. ŌĆó Johnson range of products and application for Mining :
- 22. Pu Panels: ŌĆó The basic purpose of using Pu in place of SS panels is: ŌĆó Less weight resulting in less over all deck weight which in-turn increases over all TPH of the system. ŌĆó In specific applications SS gives less wearable life where Pu performs better I.e ŌĆō Iron Ore & Coke. ŌĆó Uses can be found in: ŌĆó CHP(Coal Handling Plant). ŌĆó Coal Washery in dewatering application. ŌĆó Iron ore wet plants in fine separation and dewatering application.
- 23. Hardox Sizing Panels /Preforated Plates: ŌĆó Used in predominantly sizing application which are highly abrasive in nature with substantial impact on the panels in expected. ŌĆó Applications: ŌĆó Bauxite handling units. ŌĆó Iron ore pellet plants. ŌĆó Sinter Plant ŌĆōSteel Plant. ŌĆó Coke Plant ŌĆō Steel Plant.
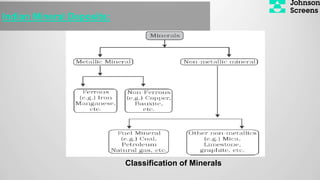
- 24. Indian Mineral Deposits: Classification of Minerals
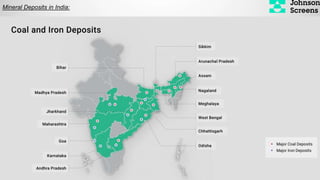
- 25. Mineral Deposits in India:
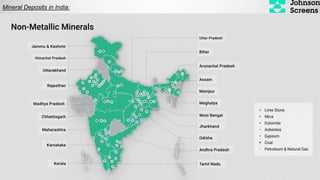
- 26. Mineral Deposits in India:
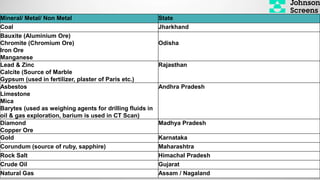
- 27. Mineral/ Metal/ Non Metal State Coal Jharkhand Bauxite (Aluminium Ore) Chromite (Chromium Ore) Iron Ore Manganese Odisha Lead & Zinc Calcite (Source of Marble Gypsum (used in fertilizer, plaster of Paris etc.) Rajasthan Asbestos Limestone Mica Barytes (used as weighing agents for drilling fluids in oil & gas exploration, barium is used in CT Scan) Andhra Pradesh Diamond Copper Ore Madhya Pradesh Gold Karnataka Corundum (source of ruby, sapphire) Maharashtra Rock Salt Himachal Pradesh Crude Oil Gujarat Natural Gas Assam / Nagaland