Battle of gettysburg
- 1. BATTLE OF GETTYSBURG By: Michael Chabot
- 4. THESIS The Battle of Gettysburg was the turning point of the civil war, in which all hope of an independent Confederacy was lost, Lee’s Army was badly wounded, and all hope of foreign aid was crushed
- 5. FACTS • Fighting occurred between Jul 1-3 1863 • General Lee commanded The Army of Northern Virginia- numbering 75,000 men • General Meade commanded The Army of the Potomac-85,000 men • General Hooker was originally in charge of the union forces, but was replaced by General Meade three days earlier for a dispute over forces defending Harpers Ferry
- 6. FACTS • More men would fight and die in this battle than any other conflict in American History • 569 tons of ammunition fired • 46,000-50,000 casualties • 23,049 Union to 28,063 Confederate • 9 of the 120 Generals present at the battle were killed • 63 medal of honors awarded
- 7. CAUSES FOR LEE’S NORTHERN CAMPAIGN • He had just defeated Union forces at the battle of Chancellorsville • Wanted to bring the fighting to the north for only the second time, after his first ended in failure at the battle of Antietam. • Victory in the North could bring much needed supplies to the South, release the besieged fort at Vicksburg, and add to the growing wave of Northerners favoring peace.
- 8. FIRST ACTION • The first conflict of the battle was a Calvary fight on June 9 1863 • 9,500 confederate cavalry under famed commander Jeb Stuart fought against Alfred Pleasonton’s 8,000 cavalry and 3,000 infantry • Stuart’s forces repelled Pleasonton’s • However for the first time Union cavalry was able to stand up to the confederacy, foreshadowing events to come
- 10. TROOP MOVEMENTS • By the middle of June lee’s army was ready to cross the Potomac, and enter into the North • After he defeated Garrisons guarding the river the army began taking supplies from farmers on the way • Lee ordered that no civilian be hurt, but 40 African Americans believed to be run a ways were sent back to the south in chains • Also property from northern farmers was taken and paid for with useless confederate currency
- 11. TROOP MOVEMENTS CONTINUED • On June 29 General Lee learned that the Union Army had crossed the Potomac River • Lee put a detachment of his army under General Heth into the town of Cashtown which is 8 miles South of Gettysburg • General Heth sent some of his brigade under General Pettigrew to search for supplies in neighboring Gettysburg • General Pettigrew noticed union forces arriving in the town • Upon reporting this to General Heth, he ordered two brigades to advance on Gettysburg
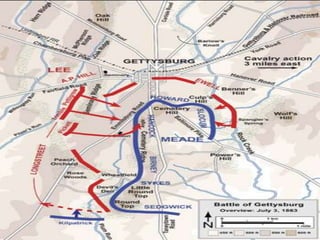
- 13. DAY 1 • Seeing the advancement of Confederates on Gettysburg, Commanding general Budford set his forces on the high ground • Herr Ridge, McPherson Ridge, and Seminary Ridge • Budford chose these positions to give them a superior advantage to the far greater infantry force, and to stop the Confederates from gaining Cemetery Ridge, Cemetery Hill, or Culp’s Hill
- 14. DAY 1 • The two Divisions lead by General James Archer, and Joseph Davis launched an attack on Union dismounted Calvary troops • The Union Forces were able to delay the Confederates from behind fence posts • The confederates eventually pushed the Union to McPherson Ridge where more Union forces arrived • Two divisions lead by General Ewell marched West towards Chashtown • However Union forces met them in root and were able to keep them in Gettysburg
- 15. DAY 1 • This move caused the Union army to have a semicircle defensive position • Later in the day after more forces had arrived, the Confederate Second Core lead by General Rhodes and Early assaulted the Union forces North of the town • They were able to outflank the Union, and caused the Union flank to crumble • By later that afternoon both flanks of the Union army had collapsed, and General Howard ordered a retreat to the high ground to the South
- 16. DAY 1 • General Meade then sent Norristown native General Winfield S Hancock to assume command of the battlefield until his arrival • The Confederate forces missed a great opportunity to win the battle because of Ewells failure to order an assault on the weakly defended cemetery hill • The first day of battle ranks as the 23 rd biggest battle of the war • ¼ of the union army and 1/3 of the Confederates fought
- 19. DAY 2 • At this point the full strength of both armies had arrived • The Union forces were in a fishhook formation from Culp’s Hill along Cemetery Ridge to Little Round top in the south • Lee hoped that General Longstreet’s Corps could defeat the Union left flank and roll up the Union line
- 20. DAY 2 • The plan called for Longstreet’s sending of troops in waves to prevent the Union forces from shifting, as well as a simultaneous demonstration (fake show of power) from General Johnson’s Corps, in order to confuse the Union • However Lee’s plans were based on bad intelligence because his best Calvary commander Jeb Stuart had not yet returned
- 21. DAY 2 • General Longstreet’s forces hit the left flank of the Union line • Meade sent 20,000 reinforcements to help defend the flank • Assault did not follow Lee’s plan because one of the Corps deviated more East than intended • As the fighting continued there were only small forces on the crucial little round top • A brigade of only four regiments was able to hold off repeated assaults by a full brigade of 20 regiments lead by General Law • The key defense by the Union was ordered By Col Chamberlain in which the 20th Maine Regiment did a bayonet charge forcing the Confederates back
- 22. DAY 2 • With all of the focus on the left flank of the Union, only one Brigade lead by General Greene was left • Greene had ordered well dug out defensive positions, and because of this the Union successfully defended Culp’s hill • Jeb Stuart’s Calvary finally arrived at noon time and played no role in the days battle
- 24. DAY 3 • At 1pm on the third day 150-170 confederate cannons were shot at the Union center in an attempt to weaken the line • The Union fired back 15 minutes later with 80 cannons • However the Confederate cannons over shot and nearly every cannonball fell over the heads of the Union • At 3pm the firing stopped due to the Confederate lack of ammunition
- 25. DAY 3 • Under General Pickett’s command 12,500 men marched on flat terrain towards the defending Union forces lead by General Hancock • This attack is known as Picket’s charge • There was cannon fire being shot on each flank of the Confederate troops, as well as direct fire from the Union • The charge failed miserably with nearly half of the assailants dyeing • Confederate General Armistead was able to reach the Union line at a point known as the angle • This was the closest the Confederacy ever came to winning their independence
- 27. Confederate Corps Casualties (k/w/m) First Corps 7665 (1617/4205/1843) Second Corps 6686 (1301/3629/1756) Third Corps 8495 (1724/4683/2088) Cavalry Corps 380 (66/174/140) Union Corps Casualties (k/w/m) I Corps 6059 (666/3231/2162) II Corps 4369 (797/3194/378) III Corps 4211 (593/3029/589) V Corps 2187 (365/1611/211) VI Corps 242 (27/185/30) XI Corps 3807 (369/1924/1514) XII Corps 1082 (204/812/66) Cavalry Corps 852 (91/354/407) Artillery Reserve 242 (43/187/12)
- 29. AFTERMATH • The town of Gettysburg became a hospital • Every house, church, and building was filled with injured soldiers • 5,000 animals, and 8,000 bodies needed to be buried or burned quickly • The stench of death lingered for weeks • Many became critically ill from the smell
- 30. AFTERMATH • Lee’s army retreated towards Cashtown, and back to the south • Meade sent his army in pursuit • The Union army trapped the Confederates against the raging Potomac • However before the Union could crush Lee’s army, The Army of Northern Virginia successfully crossed the Potomac • Meade would fail to catch Lee, and both armies would set up across from each other on the Rappahannock River • At the same time the major strong point of the Confederate Western front at Vicksburg was captured by General Ulysses S Grant • Lincoln believed that a successful pursuit of the Confederates would end the war • Meade's failure at this lead to heavy criticism and his replacement
- 31. AFTERMATH • This battle hurt the Confederacy both militarily and Politically • Vice President Andrew Stephens wanting to negotiate a truce was turned back by Lincoln upon hearing of the success at Gettysburg • Also any hope of foreign aid was crushed • This battle became a key symbol of “The Lost Cause”
- 32. GETTYSBURG ADDRESS • Abraham Lincoln set out four months later to dedicate the Soldier’s National Cemetery • Lincoln redefined the purpose of the war as well as honoring those who had died by delivering his historic Gettysburg Address • The words “Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal” still inspire Americans
- 34. WORKS CITED "American Civil War Battle Gettysburg Pennsylvania July 1-3 1863." Gettysburg Battle American Civil War July 1863. Web. 28 May 2012. "Civil War Trust." The Battle of Gettysburg Summary & Facts. Web. 28 May 2012. "Military History Online - Battle of Gettysburg." Military History Online - Battle of Gettysburg. Web. 28 May 2012.