Baux
- 1. Challis Hodge, VP User Experience Bridge Worldwide challis@challishodge.com
- 3. Main Entry: baux Pronunciation: bO Function: business term Etymology: French 1 : One whose profession is to save businesses and business stakeholders from themselves.
- 4. A match made in heaven!
- 5. What is Experience Planning?
- 6. “A systematic series of actions aimed at structuring, planning for, and facilitating an intentional experience.”
- 7. Why do we need UX People to do this?
- 8. “Experience design, or “design for experience” is a name for enlarging scope to consider patterns of life, goals, activity, context, repeated use, learning, sharing, emotion, and more…while applying The Design Process.” Marc Rettig
- 9. UX Practitioners seek to… -Account for and minimize bias. - Bring a customer perspective to problems through deep understanding. - Facilitate a balance between business goals, user needs and technology.
- 10. Bias is another way of saying ‘unique perspective’ Everyone has one!
- 11. Bias is good but it needs to be controlled, harnessed and accounted for.
- 12. What if your corporate website redesign initiative was being led by…
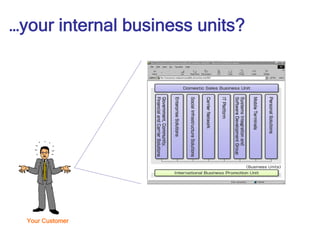
- 13. …your internal business units? Your Customer
- 14. …your marketing group? Your Customer
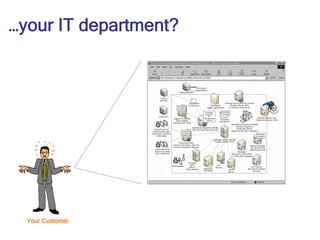
- 15. …your IT department? Your Customer
- 16. …your creative group? Your Customer
- 17. Sometimes bias distorts or blocks your vision
- 18. Flo …a story
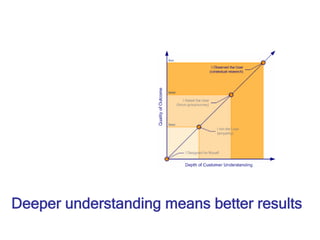
- 20. Deeper understanding means better results
- 22. “You can fix it on paper with an eraser, or you can fix it on the construction site with a sledge hammer.” --Frank Lloyd Wright Not correcting user experience problems until development can cost 10 times more than in design and can increase to 100 times more after launch. Source: Software Engineering: A Practitioners Approach, Usability Engineering, 1993
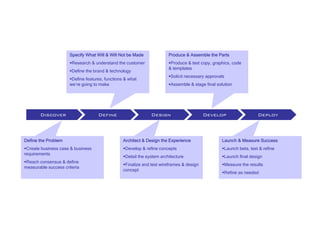
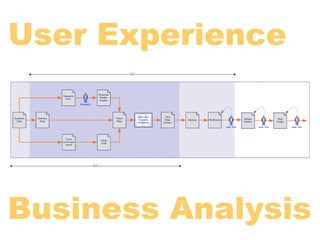
- 23. Specify What Will & Will Not be Made Produce & Assemble the Parts Research & understand the customer Produce & test copy, graphics, code & templates Define the brand & technology Solicit necessary approvals Define features, functions & what we’re going to make Assemble & stage final solution Discover Discover Define Design Develop Deploy Define the Problem Architect & Design the Experience Launch & Measure Success Create business case & business Develop & refine concepts Launch beta, test & refine requirements Detail the system architecture Launch final design Reach consensus & define Finalize and test wireframes & design Measure the results measurable success criteria concept Refine as needed
- 25. “The end of all thought must be action” Aldus Huxley