Beautiful way to save our planet
1 like59 views
The document discusses how orchids and their velamen roots help protect the planet by absorbing atmospheric pollutants. The velamen is a spongy, multi-layered tissue that covers orchid roots and is capable of absorbing moisture, nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur, and pollutants including carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, methane, nitric oxide, and sulfur dioxide from the air. This allows orchids to grow in locations with improved exposure and reduced competition from other plants. Orchids also possess a CO2 concentrating mechanism that operates by reducing CO2 into carbohydrates at night and day, helping the plant more efficiently convert atmospheric carbon dioxide into carbohydrates through photosynthesis.
1 of 21
Download to read offline




















Recommended
Carbon cycle ppt



Carbon cycle pptIbad khan
Ìı
Carbon cycle ppt
definition of Carbon cycle ppt
types of Carbon cycle ppt
discovery of Carbon cycle ppt
importance of Carbon cycle ppt
steps of Carbon cycle ppt
carbon cycle in water
harmful effect of Carbon cycle ppt
Cyclingofmaterials



Cyclingofmaterials2el3amrakan
Ìı
The document summarizes key cycles in ecosystems, including the carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and water cycles. It explains that carbon and other elements are recycled through these cycles, which involve the uptake of elements by plants and animals, their release through respiration and decay, and their return to the environment. It emphasizes the roles of photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and bacteria in facilitating the movement of elements through the cycles. It also notes that human activity like burning fossil fuels has increased the carbon dioxide level in the atmosphere and contributed to global warming.Carbon Cycle



Carbon CycleSamuel McCabe
Ìı
Carbon is one of the most important elements and is the main building block of organisms. It can be found in many everyday items and is readily available on Earth. Carbon dioxide in the air is used by plants through photosynthesis and enters animals when they eat food, then it is released back into the air through respiration. Fossil fuels are formed from decayed plants and animals over millions of years and release carbon dioxide when burned.Carbon Cycle



Carbon Cycleguestdb7f94b
Ìı
The document discusses the carbon cycle, which involves the movement of carbon between different reservoirs on Earth, including the atmosphere, oceans, biosphere, and lithosphere. Carbon cycles through these reservoirs through various processes on timescales ranging from years to millions of years. Key aspects of the carbon cycle include photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, weathering of rocks, deep ocean storage, and the formation and combustion of fossil fuels.C am.ppt



C am.pptnidhi.d
Ìı
This document summarizes Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM), a carbon fixation pathway used by some plants as an adaptation to arid conditions. CAM allows plants to collect carbon dioxide at night through open stomata and store it as an acid, then use the stored carbon dioxide for photosynthesis during the day when stomata are closed. This reduces water loss compared to C3 plants. Key benefits of CAM include keeping stomata closed during the day to reduce evapotranspiration and water loss. It was first observed in the Crassulaceae family.Photosynthesis3



Photosynthesis3Maria Donohue
Ìı
The document discusses the carbon cycle and how carbon moves between organic and inorganic forms through photosynthesis and cellular respiration. It describes how producers convert carbon dioxide into organic compounds through photosynthesis, and how consumers and producers return carbon dioxide to the atmosphere through cellular respiration. It also discusses how carbon is absorbed by oceans and sediments, and incorporated into shells, coral, and limestone over long periods of time. The document then explains how humans disrupt the natural carbon cycle by burning fossil fuels, releasing carbon that has been fixed for thousands of years back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. This increased carbon dioxide is contributing to rising global temperatures and global warming.The Carbon Cycle by Tangstar Science



The Carbon Cycle by Tangstar ScienceJeff Phillips II
Ìı
1) Carbon cycles through both living and non-living components of the environment through various processes.
2) Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and cellular respiration releases it back.
3) Carbon is also stored long-term in fossil fuels through the fossilization of ancient plants and animals, and released through their combustion.Nitrogen and carbon cycle



Nitrogen and carbon cycleNoakhali Science And Technology niversity
Ìı
The document discusses the nitrogen and carbon cycles. It provides details on the key processes in each cycle, including photosynthesis, fixation, mineralization, nutrition, and denitrification for nitrogen. For carbon, it discusses photosynthesis, decomposition, and the role of plants, animals, and soil respiration. It also compares the two cycles, noting nitrogen is involved in recycling nitrogen in ecosystems while carbon dioxide released from burning fossil fuels is contributing to global warming. The document aims to explain the essential roles of nitrogen and carbon in ecosystems.Decay and the carbon cycle



Decay and the carbon cyclesue forshaw
Ìı
Decay and the Carbon Cycle discusses how decay returns materials to the environment through a natural cycle. It focuses on three key points: how plants and animals decay and return nutrients to soil, the type of organism (fungi) that causes leaves to rot, and how higher temperatures in summer cause leaves to decay faster. The document explores the factors like oxygen, water, and temperature that affect the rate of decay and how decay is useful for recycling nutrients and forming fossil fuels over time.Element Sulfur



Element SulfurMark Jasper Ticao
Ìı
Sulfur is a bright yellow nonmetallic element with an atomic number of 16. It forms cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8 under normal conditions. Though sometimes found in its pure native form, sulfur usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. It has a wide variety of industrial uses including the production of sulfuric acid, which is used to make fertilizers, and the vulcanization of rubber. Sulfur is also used as a fungicide, pesticide, bactericide in winemaking, and has applications in medicine, matches, and gunpowder.Carbon cycle in the ocean discussion



Carbon cycle in the ocean discussionLoretta Roberson
Ìı
Evald Maceno is a graduate student at UPR writing an outline for a class on coastal environments. The document outlines carbon as an element and its physical and chemical properties. It describes carbon as part of a global cycle, moving between the atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere. This carbon cycle is impacted by human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation, which increase CO2 levels and acidify the oceans. Rising ocean temperatures and acidification threaten marine life and food systems.Carbon cycle



Carbon cycleKumar Tekchandani
Ìı
Carbon cycles between the earth and atmosphere in a repeating process. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air through photosynthesis, and animals release carbon back to the air when they exhale or when dead plants and animals decompose. Some carbon becomes trapped underground in deposits like oil and coal, and is slowly released back into the atmosphere over long periods of time. Human activities like burning fossil fuels have increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect and global warming. the importance of the carbon cycle



the importance of the carbon cycleKhaleen
Ìı
The carbon cycle is a complex series of processes through which carbon atoms are recycled and reused. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and animals release carbon dioxide through respiration, allowing carbon to be reused. The carbon cycle is essential for producing food and renewable resources through photosynthesis and decomposition, and serves as the earth's waste disposal system through decomposition. It also affects the climate as carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes warming.Nitrogen cycle



Nitrogen cycleJR Ginex-Orinion
Ìı
This is a quick undetailed presentation of the components of the Nitrogen Cycle. The worksheet that goes with it is at this link
Carbon Cycle



Carbon CycleEd Stermer
Ìı
The document summarizes the carbon cycle, which is the movement of carbon between different reservoirs on Earth and in its atmosphere. Carbon continually cycles between living organisms, oceans, atmosphere, and rocks through various processes over timescales ranging from years to millions of years. Key parts of the cycle include photosynthesis fixing carbon from the atmosphere into organisms, respiration and decomposition releasing carbon back to the air, and geological processes like weathering sequestering carbon in rocks over millions of years.Carbon dioxide and oxygen cycle



Carbon dioxide and oxygen cycleEllen Joy Raballe
Ìı
Nutrient – a substance (element or compound) that promotes growth and health in living things
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen are needed in large quantities – these are known as macronutrients
Trace elements such as magnesium, sulphur and phosphorous are called micronutrients
Carbon cycle



Carbon cycleRegine Jade Tolentino
Ìı
Carbon is an essential element that cycles between the atmosphere, ocean, organisms, and geologic reservoirs as part of the carbon cycle. Photosynthesis incorporates carbon from the air and water into organic compounds, while respiration and decomposition release it back. Fossil fuels like coal and oil were formed from ancient plant and algae remains over millions of years. Burning fossil fuels returns carbon to the air, and limestone erosion also adds carbon back to the cycle through weathering. The carbon cycle continuously moves carbon between the biosphere and geosphere.The Carbon Cycle



The Carbon Cyclejoshuawright11
Ìı
Carbon is the fourth most abundant element and exists in compounds like CO2 that affect the planet. The carbon cycle transfers carbon between ecosystems on Earth. Humans disrupt this cycle by burning fossil fuels and releasing CO2, which causes global warming as it accumulates in the atmosphere and traps heat. Plants use CO2 in photosynthesis while animals use oxygen, and techniques like carbon sequestration aim to reduce CO2 levels.Presentation pbl by chinchilla



Presentation pbl by chinchillaxiaojing8328002
Ìı
Cacti and bromeliads have developed several characteristics that allow them to survive in dry conditions through drought-tolerant mechanisms. Both are CAM plants that open their stomata at night to fix carbon. Cacti have lost their leaves and use their stems for photosynthesis, which are covered in a waxy cuticle and spines to reduce water loss. Their shallow roots spread widely to maximize water intake. Bromeliads form water-storing leaf tanks and have thick, water-storing leaves covered in scales. These adaptations allow cacti and bromeliads to effectively use water resources under drought conditions.Carbon cycle (1)



Carbon cycle (1)Natthu Shrirame
Ìı
The document summarizes the carbon cycle. It describes how carbon atoms are continuously recycled between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and biosphere through various processes. Carbon is absorbed by plants through photosynthesis and enters the biosphere through consumption. It is released through respiration, decomposition, combustion, and the weathering of rocks. The cycling of carbon was balanced until human activity such as burning fossil fuels increased the release of carbon into the atmosphere.Carbon and nitrogen cycle



Carbon and nitrogen cyclesaramssantos
Ìı
The document discusses the carbon and nitrogen cycles. It describes how carbon and nitrogen move between different reservoirs on Earth, including the atmosphere, living organisms, oceans, and fossil fuels. Key steps in the carbon cycle include photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and the burning of fossil fuels. The nitrogen cycle involves nitrogen fixation, decay, nitrification, and denitrification as microbes convert nitrogen between gas, organic, and inorganic forms. Human activities like burning fossil fuels are increasing carbon dioxide levels and affecting global climate.Carbon-Oxygen Cycle



Carbon-Oxygen Cyclemelissamercer
Ìı
The document discusses the carbon/oxygen cycle which involves four main processes:
1. Photosynthesis where plants take in carbon dioxide and water to release oxygen and sugar using energy from the sun.
2. Respiration where animals take in oxygen and sugars to release carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
3. Combustion which is the burning of fossil fuels like coal, gas, and oil, releasing carbon dioxide. This over-contribution of carbon dioxide is accelerating global warming.
4. Decomposition where dead plants and animals are broken down by insects, fungi and bacteria, returning carbon and other elements to the soil and air.Carbon cycle



Carbon cyclePoonam Singh
Ìı
Carbon cycles between the atmosphere, organisms, oceans, and lithosphere. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air through photosynthesis, and animals obtain carbon by eating plants or other animals. When organisms die, decomposers release carbon back into the atmosphere or it becomes trapped in fossil fuels and sediments. Human activities like burning fossil fuels have increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.The carbon cycle



The carbon cycleslehsten0806
Ìı
Plants take in carbon dioxide through photosynthesis and convert it into sugar for energy storage. Through respiration, plants and animals release carbon dioxide as a waste product when breaking down sugar and other carbon-containing tissues. Decomposers and geological processes like the formation of fossil fuels and sedimentary rock also release carbon back into the atmosphere and oceans, completing the carbon cycle over long timescales.Carbon cycle



Carbon cycle007_wicho
Ìı
Carbon cycles between the earth and atmosphere in a repeating process. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air through photosynthesis, and animals release carbon back into the air when they exhale or when dead plants and animals decompose. Some carbon becomes trapped underground in deposits like oil and coal, and is slowly released back into the atmosphere over many years through natural processes or faster when humans burn fossil fuels. Maintaining the balance of the carbon cycle is important for regulating the earth's climate.Carbon cycle



Carbon cycleYohniki Gordon
Ìı
The carbon cycle describes the movement of carbon through Earth's atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living things. Carbon is absorbed by plants through photosynthesis and enters the biosphere, and is released back into the atmosphere through respiration and decomposition. Burning fossil fuels has increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, contributing to global climate change. The carbon cycle is essential for life and affects Earth's climate.Carbon cycle project



Carbon cycle projectaydenmcintosh
Ìı
The carbon cycle describes how carbon is transferred between living organisms and the environment in different ways. Carbon is contained in all living things and moves through cellular respiration, photosynthesis, combustion, decomposition, and sedimentation. It can be absorbed by plants through photosynthesis, released through cellular respiration and combustion, and eventually deposited as sediment over long periods of time.Carbon cycle



Carbon cycleLeira Figueroa
Ìı
The carbon cycle describes the movement of carbon through Earth's biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Carbon is exchanged between these carbon reservoirs through various biological, chemical, and geological processes. The key reservoirs and processes include:
1) Carbon is stored in the atmosphere, oceans, biosphere like plants and animals, and lithosphere like fossil fuels.
2) Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and incorporates carbon into plants. Animals obtain carbon through eating plants or other animals.
3) Carbon is released back into the atmosphere through respiration by animals and plants and the burning of fossil fuels.
4) Carbon dioxide dissolves into oceans, lakes and rivers where it is used by marine plantsRESPIRATORY SYSTEM OF THE PLANTS........



RESPIRATORY SYSTEM OF THE PLANTS........RynczyllGraceBales
Ìı
Plants breathe through a process of cellular respiration that occurs through stomata in leaves, lenticels in stems, and root hairs. This respiration rate is slower than in humans and animals. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. Different plant types like C3, C4, and CAM plants vary in how and when they fix carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, with C4 and CAM being more efficient in hot, dry conditions.AP Biology Photosynthesis C3 C4 and CAM plants



AP Biology Photosynthesis C3 C4 and CAM plantsStephanie Beck
Ìı
C3, C4, and CAM plants have evolved different carbon fixation pathways to adapt to hot, arid environments. C3 plants fix carbon directly in the Calvin cycle but lose efficiency through photorespiration. C4 plants fix carbon in the cytoplasm first before the Calvin cycle to concentrate CO2. CAM plants fix carbon at night and store it to use during the day to minimize water loss through closed stomata.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Decay and the carbon cycle



Decay and the carbon cyclesue forshaw
Ìı
Decay and the Carbon Cycle discusses how decay returns materials to the environment through a natural cycle. It focuses on three key points: how plants and animals decay and return nutrients to soil, the type of organism (fungi) that causes leaves to rot, and how higher temperatures in summer cause leaves to decay faster. The document explores the factors like oxygen, water, and temperature that affect the rate of decay and how decay is useful for recycling nutrients and forming fossil fuels over time.Element Sulfur



Element SulfurMark Jasper Ticao
Ìı
Sulfur is a bright yellow nonmetallic element with an atomic number of 16. It forms cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8 under normal conditions. Though sometimes found in its pure native form, sulfur usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. It has a wide variety of industrial uses including the production of sulfuric acid, which is used to make fertilizers, and the vulcanization of rubber. Sulfur is also used as a fungicide, pesticide, bactericide in winemaking, and has applications in medicine, matches, and gunpowder.Carbon cycle in the ocean discussion



Carbon cycle in the ocean discussionLoretta Roberson
Ìı
Evald Maceno is a graduate student at UPR writing an outline for a class on coastal environments. The document outlines carbon as an element and its physical and chemical properties. It describes carbon as part of a global cycle, moving between the atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere. This carbon cycle is impacted by human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation, which increase CO2 levels and acidify the oceans. Rising ocean temperatures and acidification threaten marine life and food systems.Carbon cycle



Carbon cycleKumar Tekchandani
Ìı
Carbon cycles between the earth and atmosphere in a repeating process. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air through photosynthesis, and animals release carbon back to the air when they exhale or when dead plants and animals decompose. Some carbon becomes trapped underground in deposits like oil and coal, and is slowly released back into the atmosphere over long periods of time. Human activities like burning fossil fuels have increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect and global warming. the importance of the carbon cycle



the importance of the carbon cycleKhaleen
Ìı
The carbon cycle is a complex series of processes through which carbon atoms are recycled and reused. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and animals release carbon dioxide through respiration, allowing carbon to be reused. The carbon cycle is essential for producing food and renewable resources through photosynthesis and decomposition, and serves as the earth's waste disposal system through decomposition. It also affects the climate as carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes warming.Nitrogen cycle



Nitrogen cycleJR Ginex-Orinion
Ìı
This is a quick undetailed presentation of the components of the Nitrogen Cycle. The worksheet that goes with it is at this link
Carbon Cycle



Carbon CycleEd Stermer
Ìı
The document summarizes the carbon cycle, which is the movement of carbon between different reservoirs on Earth and in its atmosphere. Carbon continually cycles between living organisms, oceans, atmosphere, and rocks through various processes over timescales ranging from years to millions of years. Key parts of the cycle include photosynthesis fixing carbon from the atmosphere into organisms, respiration and decomposition releasing carbon back to the air, and geological processes like weathering sequestering carbon in rocks over millions of years.Carbon dioxide and oxygen cycle



Carbon dioxide and oxygen cycleEllen Joy Raballe
Ìı
Nutrient – a substance (element or compound) that promotes growth and health in living things
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen are needed in large quantities – these are known as macronutrients
Trace elements such as magnesium, sulphur and phosphorous are called micronutrients
Carbon cycle



Carbon cycleRegine Jade Tolentino
Ìı
Carbon is an essential element that cycles between the atmosphere, ocean, organisms, and geologic reservoirs as part of the carbon cycle. Photosynthesis incorporates carbon from the air and water into organic compounds, while respiration and decomposition release it back. Fossil fuels like coal and oil were formed from ancient plant and algae remains over millions of years. Burning fossil fuels returns carbon to the air, and limestone erosion also adds carbon back to the cycle through weathering. The carbon cycle continuously moves carbon between the biosphere and geosphere.The Carbon Cycle



The Carbon Cyclejoshuawright11
Ìı
Carbon is the fourth most abundant element and exists in compounds like CO2 that affect the planet. The carbon cycle transfers carbon between ecosystems on Earth. Humans disrupt this cycle by burning fossil fuels and releasing CO2, which causes global warming as it accumulates in the atmosphere and traps heat. Plants use CO2 in photosynthesis while animals use oxygen, and techniques like carbon sequestration aim to reduce CO2 levels.Presentation pbl by chinchilla



Presentation pbl by chinchillaxiaojing8328002
Ìı
Cacti and bromeliads have developed several characteristics that allow them to survive in dry conditions through drought-tolerant mechanisms. Both are CAM plants that open their stomata at night to fix carbon. Cacti have lost their leaves and use their stems for photosynthesis, which are covered in a waxy cuticle and spines to reduce water loss. Their shallow roots spread widely to maximize water intake. Bromeliads form water-storing leaf tanks and have thick, water-storing leaves covered in scales. These adaptations allow cacti and bromeliads to effectively use water resources under drought conditions.Carbon cycle (1)



Carbon cycle (1)Natthu Shrirame
Ìı
The document summarizes the carbon cycle. It describes how carbon atoms are continuously recycled between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and biosphere through various processes. Carbon is absorbed by plants through photosynthesis and enters the biosphere through consumption. It is released through respiration, decomposition, combustion, and the weathering of rocks. The cycling of carbon was balanced until human activity such as burning fossil fuels increased the release of carbon into the atmosphere.Carbon and nitrogen cycle



Carbon and nitrogen cyclesaramssantos
Ìı
The document discusses the carbon and nitrogen cycles. It describes how carbon and nitrogen move between different reservoirs on Earth, including the atmosphere, living organisms, oceans, and fossil fuels. Key steps in the carbon cycle include photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and the burning of fossil fuels. The nitrogen cycle involves nitrogen fixation, decay, nitrification, and denitrification as microbes convert nitrogen between gas, organic, and inorganic forms. Human activities like burning fossil fuels are increasing carbon dioxide levels and affecting global climate.Carbon-Oxygen Cycle



Carbon-Oxygen Cyclemelissamercer
Ìı
The document discusses the carbon/oxygen cycle which involves four main processes:
1. Photosynthesis where plants take in carbon dioxide and water to release oxygen and sugar using energy from the sun.
2. Respiration where animals take in oxygen and sugars to release carbon dioxide, water, and energy.
3. Combustion which is the burning of fossil fuels like coal, gas, and oil, releasing carbon dioxide. This over-contribution of carbon dioxide is accelerating global warming.
4. Decomposition where dead plants and animals are broken down by insects, fungi and bacteria, returning carbon and other elements to the soil and air.Carbon cycle



Carbon cyclePoonam Singh
Ìı
Carbon cycles between the atmosphere, organisms, oceans, and lithosphere. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air through photosynthesis, and animals obtain carbon by eating plants or other animals. When organisms die, decomposers release carbon back into the atmosphere or it becomes trapped in fossil fuels and sediments. Human activities like burning fossil fuels have increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.The carbon cycle



The carbon cycleslehsten0806
Ìı
Plants take in carbon dioxide through photosynthesis and convert it into sugar for energy storage. Through respiration, plants and animals release carbon dioxide as a waste product when breaking down sugar and other carbon-containing tissues. Decomposers and geological processes like the formation of fossil fuels and sedimentary rock also release carbon back into the atmosphere and oceans, completing the carbon cycle over long timescales.Carbon cycle



Carbon cycle007_wicho
Ìı
Carbon cycles between the earth and atmosphere in a repeating process. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air through photosynthesis, and animals release carbon back into the air when they exhale or when dead plants and animals decompose. Some carbon becomes trapped underground in deposits like oil and coal, and is slowly released back into the atmosphere over many years through natural processes or faster when humans burn fossil fuels. Maintaining the balance of the carbon cycle is important for regulating the earth's climate.Carbon cycle



Carbon cycleYohniki Gordon
Ìı
The carbon cycle describes the movement of carbon through Earth's atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living things. Carbon is absorbed by plants through photosynthesis and enters the biosphere, and is released back into the atmosphere through respiration and decomposition. Burning fossil fuels has increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, contributing to global climate change. The carbon cycle is essential for life and affects Earth's climate.Carbon cycle project



Carbon cycle projectaydenmcintosh
Ìı
The carbon cycle describes how carbon is transferred between living organisms and the environment in different ways. Carbon is contained in all living things and moves through cellular respiration, photosynthesis, combustion, decomposition, and sedimentation. It can be absorbed by plants through photosynthesis, released through cellular respiration and combustion, and eventually deposited as sediment over long periods of time.Carbon cycle



Carbon cycleLeira Figueroa
Ìı
The carbon cycle describes the movement of carbon through Earth's biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. Carbon is exchanged between these carbon reservoirs through various biological, chemical, and geological processes. The key reservoirs and processes include:
1) Carbon is stored in the atmosphere, oceans, biosphere like plants and animals, and lithosphere like fossil fuels.
2) Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and incorporates carbon into plants. Animals obtain carbon through eating plants or other animals.
3) Carbon is released back into the atmosphere through respiration by animals and plants and the burning of fossil fuels.
4) Carbon dioxide dissolves into oceans, lakes and rivers where it is used by marine plantsSimilar to Beautiful way to save our planet (20)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM OF THE PLANTS........



RESPIRATORY SYSTEM OF THE PLANTS........RynczyllGraceBales
Ìı
Plants breathe through a process of cellular respiration that occurs through stomata in leaves, lenticels in stems, and root hairs. This respiration rate is slower than in humans and animals. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. Different plant types like C3, C4, and CAM plants vary in how and when they fix carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, with C4 and CAM being more efficient in hot, dry conditions.AP Biology Photosynthesis C3 C4 and CAM plants



AP Biology Photosynthesis C3 C4 and CAM plantsStephanie Beck
Ìı
C3, C4, and CAM plants have evolved different carbon fixation pathways to adapt to hot, arid environments. C3 plants fix carbon directly in the Calvin cycle but lose efficiency through photorespiration. C4 plants fix carbon in the cytoplasm first before the Calvin cycle to concentrate CO2. CAM plants fix carbon at night and store it to use during the day to minimize water loss through closed stomata.AP Bio Ch. 10 C3 c4 and cam plants



AP Bio Ch. 10 C3 c4 and cam plantsStephanie Beck
Ìı
C3 plants fix carbon through the Calvin cycle by attaching CO2 to RuBP. They lose water through transpiration and photorespiration, which decreases photosynthesis output. C4 plants fix carbon in the cytoplasm before entering the Calvin cycle through PEP carboxylase, preventing photorespiration. They thrive in hot climates. CAM plants fix carbon at night by incorporating CO2 into organic molecules and release it during the day, keeping their stomata closed to minimize water loss.20100906140958 problem based learning pbl



20100906140958 problem based learning pblismaedayu
Ìı
The document discusses the process of carbon fixation in C3, C4, and CAM plants.
C3 plants fix carbon dioxide into a three-carbon compound using the enzyme rubisco. This occurs in the mesophyll cells. C4 plants fix carbon dioxide initially in the mesophyll cells then transport it to the bundle sheath cells where the Calvin cycle occurs, allowing for more efficient fixation. CAM plants open their stomata at night to fix carbon dioxide into malic acid, then use this stored carbon during the day when their stomata are closed.Photosynthesis part 2



Photosynthesis part 2Maria Donohue
Ìı
The document summarizes the process of photosynthesis, including the light-dependent and light-independent reactions. It describes how photosystems use light energy to excite electrons and produce ATP and NADPH. The Calvin cycle then uses these products to fix carbon from CO2 and produce glucose. Challenges like photorespiration are addressed by C4 and CAM plants, which concentrate CO2 through physical or temporal separation of carbon fixation from the Calvin cycle.C4 cycle..



C4 cycle..naren
Ìı
here is the only ppt available of C4 cycle hope you will like it
do comment if you like it and share it 10 B2 Pathwys Of Photosynthsis



10 B2 Pathwys Of Photosynthsiscmoney
Ìı
The document discusses the process of photosynthesis. It describes the Calvin cycle which uses ATP and NADPH to convert CO2 into sugar. Some key points are that the Calvin cycle occurs in three phases: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration. It also discusses alternative mechanisms of carbon fixation that have evolved in hot, arid climates like C4 and CAM plants. These plants have developed ways to concentrate CO2 in their cells to minimize the process of photorespiration and maximize sugar production.48 ch10c4cam2008



48 ch10c4cam2008sbarkanic
Ìı
1) Photosynthesis requires light, carbon dioxide, and water. Plants have evolved leaf structures to supply these needs, including vascular bundles to transport water and sugars, and stomates for gas exchange.
2) When stomates close on hot or dry days to conserve water, it leads to build up of oxygen from light reactions and depletion of carbon dioxide for the Calvin cycle, causing inefficiency.
3) The enzyme RuBisCo can bind to either carbon dioxide or oxygen. Binding oxygen leads to photorespiration, which is inefficient and reduces carbon fixation. This provided selection pressure for C3, C4, and CAM photosynthesis adaptations.C4 photosynthesis



C4 photosynthesisHassaan Kamboh
Ìı
This document discusses C4 plants and their mechanism for carbon fixation. C4 plants have evolved a mechanism to fix carbon more efficiently than C3 plants in conditions like drought, heat, and low CO2/nitrogen levels. They concentrate CO2 around rubisco via a kranz anatomy structure to avoid photorespiration. The C4 mechanism involves converting phosphoenolpyruvate to oxaloacetate, then malate, transporting malate to bundle sheath cells where it is converted back to CO2 and pyruvate, regenerating phosphoenolpyruvate in a cyclic pathway. Major C4 plants include maize, sugarcane, millet, sorghum, and certainEvolutionary transitions from c 3 to c 4 plants



Evolutionary transitions from c 3 to c 4 plantsHafsa Ranjha
Ìı
C3 and C4 plants transitions adaptations of C3 plants to C4 plants
what are C3 and C4 plantsDifferent mode of carbon dioxide assimilation



Different mode of carbon dioxide assimilationManviAbhishek
Ìı
This document discusses the three main modes of carbon dioxide assimilation in plants: C3, C4, and CAM cycles. The C3 cycle fixes carbon through Calvin-Benson cycle in mesophyll cells throughout the leaf. Most plants use this cycle. The C4 cycle fixes carbon in mesophyll cells and transports it to bundle sheath cells, concentrating CO2 around Rubisco to promote photosynthesis. C4 plants include grasses. The CAM cycle fixes carbon at night and stores it as malic acid, releasing CO2 during the day to concentrate it around Rubisco. This allows CAM plants like cacti to keep their stomata closed in the day. C4 and CAM plants evolved to reduce photorespirationPhotosynthsis b



Photosynthsis bDr. Naveen Gaurav srivastava
Ìı
C4Ìıcycle may also be referred as the di-carboxylic acid cycle or the β-carboxylation pathway or Hatch and Slack cycle or cooperative photosynthesis (Karpilov, 1970). For a long time, C3Ìıcycle was considered to be the only photosynthetic pathway for reduction of CO2Ìıinto carbohydrates. Kortschak, Hartt and Burr (1965) reported that rapidly photosynthesizing sugarcane leaves produced a 4-C compound like aspartic acid and malic acid as a result of CO2Ìı– fixation.
It was later supported by M. D. Hatch and C. R. Slack (1966) and they reported that a 4-C compound oxaloacetic acid (OAA) is the first stable product in CO2Ìıreduction process. This pathway was first reported in members of family Poaceae like sugarcane, maize, sorghum, etc. (tropical grasses), but later on the other subtropical plant like Atriplex spongiosa (Salt bush), Dititaria samguinolis, Cyperus rotundus, Amaranthus etc. So, the cycle has been reported not only in the members of Graminae but also among certain members of Cyperaceae and certain dicots.
c3 & c4 Photosynthesis



c3 & c4 PhotosynthesisRashidi Yusof
Ìı
The document summarizes the key differences between C3 and C4 photosynthesis. C3 photosynthesis fixes carbon dioxide into a 3-carbon compound and occurs in most plant species. C4 photosynthesis initially fixes carbon dioxide into a 4-carbon compound and occurs in plants adapted to hot and dry climates like grasses. The C4 pathway concentrates carbon dioxide around rubisco to increase photosynthetic efficiency and reduce water loss through transpiration.Biosynhtetic pathway (dark reaction)



Biosynhtetic pathway (dark reaction)SuganyaPaulraj
Ìı
This document summarizes the dark reaction (also known as the Calvin cycle) in plant photosynthesis. There are two major pathways for carbon fixation during this reaction: the C3 cycle and the C4 cycle. The C3 cycle fixes carbon dioxide into a 3-carbon compound called 3-phosphoglycerate using the enzyme rubisco. The fixed carbon is then reduced using ATP and NADPH to produce carbohydrates like glucose. The C4 cycle acts as an adaptation for plants in hot, dry environments. It initially fixes carbon dioxide into a 4-carbon compound in mesophyll cells before it is released and incorporated into the C3 cycle in bundle sheath cells. This anatomy is known as Kranz anatomy andPhotosynthesis veg.pptx



Photosynthesis veg.pptxEshaneeSharma
Ìı
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages - the light reactions where light energy is captured to make ATP and NADPH using chlorophyll, and the carbon reactions where CO2 is fixed into sugars like glucose using ATP and NADPH in the Calvin cycle. Photosynthesis is vital as it provides oxygen and food, and consumes CO2. However, it is only 1-4% efficient in most plants due to photorespiration. C4 and CAM plants have evolved mechanisms to increase efficiency. Factors like sunlight, carbon dioxide, water, temperature, and pollutionCarbon sequestration and its types



Carbon sequestration and its typesKartik Patel
Ìı
about...Carbon sequestration, Co2 capture technology, types of carbon sequestration, Co2 separation, carbon sources and carbon sinks, benefits of soil sequestration of carbon, conclution.photosynthesis Presentation on Agriculture



photosynthesis Presentation on AgricultureFayzanKhan10
Ìı
photosynthesis, the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy. During photosynthesis in green plants, light energy is captured and used to convert water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds.C2 C3 C4 and CAM (1).pptx



C2 C3 C4 and CAM (1).pptxAbdullahALvi17
Ìı
This document summarizes C3, C4, and CAM photosynthesis pathways. It explains that C3 photosynthesis involves carbon fixation using RUBISCO and the Calvin cycle. C4 and CAM pathways evolved to concentrate CO2 around RUBISCO to reduce oxygenation, which increases efficiency at high temperatures. C4 pathways use Kranz anatomy in leaf veins to separate processes. While more energy intensive, C4 and CAM avoid the carbon and energy losses of photorespiration seen in tropical C3 plants.C2 C3 C4 and CAM.pptx



C2 C3 C4 and CAM.pptxBalakumaran779282
Ìı
This document summarizes C3, C4, and CAM photosynthesis pathways. It explains that C3 photosynthesis involves carbon fixation using RUBISCO and the Calvin cycle. C4 and CAM pathways evolved to concentrate CO2 around RUBISCO to reduce oxygenation, which increases efficiency at high temperatures. C4 pathways use Kranz anatomy in leaf veins to separate processes. While more energy intensive, C4 and CAM avoid the carbon and energy losses of photorespiration seen in tropical C3 plants.Recently uploaded (20)
Forging Future-Ready Conservation Districts in the Pacific Islands: Strengthe...



Forging Future-Ready Conservation Districts in the Pacific Islands: Strengthe...National Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
Breakout session on Tuesday, February 11, at 10:30 a.m.
The Southern Guam SWCD led the recent "Forging Future-Ready Conservation Districts" event, empowering Pacific Island conservation districts to address regional challenges through strategic capacity building. This session will highlight how the event cultivated leadership, enhanced collaboration, and promoted innovative conservation solutions tailored to island contexts. Participants will learn about approaches to building strong networks and fostering resilience in diverse environments.
Speaker: Erica Pangelinan, Southern Guam SWCDRECALCITRANT HALOCARBONS - Environmental Microbiology



RECALCITRANT HALOCARBONS - Environmental MicrobiologyLakshmikanthV12
Ìı
This presentation explores the role of recalcitrant halocarbons in environmental microbiology, focusing on their persistence in ecosystems and the challenges they pose to microbial degradation. It covers the mechanisms by which certain halocarbons resist breakdown, their impact on soil and water quality, and the strategies employed by microbes to metabolize these stubborn compounds. The presentation also highlights current research, environmental concerns, and potential solutions for managing halocarbon contamination in various ecosystems. Ideal for students, researchers, and environmental professionals.2025 All-America Selections Winning Plants



2025 All-America Selections Winning PlantsAll-America Selections
Ìı
These are the 2025 AAS Winners that have been "Tested Nationally & Proven Locally" for superior garden performance.
They are sure to do well in your garden!Water Quality and Human Life, 2021-02-25.pptx



Water Quality and Human Life, 2021-02-25.pptxDrSafiurRahman
Ìı
Water Quality and Human Life, 2021-02-25.pptxSustainable Plastic Waste Management 



Sustainable Plastic Waste Management Dr. Salem Baidas
Ìı
In this slideshow, you will learn about the definition, sources, types, examples, pollution effects, mitigation and control strategies, UN policy, and global statistics of plastic waste and plastic waste management. Expert Tips to Grow Grass in Arizona - Weed Control Phoenix



Expert Tips to Grow Grass in Arizona - Weed Control PhoenixBuzz Marketing Pros
Ìı
Custom Weed & Pest Control has been in business since 1989, serving the greater Phoenix metro area for both residential and commercial. We offer organic, natural and chemical pest control, with customized service to meet your specific needs. VISIT SITE: https://wekillweeds.com/
CUSTOM WEED & PEST CONTROL
Phoenix AZ 85044
602-956-3844
623-376-7743
info@wekillweeds.com·¡³¦´Ç±ô´Ç²µ¾±³¦²¹±ô·¡²Ô²µ¾±²Ô±ğ±ğ°ù¾±²Ô²µ¸é¾±±è±ğ°ù¾±²¹²Ô³å°ù±ğ²õ³Ù²¹³Ü°ù²¹³¦¾±Ã³²Ô.±è»å´Ú



·¡³¦´Ç±ô´Ç²µ¾±³¦²¹±ô·¡²Ô²µ¾±²Ô±ğ±ğ°ù¾±²Ô²µ¸é¾±±è±ğ°ù¾±²¹²Ô³å°ù±ğ²õ³Ù²¹³Ü°ù²¹³¦¾±Ã³²Ô.±è»å´ÚBenjaminCastilloElia
Ìı
¸é±ğ²õ³Ù³Ü°ù²¹³¦¾±Ã³²ÔClimate change, environmental pollution and green initiatives in Poland.pdf



Climate change, environmental pollution and green initiatives in Poland.pdfjanasek35
Ìı
The presentation describes the effects of climate change on Poland together with some of the most serious environmental pollution issues in Poland and shows some of the green initiatives and green startups from Poland. Indiana County Growing for Good Health Initiative - Using Partnerships to Rea...



Indiana County Growing for Good Health Initiative - Using Partnerships to Rea...National Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
Breakout session on Wednesday, February 12, at 9:00 a.m.
The ICCD Growing for Good Health Initiative was launched with a goal of inspiring and empowering our older adult population to prioritize nutrition and health through the benefits of growing and consuming fresh produce. Participants in this workshop will learn how the ICCD was able to utilize non-traditional partnerships to implement a unique specialty crops program to reach an undeserved population in Indiana County.
Speakers: Blake Mauthe, Indiana County Conservation District, District Educator and Douglas Beri Jr., Indiana County Conservation DistrictPresentation on Stream Action Perspectives and Cycles



Presentation on Stream Action Perspectives and CyclesSaida Islam Sejuti
Ìı
Course ppt on Stream ActionClimate change, environmental pollution and green initiatives in Slovakia.pdf



Climate change, environmental pollution and green initiatives in Slovakia.pdfjanasek35
Ìı
The presentation describes the effects of climate change on Slovakia together with some of the most serious environmental pollution issues in Slovakia and shows some of the green initiatives and green startups from Slovakia. USDA-NRCS Technical Service Provider (TSP) Program: An Overview of Processes ...



USDA-NRCS Technical Service Provider (TSP) Program: An Overview of Processes ...National Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
Breakout session on Monday, February 10, at 2:30 p.m.
TSPs provide third-party technical assistance to NRCS program participants and can be instrumental in addressing targeted resource concerns in your region. This session will discuss the process of becoming a TSP and how NRCS and partners benefit from utilizing TSPs.
Speaker: Alyson Aquino, Natural Resources Conservation ServiceEnergy-Policy-Scenarios-of-Bangladesh.pptx



Energy-Policy-Scenarios-of-Bangladesh.pptxSaida Islam Sejuti
Ìı
MS course(Natural Resource)Presentation slidesGreen and Dark Green Minimalist Restoring The Forest Presentation.pptx



Green and Dark Green Minimalist Restoring The Forest Presentation.pptxmymddolui
Ìı
Forests are the lungs of the world that absorb carbon and provide oxygen. However, deforestation threatens their sustainability. Reforestation is an important solution to restore forests and maintain the balance of ecosystems and the environment.
H2Ohio: Navigating the Waters of Opportunity and Challenge



H2Ohio: Navigating the Waters of Opportunity and ChallengeNational Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
Breakout session on Tuesday, February 11, at 2:45 p.m.
H2Ohio addresses urgent water quality problems, such as algal blooms from agricultural runoff. Starting in 2020, H2Ohio has encountered challenges in contract management and efficient program delivery. With more than $60 million in annual support, the initiative works with local SWCDs to implement BMPs across 1.8 million acres, which creates opportunity and trials along the way.
Speakers: Terry Mescher and Kip Studer, Ohio Department of AgricultureNavigating NRCS Policy for Certified Conservation Planners



Navigating NRCS Policy for Certified Conservation PlannersNational Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
Breakout session on Monday, February 10, at 3:45 p.m.
In August 2024, NRCs updated Conservation Planning Policy (Title 180, General Manual, Part 409) to clarify and streamline the planner designation levels and requirements. During this session, representatives from the NRCS Conservation Planning Branch will provide an overview of the conservation certification requirements and changes from the recent policy updates.
Speaker: Breanna BarlowForging Future-Ready Conservation Districts in the Pacific Islands: Strengthe...



Forging Future-Ready Conservation Districts in the Pacific Islands: Strengthe...National Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
·¡³¦´Ç±ô´Ç²µ¾±³¦²¹±ô·¡²Ô²µ¾±²Ô±ğ±ğ°ù¾±²Ô²µ¸é¾±±è±ğ°ù¾±²¹²Ô³å°ù±ğ²õ³Ù²¹³Ü°ù²¹³¦¾±Ã³²Ô.±è»å´Ú



·¡³¦´Ç±ô´Ç²µ¾±³¦²¹±ô·¡²Ô²µ¾±²Ô±ğ±ğ°ù¾±²Ô²µ¸é¾±±è±ğ°ù¾±²¹²Ô³å°ù±ğ²õ³Ù²¹³Ü°ù²¹³¦¾±Ã³²Ô.±è»å´ÚBenjaminCastilloElia
Ìı
Indiana County Growing for Good Health Initiative - Using Partnerships to Rea...



Indiana County Growing for Good Health Initiative - Using Partnerships to Rea...National Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
USDA-NRCS Technical Service Provider (TSP) Program: An Overview of Processes ...



USDA-NRCS Technical Service Provider (TSP) Program: An Overview of Processes ...National Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
H2Ohio: Navigating the Waters of Opportunity and Challenge



H2Ohio: Navigating the Waters of Opportunity and ChallengeNational Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
Navigating NRCS Policy for Certified Conservation Planners



Navigating NRCS Policy for Certified Conservation PlannersNational Association of Conservation Districts
Ìı
Beautiful way to save our planet
- 1. The Beautiful way to protect our planet Murugan V Chennai
- 3. Orchid Clean Atmosphere Absorbs Atmospheric Pollutions 1.Carbon monoxide (CO) 2.Carbon di oxide (CO2) 3. 5.Methane (CH3) 4.Nitric oxide (NO) 5.Sulphur di Oxide (SO2) 6.Other Pollutions 7.Moisture Etc
- 4. Velamen Absorbs Atmospheric Pollutions 1.Carbon monoxide (CO) 2.Carbon di oxide (CO2) 3. 5.Methane (CH3) 4.Nitric oxide (NO) 5.Sulphur di Oxide (SO2) 6.Other Pollutions 7.Moisture Etc
- 5. Velamen Absorbs Atmospheric Pollutions 1.Carbon monoxide (CO) 2.Carbon di oxide (CO2) 3. 5.Methane (CH3) 4.Nitric oxide (NO) 5.Sulphur di Oxide (SO2) 6.Other Pollutions 7.Moisture Etc
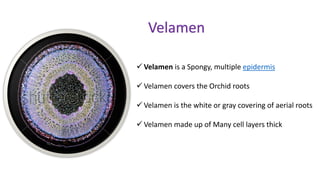
- 6. Velamen  Velamen is a Spongy, multiple epidermis  Velamen covers the Orchid roots  Velamen is the white or gray covering of aerial roots  Velamen made up of Many cell layers thick
- 7. Velamen Velamen capable of absorbing atmospheric moisture and nutrients, The roots of orchids are associated with symbiotic fungi or bacteria; the latter may fix nutrients from the air. This functionality allows the orchid to exist in locations that provide a reproductive or vegetative advantage such as improved exposure or reduced competition from other plants
- 8. Velamen  Velamen capable of absorbing atmospheric moisture & (C,N,S,K,P Etc)  Orchids roots are associated with symbiotic fungi or bacteria; the latter may fix nutrients from the air  This functionality allows the orchid to exist in locations that provide a reproductive or vegetative advantage such as improved exposure or reduced competition from other plants
- 9. Orchid protect our Planet All the way
- 10. CAM Plant Orchid To increase their intracellular CO2 concentration at the site of its fixation which allowed the primary Carboxylating enzyme rubisco to function more efficiently. The CO2 concentrating mechanism possessed by Orchids operates by sequentially Reducing CO2 into carbohydrates at two different times of day. The initial reduction of CO2 into a four-carbon sugar is done at night – when CAM plant stomata are open - by the enzyme PEP-carboxylase. Then, during the day when CAM plant stomata are closed, the four-carbon sugar is decarboxylated, increasing the plant's intercellular CO2 concentration, and the resulting CO2 is subsequently reduced back into a carbohydrate,
- 11. Photo Synthesis
- 13. Tree Coal Coconut shell Coconut husk





