Bench terracing
Download as PPTX, PDF27 likes36,227 views
Bench terracing involves constructing level or sloped platforms across a hillside to reduce soil erosion and facilitate agriculture. It has been used for thousands of years around the world. Bench terracing is well-suited to steep slopes under 30% with stable soil. It can improve crop yields by slowing runoff, increasing infiltration, and allowing different crops on benches. However, bench terracing requires significant labor to construct and maintain properly to prevent failures. Examples of historic and current bench terracing can be seen around the world, from the Philippines to France, the Middle East, and Asia.
1 of 35
Downloaded 183 times

































Recommended
Bunds and their design



Bunds and their designUtkarsh Jain
Ėý
Bunds are embankment structures constructed across land slopes to obstruct surface runoff. There are two main types: contour bunds and graded bunds. Contour bunds have no longitudinal slope and are suitable for areas with annual rainfall under 600 mm and permeable soils with slopes less than 6%. Graded bunds have a slope to safely dispose of excess runoff and are recommended for high rainfall regions and impermeable soils. The design of bunds considers factors like rainfall, soil type, slope, spacing between bunds, size, length, and area lost due to construction.Gully classification and its contol measures



Gully classification and its contol measuresDr. Sanjay Singh Chouhan
Ėý
This document provides information on gully classification and control measures. It defines a gully and describes the factors that influence gully formation. It then discusses different ways of classifying gullies based on size, shape, dimensions, and state of activity. The document outlines the typical stages of gully development. It presents various biological, temporary, and permanent engineering measures that can be used to control gullies, such as vegetative methods, check dams, brush dams, and loose rock dams. The overall aim of gully control is to reduce surface runoff and convey runoff through the gully in a non-erosive manner until vegetation can stabilize the area.Grassed water ways



Grassed water waysDr. Sanjay Singh Chouhan
Ėý
This document discusses the design and construction of grassed waterways. It begins by defining grassed waterways as natural or man-made channels with vegetation cover used to safely transport runoff from fields. It then discusses the purposes of grassed waterways, which include preventing erosion and sedimentation while transporting water. The document provides details on the design process, including calculating dimensions based on watershed characteristics and expected runoff. It recommends shapes, grades, and flow velocities for effective design. Construction and maintenance are also outlined, emphasizing establishing vegetation cover and conducting repairs to ensure proper functioning of grassed waterways over time.Water erosion



Water erosionUniversity of Agriculture Faisalabad
Ėý
This document discusses water erosion, which is the removal of soil by water. It defines erosion as the detachment, transportation, and deposition of soil. The main causes of erosion are misuse of land, deforestation, and poor soil management. The agents of erosion are wind, water, temperature, and biological factors. Water erosion specifically refers to the removal of soil particles by rain or flowing water. The forms of water erosion are rain splash, sheet, rill, gully, and stream erosion. Climate, soil properties, and topography affect the rate of water erosion.Chapter 5



Chapter 5mengistuzantet
Ėý
This document discusses various soil erosion control measures, including biological/agronomic practices like mulching, crop management, and soil management, as well as mechanical/engineering practices like terraces, bunds, vegetated waterways, and gully control. It provides details on the design of terraces, including the factors that influence terrace spacing, length, and cross-section. The key principles of erosion control are reducing rain drop impact, runoff volume and velocity, while increasing soil resistance to erosion. Agronomic practices are preferred where possible due to lower cost and easier integration with farming. Soil moisture constants



Soil moisture constantsBaskar Selvam
Ėý
Soil is the home of million of organisms. In agriculture, from seed to grain, soil is a prima factor. It also acts a medium to store water for plants and form of water in soil called soil moisture. Some parameters to check the soil moisture called soil moisture constants. So, soil and water relationship is essential in agriculture.Erosion control measures



Erosion control measuresDr. Sanjay Singh Chouhan
Ėý
This document discusses various erosion control measures for soil and water conservation. It describes agronomic measures like contour cropping, strip cropping, and mulching which control erosion by reducing rain drop impact and increasing infiltration. Mechanical measures like bunding and terracing are also discussed. Bunds are embankments constructed across slopes to slow water flow, while terraces convert steep slopes into level platforms separated by retaining walls to control runoff. Different types of bunding, terracing and their applications are explained in detail.Water harvesting and its technique



Water harvesting and its techniqueDr. Sanjay Singh Chouhan
Ėý
water harvesting, runoff harvesting, rain water harvesting, roof water harvesting, flood water harvesting, farm pondIrrigation scheduling



Irrigation schedulingbabu kakumanu
Ėý
describes the irrigation and irrigation requirements of different crops. this ppt also describes about different methods to measure the soil moisture availability.Terraces:Soil Water Conservation structure



Terraces:Soil Water Conservation structureMoudud Hasan
Ėý
This document discusses different types and methods of terrace construction. It describes how terraces are classified based on their alignment, cross-section, grade, and outlets. Terraces help reduce soil erosion by interrupting the flow of surface runoff water down slopes. The key aspects of terrace design include specifying the proper spacing, designing stable channels, and developing farmable cross-sections. Construction requires machinery like bulldozers and consideration of soil and weather conditions.Universal Soil Loss Equation.pptx



Universal Soil Loss Equation.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
Ėý
The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) is a widely used method for estimating average annual soil loss. It was initially proposed in 1958 and modified to its current form in 1978. The USLE estimates soil loss as a function of rainfall erosivity, soil erodibility, slope length and steepness, crop management practices, and conservation support practices. It is used to predict soil loss, guide crop and management selections, and determine conservation needs. However, the USLE is empirical and only estimates average annual soil loss from sheet and rill erosion without considering sediment deposition.IRRIGATION SYSTEMS IN GREENHOUSE



IRRIGATION SYSTEMS IN GREENHOUSEpramodrai30
Ėý
This document discusses various irrigation systems used in greenhouses. It begins by defining crop water needs and evapotranspiration. It then describes different types of irrigation systems including overhead systems like sprinklers and booms, surface systems like drip and perimeter watering, and subsurface systems like ebb and flow, capillary mats, and floor flooding. Key components of drip irrigation systems like pumps, filters, fertigation equipment, and piping networks are also explained. The advantages of drip irrigation systems for greenhouse crops are highlighted.LAND CAPABILITY CLASSIFICATION



LAND CAPABILITY CLASSIFICATIONdebaaaaaaaa
Ėý
The document discusses land capability classification, which groups land into classes based on inherent limitations from soil, topography, drainage and climate. It aims to guide land use according to capability. There are 8 land capability classes ranging from Class I land with few limitations to Class VIII land only suitable for wildlife or watershed use. Within classes II-IV are subclasses that further specify limitations from erosion (e), wetness (w), soil properties (s) or climate (c). The classification enables predicting safe land use and required conservation practices.Universal soil loss equation ; soil loss measurement



Universal soil loss equation ; soil loss measurementDr. Sanjay Singh Chouhan
Ėý
Universal soil loss equation, soil loss estimation, factors of USLE, its use and limitation, soil loss measurement by multi slot divisor and coshocton wheel samplerMB PLOUGH.pptx



MB PLOUGH.pptxSatishPatilVk
Ėý
This document discusses the design of a mouldboard plow (MB plow). It begins with an introduction to plows and their importance. It then discusses the types of MB plows and their main components. The document provides details on different types of mouldboards, shares, and landsides. It concludes with the steps involved in designing an MB plow, including determining key specifications, angles, required tractor power, and calculating and designing the individual components.Forms of water erosion



Forms of water erosionpoornimsundarraj
Ėý
Splash erosion is caused by the impact of raindrops and is determined by climate, soil properties, topography, and plant cover. Sheet erosion involves the uniform removal of a thin layer of soil by splash erosion and the transportation of detached particles by surface runoff. Rill erosion occurs when sheet erosion advances to form shallow channels, and gully erosion is the most advanced stage where channels cannot be smoothed out by cultivation and are formed through water and channel erosion processes. Gullies are classified based on their shape, activity level, and dimensions, and progress through formation, development, healing, and stabilization stages over time.Water erosion control measures



Water erosion control measuresSouvik Ghosh
Ėý
Water erosion control measures aim to limit land damage from erosion. Mechanical measures include diversion drains, terracing, contour bunding, and waterways to redirect water flow. Agronomical measures include contour farming, strip cropping, conservation tillage, crop rotation and mixed cropping, and mulching to stabilize soil and reduce runoff. Properly implementing these control techniques can help reduce soil loss and land degradation caused by water erosion.Soil moisture conservation techniques



Soil moisture conservation techniquesMANU MOHAN
Ėý
This document discusses various in-situ soil moisture conservation techniques. It introduces the topic and explains that these techniques are recommended in addition to large-scale watershed management structures to increase moisture availability for crops. The techniques aim to increase infiltration and temporarily store water at the soil surface. The document then describes several specific techniques in detail, including deep tillage, mulching, basin listing, broad-based beds and furrows, ridges and furrows, and compartmental bunding. It explains the principles and benefits of each technique for conserving soil moisture.Soil Loss Measurement Techniques.pptx



Soil Loss Measurement Techniques.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
Ėý
This presentation describes about Soil loss measurement techniques, Runoff plots, Multislot divisors, Coshocton Wheel samplerTerraces and their design



Terraces and their designUtkarsh Jain
Ėý
THIS PPT COVERS ABOUT TERRACE AND ITS TYPES
TOPICS COVERED ARE TERRACE TYPES;BROAD BASE, BENCH TERRACE
BENCH TERRACE DESIGN AND TYPES ARE ALSO COVERED IN PPTClassification of soil water



Classification of soil waterSHIVAJI SURYAVANSHI
Ėý
The document classifies and describes the three main classes of soil water:
1) Capillary water, which exists in pore spaces by molecular attraction and surface tension, held at tensions from 1/3 to 15 atmospheres.
2) Gravitational water, which will drain out of soil pores due to gravity if drainage is provided, and is not available for plant growth.
3) Hygroscopic water, which is absorbed by oven-dried soil exposed to moist air and is held very tightly by adsorption forces at tensions from 10,000 to 31 atmospheres, making it unavailable to plants.Tillage and Primary Tillage Implements



Tillage and Primary Tillage ImplementsAjay Singh Lodhi
Ėý
Tillage involves mechanically manipulating soil to provide favorable conditions for crop production. It includes breaking up and loosening the soil through operations like plowing. The objectives of tillage are to prepare seed beds, add organic matter, destroy weeds, aerate the soil, increase water absorption, and reduce erosion. Plowing is a primary tillage operation that uses implements like indigenous plows pulled by animals or moldboard plows pulled by tractors. These plows cut, lift, and invert soil to prepare fields for planting. Tillage can be classified into primary and secondary operations, with primary tillage like plowing performing deeper soil manipulation.Soil and moisture conservation techniques



Soil and moisture conservation techniquesCollege of Agriculture, Balaghat
Ėý
This document discusses various soil and moisture conservation techniques, which are divided into agronomic and engineering measures. Agronomic measures include conservation tillage, deep tillage, contour farming, strip cropping, mulching, and growing cover crops. These are used where land slopes are less than 2%. Engineering measures include bunding, terracing, trenching, and subsoiling, which are constructed barriers used on slopes greater than 2% to retain runoff. Broad bed furrows are also discussed as a technique using beds and furrows to store moisture and drain excess water.Planning and design of green house



Planning and design of green houseAjay Singh Lodhi
Ėý
The document discusses planning and design considerations for greenhouses. It covers site selection factors like solar exposure, drainage, wind protection and orientation. Greenhouse structural designs can be straight-sided walls with arched or gabled roofs, or hoop-style frames. Designs must withstand wind and snow loads. Covering materials are selected based on light transmission, durability, thermal properties and service life. The ideal covering transmits visible light, absorbs UV rays, reflects infrared to prevent overheating, is low-cost, and lasts 10-20 years.Seed drill caliberation



Seed drill caliberationsaurabhtripathi209
Ėý
The document discusses components and calibration of a seed drill. It provides details on:
1) The main components of a seed drill including the frame, seed box, seed metering mechanism, furrow openers, covering device, and transport wheels.
2) The process of calibrating a ground wheel driven seed drill which involves determining the drill width and length to cover a hectare, revolutions to cover that length, collecting seeded amounts, and adjusting the rate control until the desired rate is reached.
3) Additional details on calculating seeding rates based on drill specifications and adjusting row spacing using the planting disc configuration.Soil loss estimation



Soil loss estimationUtkarsh Jain
Ėý
THIS PPT COVERS ABOUT UNIVERSAL SOIL LOSS EQUATION ITS USES AND LIMITATIONS AND MODIFIED UNIVERSAL SOIL LOSS EQUATION.agricultural drainage



agricultural drainagehamoodrehman7
Ėý
agricultural drainage its types benefits of drainage and components problems of drainage and their solutionWatershed management



Watershed managementMANORANJAN ROUT
Ėý
Watershed management aims to enable sustainable production and minimize hazards to natural resources like soil and water. A watershed is a geographical area that drains to a common water body. Key components of watershed management programs include soil and water conservation measures, water harvesting, and crop management and alternate land use systems suited to land capability. The overall objectives are improved livelihoods through increased incomes while protecting watershed resources.Contouring, Terracing and Strip Planting by Muhammad Zuhair.pptx



Contouring, Terracing and Strip Planting by Muhammad Zuhair.pptxFarhanAhmad230
Ėý
Contouring, Terracing and Strip Planting by Muhammad Zuhair
class presentation by Farhan Ahmad group4.Land Preparation.pptx



4.Land Preparation.pptxKarloanthonytEstillo
Ėý
This document discusses land preparation and tillage practices. It covers the aims of land preparation such as loosening soil, improving aeration and water infiltration. It describes different tillage operations including primary tillage using implements like moldboard plows and disc plows, and secondary tillage using cultivators and harrows. Conservation tillage systems are introduced, including no-tillage, mulch tillage, and ridge tillage. The advantages and disadvantages of animal, human, and machine power for tillage are presented. The document stresses that tillage can impact soil fertility positively or negatively, and should aim for minimum soil disturbance.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Irrigation scheduling



Irrigation schedulingbabu kakumanu
Ėý
describes the irrigation and irrigation requirements of different crops. this ppt also describes about different methods to measure the soil moisture availability.Terraces:Soil Water Conservation structure



Terraces:Soil Water Conservation structureMoudud Hasan
Ėý
This document discusses different types and methods of terrace construction. It describes how terraces are classified based on their alignment, cross-section, grade, and outlets. Terraces help reduce soil erosion by interrupting the flow of surface runoff water down slopes. The key aspects of terrace design include specifying the proper spacing, designing stable channels, and developing farmable cross-sections. Construction requires machinery like bulldozers and consideration of soil and weather conditions.Universal Soil Loss Equation.pptx



Universal Soil Loss Equation.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
Ėý
The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) is a widely used method for estimating average annual soil loss. It was initially proposed in 1958 and modified to its current form in 1978. The USLE estimates soil loss as a function of rainfall erosivity, soil erodibility, slope length and steepness, crop management practices, and conservation support practices. It is used to predict soil loss, guide crop and management selections, and determine conservation needs. However, the USLE is empirical and only estimates average annual soil loss from sheet and rill erosion without considering sediment deposition.IRRIGATION SYSTEMS IN GREENHOUSE



IRRIGATION SYSTEMS IN GREENHOUSEpramodrai30
Ėý
This document discusses various irrigation systems used in greenhouses. It begins by defining crop water needs and evapotranspiration. It then describes different types of irrigation systems including overhead systems like sprinklers and booms, surface systems like drip and perimeter watering, and subsurface systems like ebb and flow, capillary mats, and floor flooding. Key components of drip irrigation systems like pumps, filters, fertigation equipment, and piping networks are also explained. The advantages of drip irrigation systems for greenhouse crops are highlighted.LAND CAPABILITY CLASSIFICATION



LAND CAPABILITY CLASSIFICATIONdebaaaaaaaa
Ėý
The document discusses land capability classification, which groups land into classes based on inherent limitations from soil, topography, drainage and climate. It aims to guide land use according to capability. There are 8 land capability classes ranging from Class I land with few limitations to Class VIII land only suitable for wildlife or watershed use. Within classes II-IV are subclasses that further specify limitations from erosion (e), wetness (w), soil properties (s) or climate (c). The classification enables predicting safe land use and required conservation practices.Universal soil loss equation ; soil loss measurement



Universal soil loss equation ; soil loss measurementDr. Sanjay Singh Chouhan
Ėý
Universal soil loss equation, soil loss estimation, factors of USLE, its use and limitation, soil loss measurement by multi slot divisor and coshocton wheel samplerMB PLOUGH.pptx



MB PLOUGH.pptxSatishPatilVk
Ėý
This document discusses the design of a mouldboard plow (MB plow). It begins with an introduction to plows and their importance. It then discusses the types of MB plows and their main components. The document provides details on different types of mouldboards, shares, and landsides. It concludes with the steps involved in designing an MB plow, including determining key specifications, angles, required tractor power, and calculating and designing the individual components.Forms of water erosion



Forms of water erosionpoornimsundarraj
Ėý
Splash erosion is caused by the impact of raindrops and is determined by climate, soil properties, topography, and plant cover. Sheet erosion involves the uniform removal of a thin layer of soil by splash erosion and the transportation of detached particles by surface runoff. Rill erosion occurs when sheet erosion advances to form shallow channels, and gully erosion is the most advanced stage where channels cannot be smoothed out by cultivation and are formed through water and channel erosion processes. Gullies are classified based on their shape, activity level, and dimensions, and progress through formation, development, healing, and stabilization stages over time.Water erosion control measures



Water erosion control measuresSouvik Ghosh
Ėý
Water erosion control measures aim to limit land damage from erosion. Mechanical measures include diversion drains, terracing, contour bunding, and waterways to redirect water flow. Agronomical measures include contour farming, strip cropping, conservation tillage, crop rotation and mixed cropping, and mulching to stabilize soil and reduce runoff. Properly implementing these control techniques can help reduce soil loss and land degradation caused by water erosion.Soil moisture conservation techniques



Soil moisture conservation techniquesMANU MOHAN
Ėý
This document discusses various in-situ soil moisture conservation techniques. It introduces the topic and explains that these techniques are recommended in addition to large-scale watershed management structures to increase moisture availability for crops. The techniques aim to increase infiltration and temporarily store water at the soil surface. The document then describes several specific techniques in detail, including deep tillage, mulching, basin listing, broad-based beds and furrows, ridges and furrows, and compartmental bunding. It explains the principles and benefits of each technique for conserving soil moisture.Soil Loss Measurement Techniques.pptx



Soil Loss Measurement Techniques.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
Ėý
This presentation describes about Soil loss measurement techniques, Runoff plots, Multislot divisors, Coshocton Wheel samplerTerraces and their design



Terraces and their designUtkarsh Jain
Ėý
THIS PPT COVERS ABOUT TERRACE AND ITS TYPES
TOPICS COVERED ARE TERRACE TYPES;BROAD BASE, BENCH TERRACE
BENCH TERRACE DESIGN AND TYPES ARE ALSO COVERED IN PPTClassification of soil water



Classification of soil waterSHIVAJI SURYAVANSHI
Ėý
The document classifies and describes the three main classes of soil water:
1) Capillary water, which exists in pore spaces by molecular attraction and surface tension, held at tensions from 1/3 to 15 atmospheres.
2) Gravitational water, which will drain out of soil pores due to gravity if drainage is provided, and is not available for plant growth.
3) Hygroscopic water, which is absorbed by oven-dried soil exposed to moist air and is held very tightly by adsorption forces at tensions from 10,000 to 31 atmospheres, making it unavailable to plants.Tillage and Primary Tillage Implements



Tillage and Primary Tillage ImplementsAjay Singh Lodhi
Ėý
Tillage involves mechanically manipulating soil to provide favorable conditions for crop production. It includes breaking up and loosening the soil through operations like plowing. The objectives of tillage are to prepare seed beds, add organic matter, destroy weeds, aerate the soil, increase water absorption, and reduce erosion. Plowing is a primary tillage operation that uses implements like indigenous plows pulled by animals or moldboard plows pulled by tractors. These plows cut, lift, and invert soil to prepare fields for planting. Tillage can be classified into primary and secondary operations, with primary tillage like plowing performing deeper soil manipulation.Soil and moisture conservation techniques



Soil and moisture conservation techniquesCollege of Agriculture, Balaghat
Ėý
This document discusses various soil and moisture conservation techniques, which are divided into agronomic and engineering measures. Agronomic measures include conservation tillage, deep tillage, contour farming, strip cropping, mulching, and growing cover crops. These are used where land slopes are less than 2%. Engineering measures include bunding, terracing, trenching, and subsoiling, which are constructed barriers used on slopes greater than 2% to retain runoff. Broad bed furrows are also discussed as a technique using beds and furrows to store moisture and drain excess water.Planning and design of green house



Planning and design of green houseAjay Singh Lodhi
Ėý
The document discusses planning and design considerations for greenhouses. It covers site selection factors like solar exposure, drainage, wind protection and orientation. Greenhouse structural designs can be straight-sided walls with arched or gabled roofs, or hoop-style frames. Designs must withstand wind and snow loads. Covering materials are selected based on light transmission, durability, thermal properties and service life. The ideal covering transmits visible light, absorbs UV rays, reflects infrared to prevent overheating, is low-cost, and lasts 10-20 years.Seed drill caliberation



Seed drill caliberationsaurabhtripathi209
Ėý
The document discusses components and calibration of a seed drill. It provides details on:
1) The main components of a seed drill including the frame, seed box, seed metering mechanism, furrow openers, covering device, and transport wheels.
2) The process of calibrating a ground wheel driven seed drill which involves determining the drill width and length to cover a hectare, revolutions to cover that length, collecting seeded amounts, and adjusting the rate control until the desired rate is reached.
3) Additional details on calculating seeding rates based on drill specifications and adjusting row spacing using the planting disc configuration.Soil loss estimation



Soil loss estimationUtkarsh Jain
Ėý
THIS PPT COVERS ABOUT UNIVERSAL SOIL LOSS EQUATION ITS USES AND LIMITATIONS AND MODIFIED UNIVERSAL SOIL LOSS EQUATION.agricultural drainage



agricultural drainagehamoodrehman7
Ėý
agricultural drainage its types benefits of drainage and components problems of drainage and their solutionWatershed management



Watershed managementMANORANJAN ROUT
Ėý
Watershed management aims to enable sustainable production and minimize hazards to natural resources like soil and water. A watershed is a geographical area that drains to a common water body. Key components of watershed management programs include soil and water conservation measures, water harvesting, and crop management and alternate land use systems suited to land capability. The overall objectives are improved livelihoods through increased incomes while protecting watershed resources.Similar to Bench terracing (20)
Contouring, Terracing and Strip Planting by Muhammad Zuhair.pptx



Contouring, Terracing and Strip Planting by Muhammad Zuhair.pptxFarhanAhmad230
Ėý
Contouring, Terracing and Strip Planting by Muhammad Zuhair
class presentation by Farhan Ahmad group4.Land Preparation.pptx



4.Land Preparation.pptxKarloanthonytEstillo
Ėý
This document discusses land preparation and tillage practices. It covers the aims of land preparation such as loosening soil, improving aeration and water infiltration. It describes different tillage operations including primary tillage using implements like moldboard plows and disc plows, and secondary tillage using cultivators and harrows. Conservation tillage systems are introduced, including no-tillage, mulch tillage, and ridge tillage. The advantages and disadvantages of animal, human, and machine power for tillage are presented. The document stresses that tillage can impact soil fertility positively or negatively, and should aim for minimum soil disturbance.Lecture 5-Soil and Water Management under Agroforestry system.pptx



Lecture 5-Soil and Water Management under Agroforestry system.pptxUmeshTimilsina1
Ėý
Soil and Water Management under Agroforestry systemPrinciple of erosion control- Introduction to contouring,strip cropping,conto...



Principle of erosion control- Introduction to contouring,strip cropping,conto...ZAPPAC1
Ėý
Principle of erosion controlManagement of Red lateritic soil and Dry land soil...pptx



Management of Red lateritic soil and Dry land soil...pptxMohanSahu35
Ėý
The document discusses the management principles of red lateritic soil and dryland soil. Red lateritic soil is rich in iron and aluminum, and found in hot, wet tropical areas. It has low organic matter and water holding capacity. Management includes adding clay or rice husk to improve physical properties, growing tolerant crops, and liming to reduce toxicity. Dryland soils have low fertility and moisture. Management involves adopting drought-resistant crop varieties and systems, mechanical methods to reduce erosion, and maintaining soil fertility.Moisture conservation practices 3102



Moisture conservation practices 3102Muhammad Faheem
Ėý
The document discusses various practices for soil moisture conservation in dryland farming areas. It describes 17 techniques including conservation tillage, mulching, crop rotation, green manuring, deep tillage, compartmental bunding, retention ditches, contour farming, stone lines, planting pits, and semi-circular bunds. These techniques aim to increase water infiltration and retention in soil by reducing runoff, impounding surface water, and modifying land configurations to harvest rainfall where it falls. Properly conserving soil moisture through these methods can help ensure sustainable agricultural production in dry regions with limited water availability.Tillage Practices and types



Tillage Practices and typesArunMK17
Ėý
Tillage is the manipulation of soil with tools & implements for loosening the surface crust & bringing about conditions favorable for the germination of seeds and the growth of crops.
soil condition resulting from tillage
good Tilth - soft, friable & properly aerated
crop emergence, establishment, growth and development
easy infiltration of water & are retentive of moisture for satisfactory growth of plants
To prepare the seed bed to a satisfactory level which promotes good germination and establishment of the seedlings
To control weeds and improve close plant-soil interaction in the rooting zone.
To loosen the soil for easy penetration and proliferation
To remove the other sprouting materials in the soil
To modify the soil temperature
To break hard soil pans and improve drainage facilities
To manage the plant residues by incorporating into the soil or to retain on the top layer to reduce erosion.
To improve the physical conditions of the soil
To harvest rain water easily and soil erosion can be minimised.
To establish specific surface configurations for sowing, irrigation, drainage, etc.
To incorporate and mix applied fertilizers and manures into the soil.
To destroy the eggs and larvae of insects and their breeding places.
Mechanical practices of soil conservation 



Mechanical practices of soil conservation Usman Khawaja
Ėý
The mechanical soil conservation practices aim to reduce runoff velocity, retain water in soil, and prevent erosion. These include making basins to collect and retain rainwater, breaking hard clay pans to improve drainage, subsoiling to promote water absorption, contour terracing to retain water and check erosion, contour trenching with pits across slopes, terrace outlets to safely remove excess water, gully control, and stream bank protection. Terracing is an expensive but important method, especially on steep land, involving constructing leveled areas at right angles to slopes. Factors like slope length and steepness, soil type, and precipitation determine terracing feasibility.Lecture 6 soil & water conservation



Lecture 6 soil & water conservationManish Bobade
Ėý
This document discusses soil and water conservation measures for fodder production. It describes soil erosion caused by water and wind, and measures to conserve soil like agronomic practices (contour cultivation, conservation tillage, mulching, cropping systems), mechanical measures (contour bunding, graded bunding, terracing), forestry measures, and agrostological measures (using grasses). It also discusses surface and subsurface drainage methods for agricultural lands.new LECTURE 3-converted.pdf



new LECTURE 3-converted.pdfDarshanUmbarkar
Ėý
This document discusses different concepts of tillage including conventional tillage, minimum tillage, zero tillage, stubble mulch tillage, and conservation tillage. Conventional tillage uses heavy plows which can create hard pans and increase soil degradation over time. Minimum tillage aims to reduce tillage operations to only what is necessary for seeding. Zero tillage plants new crops without any soil preparation or tillage by controlling weeds with herbicides. Stubble mulch tillage leaves crop residues on the soil surface year-round. Conservation tillage conserves soil and moisture by keeping organic residues on the surface rather than incorporating them into the soil.Method of irrigation



Method of irrigationSHIVAJI SURYAVANSHI
Ėý
This document provides an overview of irrigation and various methods of irrigation. It discusses the necessity, benefits and effects of irrigation. It then describes various surface irrigation methods including uncontrolled flooding, border strip method, check method, basin method and furrow method. It also discusses subsurface, sprinkler and trickle/drip irrigation methods. For each method, it provides details on how the method works and its advantages and disadvantages.Rice.pptx



Rice.pptxRutvikRabadia
Ėý
Rice is a semi-aquatic grass that thrives in warm climates and is the staple food for over half the world's population. India is the second largest producer of rice, with production in 2021-22 estimated at a record 129.66 million tonnes. There are two cultivated species of rice, Oryza sativa found in Asia, America and Europe and Oryza glaberrima found in West Africa. Common methods for growing rice include transplanted puddled lowland rice, system of rice intensification, wet seeded puddled lowland rice, and dry seeded methods with and without supplemental irrigation. Proper land preparation, seed treatment, water and fertilizer management are important for optimalengineering practices for soil conservation



engineering practices for soil conservationUsman Khawaja
Ėý
The mechanical soil conservation practices aim to reduce runoff velocity, retain water in soil, and prevent erosion. These include techniques like basin leaching, pan breaking, subsoiling, and contour terracing to improve water absorption. Contour terracing involves constructing terraces, ridges, or channels along contours to slow runoff and retain water in soil. Additional methods are gully control, pond construction, and stream bank protection.Desertification 2



Desertification 2KanwalNisa1
Ėý
Desertification is a significant global problem caused by both human and environmental factors. It involves dry land regions becoming increasingly arid and losing vegetation and wildlife. There are various types and causes of desertification including drought, overgrazing, overcultivation, and removal of trees. Countermeasures aim to prevent further desertification through reforestation, soil fixation, contour trenching, farmer-managed natural regeneration, and managed grazing. Past large-scale afforestation efforts in China's dry northwest have failed due to unsuitable climate conditions of low rainfall, though some localized successes have occurred near available water sources.Day 09 & Day 10 Primary and Secondary Tillage Imple



Day 09 & Day 10 Primary and Secondary Tillage ImpleSuyog Khose
Ėý
This document provides an overview of soil tillage. It begins by defining tillage as the mechanical manipulation of soil to provide favorable conditions for crop production. It then discusses different types of tillage like primary and secondary tillage. Specific tillage implements are described in detail like the moldboard plow, chisel plow, disc plow, and rotary plow. The functions of tillage tools like the share, moldboard, and coulter are explained. The document also covers topics like tillage adjustments, tillage methods, and selecting the proper tillage implement for different soil types.Social go



Social godhingraurvashi
Ėý
Soil erosion occurs when rain impacts unprotected soil, loosening particles that are then washed away by water and wind. This carries away the nutrient-rich topsoil, leaving the land unable to support plant life. Common causes are overgrazing, inappropriate farming like over-ploughing, lack of crop rotation, and planting down slopes rather than across. Conservation methods include contour farming, mulching, crop rotation, strip cropping planted across slopes, and grass cultivation. Mechanical measures form barriers like basins, terraces, and trenches to slow water flow and capture eroded particles.Irrigation and its types



Irrigation and its typesSULAKSHYA GAUR
Ėý
irrigation ,its benefits,disadvantages, types of irrigation including surface irrigation and its typesTillage n tilth



Tillage n tilthKrishnamayee Sethi
Ėý
Tillage and tilth involve mechanical soil manipulation to create ideal conditions for plant growth. Tillage includes primary tillage like ploughing to open soil and secondary tillage like harrowing to break clods. The objectives are to prepare seedbeds, control weeds, aerate soil, and mix amendments. On-season tillage occurs before planting while off-season tillage conditions soil for future crops. Different tillage types include subsoiling to break hardpans and puddling for rice where soil is tilled under water. The depth and number of tillage operations varies by crop needs and soil conditions.Agronomical measures to control soil erosion



Agronomical measures to control soil erosionAbhinab Mishra
Ėý
This document discusses several agronomical measures that can be used to control soil erosion, including:
1) Mulching, which covers soil with crop residues to reduce rain and wind impact;
2) Agroforestry, which incorporates trees into farming systems to reduce erosion; and
3) Conservation tillage, which leaves crop residues on fields before and after planting to decrease erosion, runoff, and pollution.TERRACING.docx



TERRACING.docxFarzanaHaris3
Ėý
Terraces are ancient erosion control practice that facilitates cultivation on steep slopes. A Terrace system consists of multiple continuous lines of embankments constructed across a field slope to check erosion under the most intense cropping system planned for the field. Runoff water intercepted by the embankments is conducted to a stable outlet through non-erosive stable channels or stored and released through soil infiltration. It reduces the length of the hillside slope, thereby reducing sheet and rill erosion and prevents the formation of gullies.Recently uploaded (20)
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatFull-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatAdministrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940



Administrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940P.N.DESHMUKH
Ėý
These presentation include information about administrative bodies such as D.T.A.B
CDL AND DCC, etc.Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena
Ėý
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
â
Soft Tissue Therapy â The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
â
Sports Taping Techniques â Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
â
Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia â A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
Ėý
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spotsâsystemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AIâthat could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?



Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?MIPLM
Ėý
Presentation of the CEIPI DU IPBA oral exam of Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit? Odoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 šÝšÝßĢs



Odoo 18 Accounting Access Rights - Odoo 18 šÝšÝßĢsCeline George
Ėý
In this slide, weâll discuss on accounting access rights in odoo 18. To ensure data security and maintain confidentiality, Odoo provides a robust access rights system that allows administrators to control who can access and modify accounting data. ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat



ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatScholarhat
Ėý
ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatAzure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatIntellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
Ėý
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory App



Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory AppCeline George
Ėý
This slide will helps us to efficiently create detailed reports of different records defined in its modules, both analytical and quantitative, with Odoo 17 ERP.NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
Ėý
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningDr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari
Ėý
Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.Báŧ TEST KIáŧM TRA GIáŧŪA KÃ 2 - TIášūNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUášĻN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Báŧ TEST KIáŧM TRA GIáŧŪA KÃ 2 - TIášūNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUášĻN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Ėý
https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmgHannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...



Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
Ėý
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ėý
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxDot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatEffective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George
Ėý
In this slide weâll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdf



Chapter 2. Strategic Management: Corporate Governance.pdfRommel Regala
Ėý
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Báŧ TEST KIáŧM TRA GIáŧŪA KÃ 2 - TIášūNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUášĻN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Báŧ TEST KIáŧM TRA GIáŧŪA KÃ 2 - TIášūNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUášĻN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Ėý
Bench terracing
- 2. Benching (Bench Terracing) Presented to: Dr. Abdul Rehman Presented by: Ali Adnan BAGF14E260 7th Agronomy College of Agriculture, University of Sargodha
- 3. Definition Bench terraces are a series of level or virtually level strips running across the slope at vertical intervals, supported by steep banks or risers. âĒ It is an engineering soil conservation practice âĒ It is also called bench terracing.
- 5. History âĒ Concept of bench terracing is old as agriculture itself. âĒ Philippines started bench terracing 2500 years ago. US soil conservation services collected evidences: âĒ In Israel, citrus orchard in southern France, ShanSi province(China) and Lebanon hill side.
- 6. Objectives âĒ To reduce run-off or its velocity and to minimize soil erosion. âĒ To conserve soil moisture and fertility and to facilitate cropping operations. âĒ To promote intensive land use and permanent agriculture on slopes and reduce shifting cultivation
- 7. Applicability This practice can: âĒ Be manage on soil having slopes up to 30 %. âĒ Be done where there is deep heavy clay soil rather than in very sandy soil. âĒ Typically not applicable for slopes of decomposed granitic material, or any significantly sandy soil, because of excessive sloughing of material and construction difficulties.
- 8. Locations and conditions for use Bench terraces are particularly suited to countries or communities with the following macro conditions: âĒ Severe erosion hazards âĒ Areas with small holdings and a dense population. âĒ Areas where there are food shortages or high unemployment rates. âĒ Areas where crops require flood irrigation
- 9. Cont.. For micro or site conditions, bench terracing is suitable in the following cases: âĒ Where there are relatively deep soils. âĒ On slopes not exceeding 25 degrees. âĒ On sites which are not dissected by gullies and not too stony.
- 10. Cut and Fill method
- 11. Types of Bench Terracing 1. Level or Table top bench terrace 2. Sloping inwards bench terrace 3. Sloping outwards bench terrace 4. Conservation type bench terrace
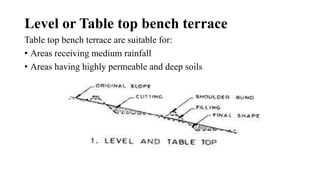
- 12. Level or Table top bench terrace Table top bench terrace are suitable for: âĒ Areas receiving medium rainfall âĒ Areas having highly permeable and deep soils
- 14. Sloping inwards bench terrace Sloping inwards bench terrace are suitable for: âĒ Areas receiving heavy rainfall. Sloping inwards bench terrace Sloping inwards bench terrace are suitable for âĒ It is useful for crops susceptible to water lodging. âĒ Runoff towards hillside.
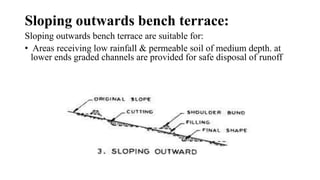
- 16. Sloping outwards bench terrace: Sloping outwards bench terrace are suitable for: âĒ Areas receiving low rainfall & permeable soil of medium depth. at lower ends graded channels are provided for safe disposal of runoff
- 18. Conservation type bench terrace In this type of terrace: âĒ Modified form of level terrace âĒ Use moisture of uncropped area âĒ Barrier is established across the land at suitable interval and the terrace is developed by pushing soil downhill and subsequent natural leveling.
- 20. Advantages âĒ Reduces the soil erosion. âĒ Aesthetical value âĒ Intensive land use. âĒ Economically beneficial. âĒ Availability of food for local area. âĒ Flood chances can be reduce. âĒ Improves the condition of the slope for plant establishment. âĒ Reduces runoff velocities and increases infiltration.
- 21. Disadvantages âĒ Highly labor demand and time consuming. âĒ Increased cost relative to alternative slope stabilization techniques. âĒ Can be complicated to design and install, and may fail if not properly designed and installed
- 22. Some examples over the world
- 23. Terraces in northern Luzon Philippines 2000-B.C
- 24. Citrus Orchard in southern France
- 26. Level bench terracing in Japan
- 27. Tea on bench terraces, Bhutan
- 28. Outward bench terrace in Korea
- 29. Terraces on eroded soils of Israel
- 30. Terraced Fields in Sa Pa, Vietnam
- 31. Rice Terrace Panorama in Bali
- 33. Grassy Terraces in Chitral, Pakistan
- 35. Thank You

