benign and malignant lesions Of-The-Vulva.ppt
- 1. Diseases of the Vulva Diseases of the Vulva Azza Alyamani Azza Alyamani Department Department of of Obstet. & Gynecol. Obstet. & Gynecol.
- 2. Vulvo-vaginal problems are among 10 leading disorders encountered by primary care clinicians. * Benign lesions of the vulva are mentioned in three categories : 1. Epithelial conditions. 2. Benign neoplastic disorders. 3. Dermatologic disorders. * VIN * Cancer vulva
- 3. Benign Conditions of the Vulva
- 4. (1) Epithelial Conditions 1) Lichen simplex . 2) Lichen sclerosis. 3) Lichen planus, erosive lichen planus.
- 5. 1) Lichen Simplex ŌĆ£ squamous cell hyperplasia ŌĆ£ * it is a local thickening of the epithelium resulting from a prolonged itching . * symptoms : pruritus and pain. * signs : white or reddish thickened ,leathery ,raised surface. usually discrete lesion but may be multiple. * treatment : ŌĆó moderate-strength steroid ointment. ŌĆó antipruritic agent.
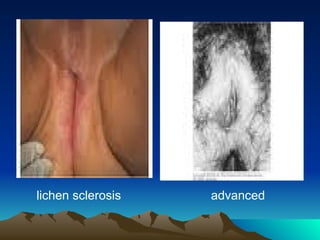
- 7. 2) Lichen Sclerosis * it is a chronic progressive disease which constrict and destroy the normal genital anatomy . In the long term ,labia minora are lost ,labia majora flatten ,clitoris becomes inverted . * frequently found on the vulva of postmenopausal women & can involve all the genital area from mons to the anal area.
- 8. * combinations of lichen sclerosis & epithleal hyperplasia or carcinoma are possible. * symptoms: intense pruritus , dyspareunia and burning pain. * signs: thin inelastic atrophic skin ,white with a crinkled , tissue paper appearance.
- 9. * diagnosis: multiple biopsies is necessary. it reveals a thin atrophic epithelium with inflammatory cells lining the basement membrane. * treatment: ŌŚÅ potent topical steroids. 80% of lesions respond. long term therapy with low potent steroids may be necessary. ŌŚÅ other local treatments are: esrtogen cream and anaesthetics.
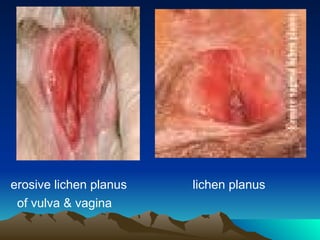
- 11. 3) Lichen planus * it is a purplish ,polygonal papules that may appear in their erosive form. * it involve the vulva ,the vagina and the mouth ( vulval ŌĆō vaginal ŌĆōgingival syndrome ). * symptoms: vulval burning , severe dyspareunia when vaginal stenosis develop in advanced stages. * treatment: topical and systemic steroids .
- 12. erosive lichen planus lichen planus of vulva & vagina
- 13. (2) Benign Neoplastic condions 1) epidermal inclusion and sebaceous cysts. 2) vulvar varicosities. 3) fibromas and lipomas. 4) clitoromegaly.
- 14. 1) epidermal inclusion & sebaceous cysts * they are nontender , mobile , spherical ,slow growing cysts located below the epidermis. * sebaceous cysts are firmer bec. they are filled with dry caseous material. * treatment : most of inclusion cysts require no ttt. if they are asymptomatic, or surgical excision.
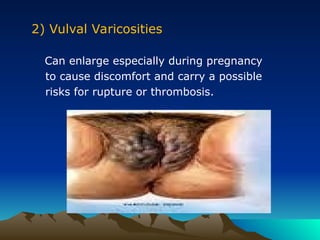
- 15. 2) Vulval Varicosities Can enlarge especially during pregnancy to cause discomfort and carry a possible risks for rupture or thrombosis.
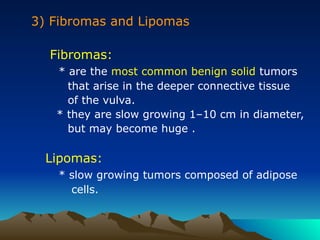
- 16. 3) Fibromas and Lipomas Fibromas: * are the most common benign solid tumors that arise in the deeper connective tissue of the vulva. * they are slow growing 1ŌĆō10 cm in diameter, but may become huge . Lipomas: * slow growing tumors composed of adipose cells.
- 17. Vulval Fibroma
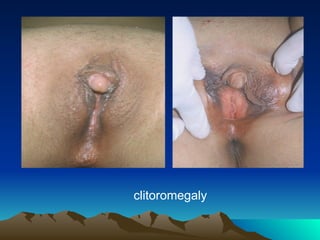
- 18. 4) Clitoromegaly * may develop after birth in response to excessive androgen exposure . It is a sign virillization. * diagnosed when the clitorial length exceeds 30 mm or the width at the base exceeds 10 mm.
- 19. clitoromegaly
- 20. ( 3) Dermatologic Disorders 1) Psoriasis. 2) Behcet ŌĆ▓s syndrome. 3) Crohn ╬äs disease . 4) Acanthosis nigricans .
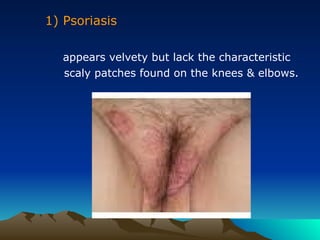
- 21. 1) Psoriasis appears velvety but lack the characteristic scaly patches found on the knees & elbows.
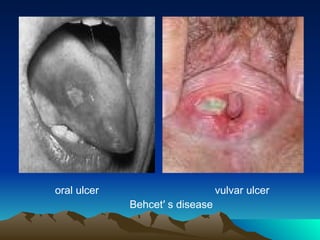
- 22. 2) Behcet ŌĆ▓s syndrome * ulcers in the vulval , oral and ocular areas. * genital lesions can result over time in a scarred vulva. * etiology : is unknown. * diagnosis : based on the concurrence ulcers in vulva ,mouth & ocular involvement ,the recurrent nature of the disease and exclusion of syphilis and CrohnŌĆÖs disease. * treatment : no effective ttt.
- 23. oral ulcer vulvar ulcer BehcetŌĆ▓ s disease
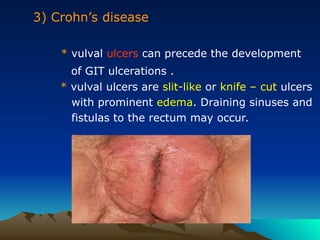
- 24. 3) CrohnŌĆÖs disease * vulval ulcers can precede the development of GIT ulcerations . * vulval ulcers are slit-like or knife ŌĆō cut ulcers with prominent edema. Draining sinuses and fistulas to the rectum may occur.
- 25. 4) Acanthosis nigricans * most commonly found in the axilla or the nape of the neck then vulva. * characterized by its darky pigmented velvety or warty surface . * etiology : related to insulin resistance.
- 26. Vulval Neoplasms Introduction * uncommon 5 % of female genital tract malign. most tumors are squamous cell carcinomas ,may be melanomas , adenocarcinomas and sarcomas. * postmenopausal women ,mean age 65 years. * a history of chronic vulval itching is common.
- 27. Epidemiology Two different etiologic types of vulval cancers : 1. A less common type: * in younger women . * related to HPV infection and smoking. * commonly associated with VIN .
- 28. 2. The more common type: * in old women . * unrelated to HPV infection or smoking. * concurrent VIN is uncommon. * long standing lichen sclerosis is common. 5% of patients have +ve serologic tests for syphilis , lymphogranuloma venereum and granuloma inguinale.
- 29. Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VIN) 2 types of VIN : 1. squamous cell carcinoma in situ VIN III or BowenŌĆÖs disease. 2. Adenocarcinoma in situ VIN III or PagetŌĆÖs disease.
- 30. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ: VIN III ( BowenŌĆ▓s disease ) * mean age 45 years. * symptoms: 50% asymptomatic. itching is the most common symptom. * signs: most lesions are elevated ,white ,red ,pink , brown or grey in color. 20% of lesions are warty in appearance.
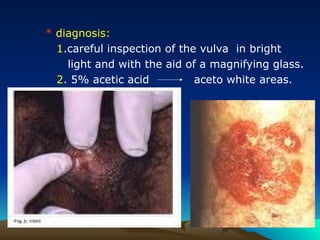
- 31. * diagnosis: 1.careful inspection of the vulva in bright light and with the aid of a magnifying glass. 2. 5% acetic acid aceto white areas.
- 32. * treatment : 1. local superficial excision. with margins of 5 mm are adequate. 2. skinning vulvectomy in extensive lesions. 3. laser therapy if lesions involves the clitoris , labia minora or perineal area.
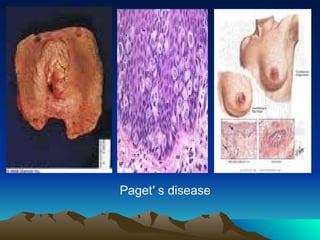
- 33. Adenocarcinoma in situ VIN III ( PagetŌĆ▓ s disease ) * occurs in white postmenopausal elderly women. also occurs in the nipple area of the breast. * 20% is associated with adenocarcinoma. * symptoms: itching and tenderness are common. * signs: well demarcated and eczematus with white plaque like lesions. * growth may progresses beyond the vulva to the mons pubis ,buttocks & thighs.
- 34. * diagnosis histologically: adenocarcinoma in situ characterized by large ,pale , pathognomonic PagetŌĆÖ s cells, typically located both in the epidermic and in the adnexal structures. * treatment: 1. local superficial excision. with margins 5-10 mm. 2. laser therapy in recurrences which are common.
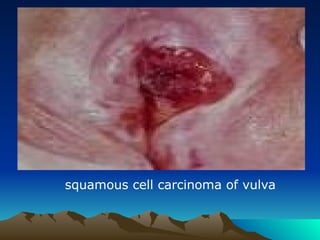
- 36. Invasive Cancer Vulva A. Squamous cell carcinoma * 90% of vulval cancers. * symptoms: ŌĆó vulval lump or ulcer. ŌĆó long standing pruritus. * signs: ŌĆó raised ,ulcerated ,pigmented or warty lesion. however , ulceration is usually an early sign. ŌĆó most lesions occur on labia majora and labia minora. Less common sites , the clitoris or the perineum. ŌĆó 5% of lesions are multifocal.
- 37. squamous cell carcinoma of vulva
- 38. * spread : ŌĆó direct extension to adjacent structures as the vagina , urethra and anus. ŌĆó lymphatic embolisation inguino femoral nodes. = initially to the superficial inguinal LN. = then to deep femoral LN. located medial to the femoral vein, LN of CloquetŌĆ▓s is the most common of this group. =then spread occurs to pelvic nodes especially the external iliac LN.
- 39. = LN metastases occurs 50% in cancer vulva. 5% of patients have metastases to pelvic LN , usually 3 or more +ve unilateral inguino femoral LN. ŌĆó hematogenous occurs late to the lungs , liver and bone rarely in the absence of lymphatic metastases.
- 40. FIGO Staging of Cancer Vulva Stage I Ia Ib Stage II Stage III Tumor limited to the vulva or perineum or both ,and 2 cm or < in diameter ,and no nodal metastases. as above + stromal invasion < 1mm. as above + stromal invasion > 1 mm. Tumor limited to the vulva or perineum or both ,and > 2 cm in diameter ,and no nodal metastases. Tumor of any size with : ŌĆó adjacent spread to the urethra &/or vagina &/or anus ŌĆó unilateral regional LN. metastasis or combination.
- 41. Stage IV IVa IVb Tumor invades any of the following pelvic : upper urethra ,bladder mucosa ,rectal mucosa ,pelvic bone or bilateral regional node metastasis ,or a combination. Any distant metastasis including pelvic lymph nodes.
- 42. Management A) Early vulval cancer * Stage I a ( penetration depth < 1mm below the basement membrane & no nodal metastases ) radical local excision ├® surgical margins 1cm, patient do not need groin dissection. * Stage I b & Stage II ( penetration > 1mm ) radical local excision +ipsilateral inguinal femoral lymphadenectomy if the lesion is unilateral and bilateral groin dissection in the midline lesions .
- 43. B) Advanced vulval cancer * Stage III ( involves the proximal urethra ,anus or rectovaginal septum ) radical vulvectomy which includes a bowel, urinary stroma or rectovaginal septum. + bilateral groin dissection. Preoperative radiation or chemo-radiation should be used to shrink the 1ry tumor ,followed by more conservative surgical excision.
- 44. C) Positive lymph nodes Radiation used with > one nodal mico metastasis (<5mm), or evidence of extra nodal spread . postoperative radiation to both groins and to the pelvis. Prognosis: = it correlate significantly with LN status. with ŌĆōve nodes have a 5-ys survival rate is 90%. with +ve nodes have a 5-ys survival rate is 50%. = patient with no involved node have a good prognosis regardless of stage.
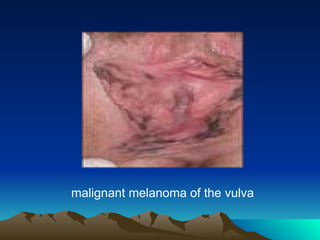
- 45. Malignant Melanoma * the 2nd most common vulvar cancer. * may arise de novo or from a preexisting nevus. commonly involve labia minora or clitoris. * occurs in postmenopausal white women. * diagnosis : any pigmented lesion of the vulva requires excisional biopsy for histopathology. * usually smaller lesions and tend to metastasized early.
- 46. malignant melanoma of the vulva
- 47. * prognosis: correlates to the depth of penetration into the dermis. The 5-ys survival rate is 30%. * superficial lesion radical local excision alone with margins of 1 cm, is adequate. * deeper lesions 1 mm or > radical local excision + ipsilateral inguinal femoral lymphadenectomy. * adjuvant therapy: = nonspecific immuno stimulants. = chemotherapy. = vaccines.