Benign Cervical Lesions
- 1. Benign Cervical Lesions By Dr. Esraa Alnabilsy â Saturday 13 / 1 / 2018
- 2. CONTENTS: 1. Introduction. 2. Cervical Polyps. 3. Cervical Ectropion. 4. Cervical Stenosis. 5. Nabothian Follicles.
- 4. Definition: Benign cervical Lesions: Are non cancerous cervical tumors that donât metastasize or invade the surrounding tissues & not a life threatening Conditions. The following are examples of the BCL: Cervical polyps, Cervical ectropion. Cervical fibroids, Cervical stenosis & Nabothian follicles.
- 6. They are benign tumors arising from the endocervical epithelium & maybe seen as smooth reddish protrusion in the cervix. Cervical Polyps Definition
- 7. like HPV, yeast infection, Herpes
- 8. ï Types: Ectocervical & endocervical. ï Signs & Symptoms: asymptomatic. ï Investigations: Itâs usually diagnosed when performing routine pelvic examination but other investigations can be done to exclude other causes like: Cervical smear, Biopsy, & Colposcopy.
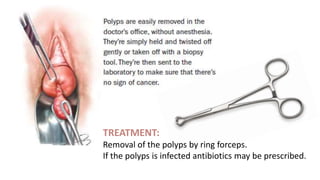
- 9. TREATMENT: Removal of the polyps by ring forceps. If the polyps is infected antibiotics may be prescribed.
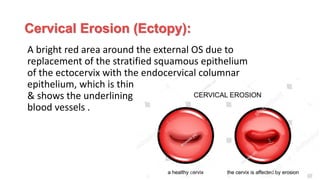
- 12. Cervical Erosion (Ectopy): A bright red area around the external OS due to replacement of the stratified squamous epithelium of the ectocervix with the endocervical columnar epithelium, which is thin & shows the underlining blood vessels .
- 13. ï§Chronic cervicitis: - Infection discharge produces denuded area around external os. - Columnar epithelium grows from the cervical canal to cover the denuded area. ï§Congenital erosion: - Persistence of the intra-uterine condition where the columnar epithelium covers an area on the ectocervix. ï§Hormonal erosion: - Excess estrogen causes the columnar epithelium to grow & replace the stratified squamous epithelium.
- 14. Clinical features: most patients have no complaint ( see during speculum examination ).or it can be associated with: 1- Excessive Mucoid vaginal discharge. 2- Brown intermenstrual discharge. 3- Slight postcoital bleeding ( should investigated ). 4- During pregnancy slight bleeding ( could be a cause of early pregnancy bleeding or APH ). 5- Sometimes cause pain during or after cervical screening.
- 15. Investigations:
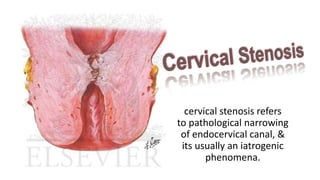
- 17. cervical stenosis refers to pathological narrowing of endocervical canal, & its usually an iatrogenic phenomena.
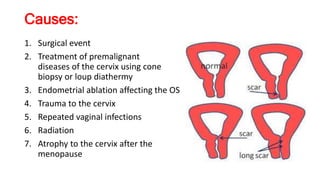
- 18. Causes: 1. Surgical event 2. Treatment of premalignant diseases of the cervix using cone biopsy or loup diathermy 3. Endometrial ablation affecting the OS 4. Trauma to the cervix 5. Repeated vaginal infections 6. Radiation 7. Atrophy to the cervix after the menopause
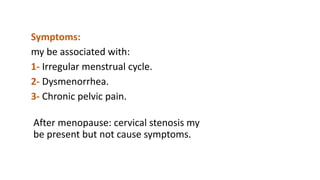
- 19. Symptoms: my be associated with: 1- Irregular menstrual cycle. 2- Dysmenorrhea. 3- Chronic pelvic pain. After menopause: cervical stenosis my be present but not cause symptoms.
- 20. Complications due to cervical stenosis include: 1- Hematometra ( collection or retention of blood in the uterus ). 2- Pyometra ( defined as an infection in the uterus ). 3- Infertility ( because sperm canât pass through the cervix to fertilize the egg ).
- 21. Diagnosis: Clinical Evaluation: 1- May be suspect based on symptoms & signs. 2- Inability to obtain sample of tissue from the cervix for diagnostic test ( pap or HPV test ). 3- Confirm the diagnosis by trying to pass a probe through the cervix into the uterus. If cervical stenosis cause symptoms or uterine abnormality ( Hematometra ) cervical cytology & endometrial biopsy should be done to exclude cancer.
- 22. Treatment: 1- physically widening the cervix with instruments called dilators ( inserted one by one until the appropriate dilation has been reached). Under ultrasound or hystroscopic guidance. 2- In some cases, the doctor will then insert a cervical stent, which is a tube that can keep the cervix from re-closing. The stent may remain in the cervix for 4-6 weeks.
- 25. What is the Nabothian cyst? ï§ Nabothian cysts are tiny cysts filled with mucus (that is secreted by the cervical glands), form on the surface of cervix. ï§ Sometimes these tiny bumps (âŦاŲŲØŠŲØĄØ§ØŠâŽ) are called cervical cysts, mucinous retention cysts, or epithelial cysts. ï§ Nabothian cysts are common. But they arenât a threat to health, & they arenât a sign of cervical cancer.
- 27. âĒ SO Nabothian cysts are mucus filled cysts in the surface of the uterus. âĒ Most often caused when Stratified Squamous Epithelium of the Ectocervix ( towards the vagina ) grows over the Simple Columnar Epithelium of the Endocervx ( towards the uterus ).
- 28. Symptoms of Nabothian cysts: ï§ Nabothian cysts range in size from a few millimeters to 4 centimeters in diameter. ï§ Theyâre smooth & appear white or yellow in color. ï§ These cysts donât cause pain, discomfort, or other symptoms. But they maybe a cause for bleeding between periods, unusual discharge, or pelvic pain.
- 29. Diagnosing of Nabothian cysts: o Nabothian cysts can be screened & diagnosed during a pelvic examination. They can sometimes be seen on a pelvic ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan. o After discovering these small white bumps on cervix, the doctor may break a cyst to confirm the diagnosis or may use a colposcopy ( âŦاŲŲ ŲØĻŲ⎠âŦØŠŲØļŲØąâŽ ) to make an accurate diagnosis.
- 30. Colposcopy
- 31. doctor may take a biopsy of a cyst if they suspect that the patient might have a type of neoplasia affecting mucus production. This condition, called adenoma malignum, is very rare and is not a cause for concern. This involves magnifying the area to distinguish Nabothian cysts from other types of bumps
- 32. Management & Treatment Of Nabothian Cysts: Nabothian cysts are benign & usually donât require treatment, In rare cases the cysts may become large & distort in the shape & size of the cervix. If itâs severe, it can make a routine cervical examination difficult or impossible!
- 33. ïķ In this case doctor may recommend removal of the cyst in order to examine the cervix, These examinations can ensure reproductive health & help the doctor identify problems with cervix early. ïķ Surgeries & procedures for Nabothian cysts: Nabothian cysts that need treatment can be removed through: 1-Excision. 2-Electrocautery ablation. 3-cryotherapy.
- 34. 1- Excision: In excision method uses scalpel or blade to remove the excessive growth. 2- Electrocautery ablation: In electrocautery ablation uses electric current to remove the cyst, The heat generated by the electric current is flowing over the cyst for removing purpose of the cyst. 3- Cryotherapy: To remove the cyst also In cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen for freezes & shrinkage the cyst. This procedure is less invasive than excision or ablation.
- 35. THE END .. THANK YOU Designed By Esraa Alnabilsy