Acid base balance and Buffers
- 1. ACIDâBASE BALANCE/ BLOOD BUFFERS: Aaser Abdelazim, PhD Lecturer of medical biochemistry and molecular biology 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 74 Lecturer of medical biochemistry and molecular biology Zagazig university asr@zu.edu.eg
- 2. ACIDâBASE BALANCE/ BLOOD BUFFERS: 75 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011
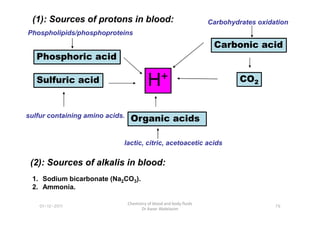
- 3. H+ Carbonic acid CO2 Phosphoric acid Sulfuric acid Organic acids (1): Sources of protons in blood: Carbohydrates oxidation Phospholipids/phosphoproteins sulfur containing amino acids. 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 76 Organic acids sulfur containing amino acids. lactic, citric, acetoacetic acids (2): Sources of alkalis in blood: 1. Sodium bicarbonate (Na2CO3). 2. Ammonia.
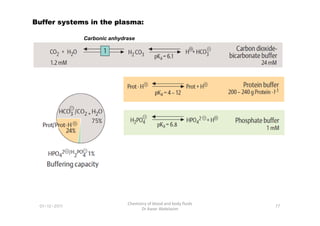
- 4. Buffer systems in the plasma: Carbonic anhydrase 77 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011
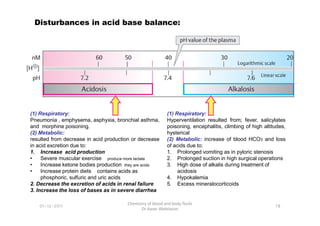
- 5. (1) Respiratory: Disturbances in acid base balance: (1) Respiratory: 78 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 (1) Respiratory: Pneumonia , emphysema, asphyxia, bronchial asthma, and morphine poisoning. (2) Metabolic: resulted from decrease in acid production or decrease in acid excretion due to: 1. Increase acid production âĒ Severe muscular exercise produce more lactate âĒ Increase ketone bodies production they are acids âĒ Increase protein diets contains acids as phosphoric, sulfuric and uric acids 2. Decrease the excretion of acids in renal failure 3. Increase the loss of bases as in severe diarrhea (1) Respiratory: Hyperventilation resulted from; fever, salicylates poisoning, encephalitis, climbing of high altitudes, hysterical (2) Metabolic: increase of blood HCO3 and loss of acids due to: 1. Prolonged vomiting as in pyloric stenosis 2. Prolonged suction in high surgical operations 3. High dose of alkalis during treatment of acidosis 4. Hypokalemia 5. Excess mineralocorticoids
- 6. Hemoglobin Aaser Abdelazim, PhD Lecturer of medical biochemistry and molecular biology 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 79 Lecturer of medical biochemistry and molecular biology Zagazig university asr@zu.edu.eg
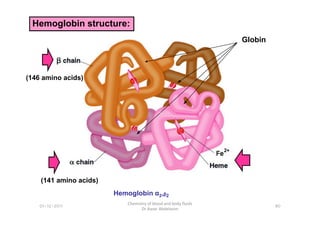
- 7. Hemoglobin structure: Globin (146 amino acids) 80 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 (141 amino acids) Hemoglobin Îą2,áĩĶ2
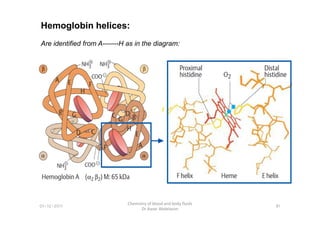
- 8. Hemoglobin helices: Are identified from A-------H as in the diagram: 81 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011
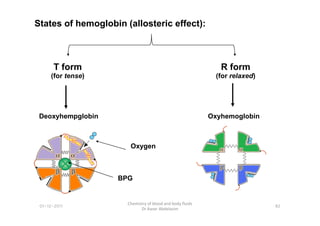
- 9. States of hemoglobin (allosteric effect): T form (for tense) R form (for relaxed) Deoxyhempglobin Oxyhemoglobin 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 82 Deoxyhempglobin Oxyhemoglobin BPG Oxygen
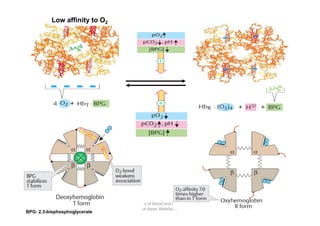
- 10. Low affinity to O2 83 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 BPG: 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
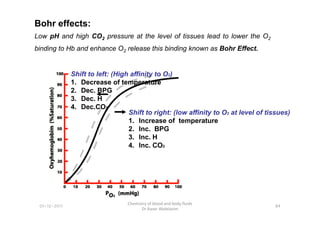
- 11. Shift to left: (High affinity to O2) 1. Decrease of temperature 2. Dec. BPG 3. Dec. H 4. Dec.CO2 Shift to right: (low affinity to O2 at level of tissues) Low pH and high CO2 pressure at the level of tissues lead to lower the O2 binding to Hb and enhance O2 release this binding known as Bohr Effect. Bohr effects: 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 84 Shift to right: (low affinity to O2 at level of tissues) 1. Increase of temperature 2. Inc. BPG 3. Inc. H 4. Inc. CO2
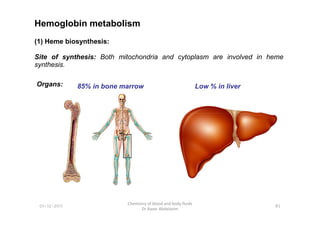
- 12. Hemoglobin metabolism (1) Heme biosynthesis: Site of synthesis: Both mitochondria and cytoplasm are involved in heme synthesis. Organs: 85% in bone marrow Low % in liver 85 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011
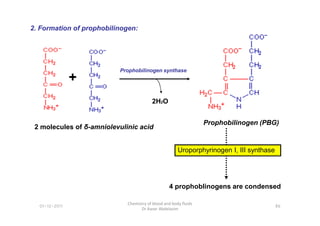
- 13. 2. Formation of prophobilinogen: + 2H2O Prophobilinogen synthase Uroporphyrinogen I, III synthase 4 prophoblinogens are condensed 86 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 2 molecules of Îī-amniolevulinic acid Prophobilinogen (PBG)
- 14. Steps of heme synthesis: 1. Synthesis of ALA (5-aminolevulinic acid/Îī-amniolevulinic acid): Occurs in mitochondria Succinyl-CoA + Glycine H 87 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 ALA synthase CoASH Îī-amniolevulinic acid PLP CO2
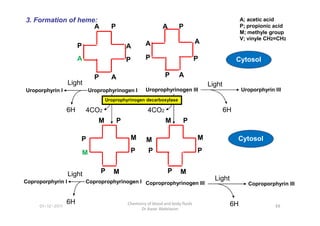
- 15. A P A A A P P P Uroprophyrinogen III A P A A A P P P Uroprophyrinogen I Uroporphyrin III 6H Light Uroporphyrin I 6H Light 4CO2 4CO2 A; acetic acid P; propionic acid M; methyle group V; vinyle CH2=CH2 Cytosol Uroprophyrinogen decarboxylase 3. Formation of heme: 6H 6H 4CO2 M P M M M P P P Coproprophyrinogen III Coproporphyrin III 6H Light M P M M M P P P 4CO2 Coproprophyrinogen I Coproporphyrin I 6H Light Cytosol 88 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011
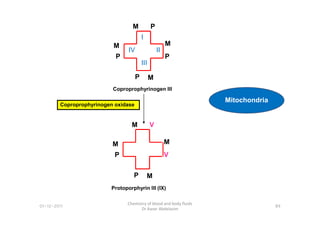
- 16. Coproprophyrinogen III M P M M M P P P I III II IV Mitochondria Coproprophyrinogen oxidase M V M M M P P V Protoporphyrin III (IX) 89 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011
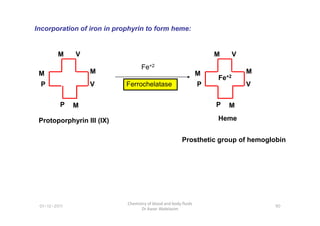
- 17. M V M M M P P V Fe+2 Ferrochelatase M V M M M P P V Fe+2 Incorporation of iron in prophyrin to form heme: Prosthetic group of hemoglobin 90 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 Heme Protoporphyrin III (IX)
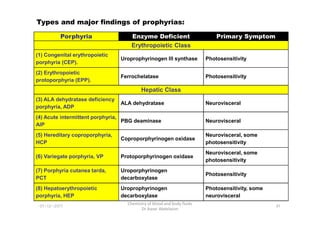
- 18. Porphyria Enzyme Deficient Primary Symptom Erythropoietic Class (1) Congenital erythropoietic porphyria (CEP). Uroprophyrinogen III synthase Photosensitivity (2) Erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP). Ferrochelatase Photosensitivity Hepatic Class (3) ALA dehydratase deficiency porphyria, ADP ALA dehydratase Neurovisceral Types and major findings of prophyrias: 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 91 (4) Acute intermittent porphyria, AIP PBG deaminase Neurovisceral (5) Hereditary coproporphyria, HCP Coproporphyrinogen oxidase Neurovisceral, some photosensitivity (6) Variegate porphyria, VP Protoporphyrinogen oxidase Neurovisceral, some photosensitivity (7) Porphyria cutanea tarda, PCT Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase Photosensitivity (8) Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria, HEP Uroprophyrinogen decarboxylase Photosensitivity, some neurovisceral
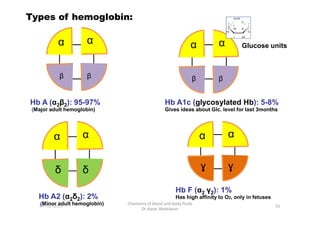
- 19. Types of hemoglobin: Îą Îą áĩĶ áĩĶ Hb A (Îą2Îē2): 95-97% (Major adult hemoglobin) Îą Îą áĩĶ áĩĶ Hb A1c (glycosylated Hb): 5-8% Gives ideas about Glc. level for last 3months Glucose units 92 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 Îą Îą ÉĢ ÉĢ Hb F (Îą2 Îģ2): 1% Has high affinity to O2, only in fetuses Îą Îą Îī Îī Hb A2 (Îą2Îī2): 2% (Minor adult hemoglobin)
- 20. Îą Îą áĩĶ- thalassemia Îą- thalassemia áĩĶ áĩĶ Hemoglobinopathies: Sickle cell anemia Thalassemia HbS (2 normal Îą chains and 2 mutant Îē-chains) 93 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 Îą Îą áĩĶ áĩĶ Normal cells Sickle cells Deleted áĩĶ-chains gene Deleted Îą-chains gene
- 21. Abnormal derivatives of hemoglobin: (1) Met-hemoglobin (Met-Hb): 1. Free radicals as H2O2 2. Drugs 3. Endogenous oxidants 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 94 Ferrous heme Ferric heme Met-Hb (Induce hypoxia and cyanosis. ) NADH+H+ cytochrome B5 reductase.
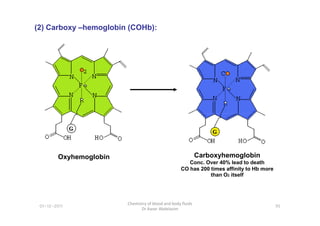
- 22. (2) Carboxy âhemoglobin (COHb): 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 95 Oxyhemoglobin Carboxyhemoglobin Conc. Over 40% lead to death CO has 200 times affinity to Hb more than O2 itself
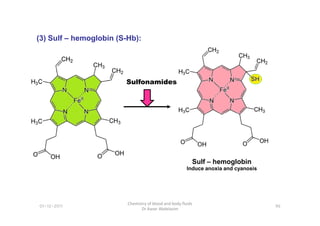
- 23. (3) Sulf â hemoglobin (S-Hb): Sulfonamides 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 96 Sulf â hemoglobin Induce anoxia and cyanosis
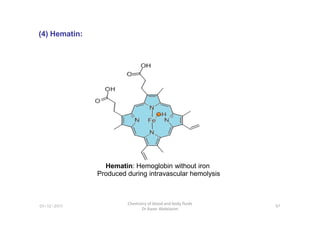
- 24. (4) Hematin: 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 97 Hematin: Hemoglobin without iron Produced during intravascular hemolysis
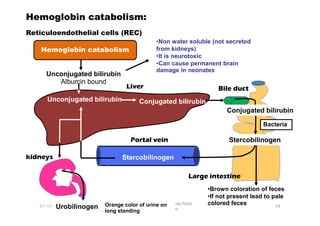
- 25. Hemoglobin catabolism Reticuloendothelial cells (REC) Unconjugated bilirubin Albumin bound âĒNon water soluble (not secreted from kidneys) âĒIt is neurotoxic âĒCan cause permanent brain damage in neonates Liver Bile duct Hemoglobin catabolism: Unconjugated bilirubin Conjugated bilirubin Conjugated bilirubin 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 98 Stercobilinogen Urobilinogen Orange color of urine on long standing âĒBrown coloration of feces âĒIf not present lead to pale colored feces Portal vein kidneys Large intestine Bacteria Conjugated bilirubin Stercobilinogen Stercobilinogen
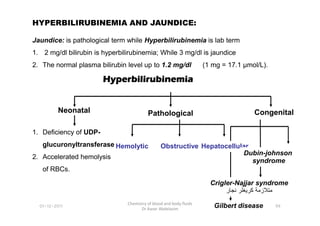
- 26. HYPERBILIRUBINEMIA AND JAUNDICE: Jaundice: is pathological term while Hyperbilirubinemia is lab term 1. 2 mg/dl bilirubin is hyperbilirubinemia; While 3 mg/dl is jaundice 2. The normal plasma bilirubin level up to 1.2 mg/dl (1 mg = 17.1 Âĩmol/L). Hyperbilirubinemia Hyperbilirubinemia Hyperbilirubinemia Hyperbilirubinemia Neonatal Pathological Congenital 99 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 Neonatal Pathological Congenital 1. Deficiency of UDP- glucuronyltransferase 2. Accelerated hemolysis of RBCs. Hemolytic Obstructive Gilbert disease Crigler-Najjar syndrome âŦŲØŽØ§ØąâŽ âŦŲØąŲØšŲØąâŽ âŦŲ ؊اŲØēŲ ØĐ⎠Hepatocellular Dubin-johnson syndrome
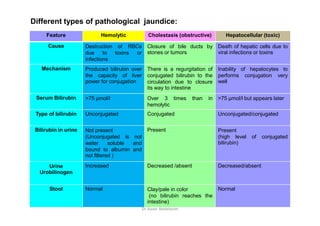
- 27. Different types of pathological jaundice: Feature Hemolytic Cholestasis (obstructive) Hepatocellular (toxic) Cause Destruction of RBCs due to toxins or infections Closure of bile ducts by stones or tumors Death of hepatic cells due to viral infections or toxins Mechanism Produced bilirubin over the capacity of liver power for conjugation There is a regurgitation of conjugated bilirubin to the circulation due to closure its way to intestine Inability of hepatocytes to performs conjugation very well Serum Bilirubin >75 Âĩmol/l Over 3 times than in hemolytic >75 Âĩmol/l but appears later Type of bilirubin Unconjugated Conjugated Unconjugated/conjugated 100 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 Type of bilirubin Unconjugated Conjugated Unconjugated/conjugated Bilirubin in urine Not present (Unconjugated is not water soluble and bound to albumin and not filtered ) Present Present (high level of conjugated bilirubin) Urine Urobilinogen Increased Decreased /absent Decreased/absent Stool Normal Clay/pale in color (no bilirubin reaches the intestine) Normal
- 28. HEMOSTASIS AND BLOOD COAGULATION Aaser Abdelazim, PhD Lecturer of medical biochemistry and molecular biology 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 101 Lecturer of medical biochemistry and molecular biology Zagazig university asr@zu.edu.eg
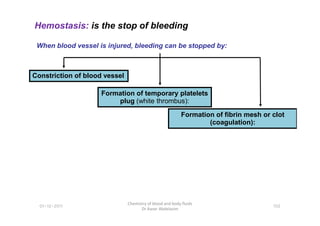
- 29. Hemostasis: is the stop of bleeding When blood vessel is injured, bleeding can be stopped by: Constriction of blood vessel Formation of temporary platelets plug (white thrombus): Formation of fibrin mesh or clot 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 102 Formation of fibrin mesh or clot (coagulation):
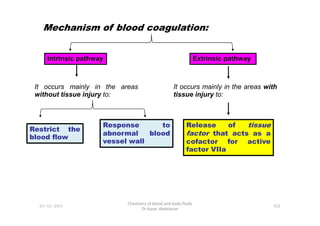
- 30. Mechanism of blood coagulation: Intrinsic pathway Extrinsic pathway It occurs mainly in the areas without tissue injury to: It occurs mainly in the areas with tissue injury to: 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 103 Restrict the blood flow Response to abnormal blood vessel wall Release of tissue factor that acts as a cofactor for active factor VIIa
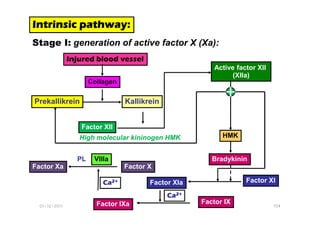
- 31. Intrinsic pathway: Intrinsic pathway: Intrinsic pathway: Intrinsic pathway: Stage I: generation of active factor X (Xa): Prekallikrein Kallikrein Collagen Active factor XII (XIIa) Injured blood vessel + 01-12-2011 104 Factor XII High molecular kininogen HMK HMK Bradykinin Factor XI Factor XIa Factor IX Factor IXa Ca Ca Ca Ca2+ 2+ 2+ 2+ Factor X Factor Xa PL Ca Ca Ca Ca2+ 2+ 2+ 2+ VIIIa
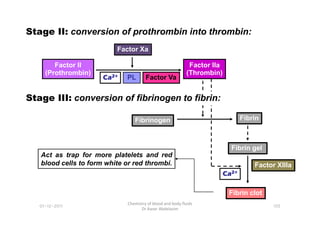
- 32. Stage II: conversion of prothrombin into thrombin: Factor Xa Factor II (Prothrombin) Factor IIa (Thrombin) Ca Ca Ca Ca2+ 2+ 2+ 2+ PL Factor Va Stage III: conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin: 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 105 Fibrinogen Fibrin Fibrin gel Factor XIIIa Ca Ca Ca Ca2+ 2+ 2+ 2+ Fibrin clot Act as trap for more platelets and red blood cells to form white or red thrombi.
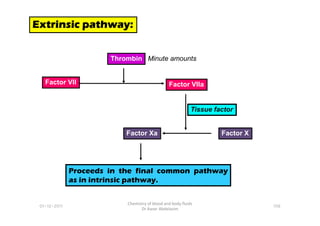
- 33. Extrinsic pathway: Extrinsic pathway: Extrinsic pathway: Extrinsic pathway: Factor VII Factor VIIa Thrombin Minute amounts Tissue factor 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 106 Factor X Factor Xa Tissue factor Proceeds in the final common pathway as in intrinsic pathway.
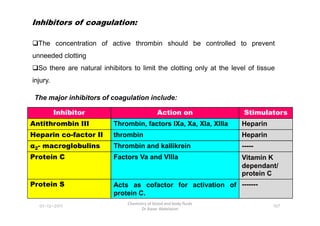
- 34. Inhibitors of coagulation: The concentration of active thrombin should be controlled to prevent unneeded clotting So there are natural inhibitors to limit the clotting only at the level of tissue injury. Inhibitor Action on Stimulators The major inhibitors of coagulation include: 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 107 Inhibitor Action on Stimulators Antithrombin III Thrombin, factors IXa, Xa, XIa, XIIIa Heparin Heparin co-factor II thrombin Heparin Îą2- macroglobulins Thrombin and kallikrein ----- Protein C Factors Va and VIIIa Vitamin K dependant/ protein C Protein S Acts as cofactor for activation of protein C. -------
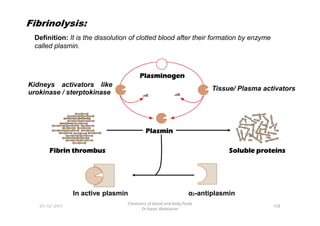
- 35. Fibrinolysis: Definition: It is the dissolution of clotted blood after their formation by enzyme called plasmin. Tissue/ Plasma activators Kidneys activators like urokinase / sterptokinase Plasminogen Plasminogen Plasminogen Plasminogen 108 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 Fibrin thrombus Fibrin thrombus Fibrin thrombus Fibrin thrombus Soluble proteins Soluble proteins Soluble proteins Soluble proteins Plasmin Plasmin Plasmin Plasmin Îą2-antiplasmin In active plasmin
- 36. Hemophilia: Hemophilia: Hemophilia: Hemophilia: Definition: These are a group of inherited diseases at which clotting factors are deficient Hemophilia: Hemophilia: Hemophilia: Hemophilia: Hemophilia A Hemophilia C Hemophilia B 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 109 Deficiency of factor VIII. Von Willbrand disease Deficiency of factor IX.
- 37. BLOOD GROUPS: Donor Recipient Antigens Antibodies 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 110 Proteins with oligosaccharides
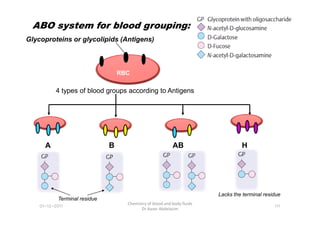
- 38. ABO system for blood grouping: Glycoproteins or glycolipids (Antigens) RBC 4 types of blood groups according to Antigens 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 111 A B AB H Terminal residue Lacks the terminal residue
- 39. ABO system: Blood group A B AB O Genotypes AA and AO BB and BO AB OO Antigens A B A and B H Antibodies Anti-A Anti-B ------ Anti-A and Anti-B Frequency in central Europe 40% 16% 4% 40% 112 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011 Compatibility : Blood group Compatible Take Give A From A A B From B B AB From A or B or AB (all) Only AB O Only from O All
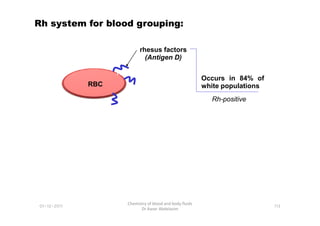
- 40. Rh system for blood grouping: RBC rhesus factors (Antigen D) Occurs in 84% of white populations RBC Rh-positive 113 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 01-12-2011
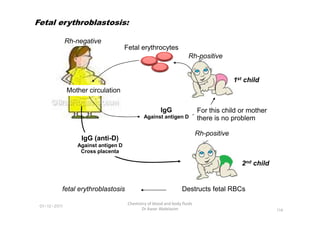
- 41. Rh-positive Rh-negative Fetal erythrocytes Mother circulation IgG For this child or mother 1st child Fetal erythroblastosis: 01-12-2011 Chemistry of blood and body fluids Dr Aaser Abdelazim 114 IgG Against antigen D For this child or mother there is no problem Rh-positive 2nd child IgG (anti-D) Against antigen D Cross placenta Destructs fetal RBCs fetal erythroblastosis