Bfs bio Evolution intro
- 1. 2006-2007 by Natural Selection EvolutionĄ
- 2. What is Evolution? Evolution changes in living organisms over time explains how modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms Evolution! Evolution! Evolution! Why do we accept this as a Scientific Principle?
- 3. What do we know? There are many different creatures on Earth How do we know this? Diversity of Life on Earth OBSERVATION How did all these creatures come about? What accounts for all this biological diversity? Biodiversity of Life on Earth
- 4. What do we know? All creatures have common characteristics How do we know this? Unity of Life on Earth How could all of life have the same basic features? OBSERVATION DNA cells
- 5. What do we know? The Earth is very old How do we know this? Radioactive Dating of the Rocks TESTING & OBSERVATION Life is very old! WhatĄŊs happened to life during those billions of years?
- 6. What do we know? Creatures have changed over time How do we know this? Fossil Record OBSERVATION
- 7. What has the fossil record shown us? Many creatures that lived in the past donĄŊt exist today Origin of new species OBSERVATION
- 8. What has the fossil record shown us? The creatures alive today havenĄŊt always been around Different species lived in the past OBSERVATION
- 9. What has the fossil record shown us? Many creatures in the past looked like living ones we see today Ą° Family TreeĄą Relatives with similar, but not the same traits OBSERVATION
- 10. Homolog structure: Similar structure and position, but different function Courtesy of Prof. Ken Sytsma http://evolution.berkeley.edu Analog structure: Similar function, but different origin
- 11. ItĄŊs Critical (and often difficult) to distinguish Homology from Analogy Homology is the key to establishing phylogenies.
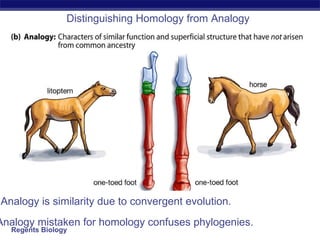
- 12. Distinguishing Homology from Analogy Analogy is similarity due to convergent evolution. Analogy mistaken for homology confuses phylogenies.
- 13. Another Set of Analogies Created by Convergent Evolution Ocotillo of the US southwest Allauidia of Madagascar
- 14. Quick review, so farĄ. Many different species alive today All life shares common characteristics The Earth is very old Life is very old Life has changed over time The changes have been little changes over long periods of time Evolution But how does this work?
- 15. What do we know? Populations are a mix of different individuals How do we know this? OBSERVATION Variation
- 16. What do we know? Organisms have more offspring than the environment can support Not everybody survives How do we know this? OBSERVATION Over-production Competition
- 17. How does that work? Variation Over-Production & Competition Natural Selection Nature selects the ones that Ą°fitĄą the environment better Ą survive & reproduce Adaptation
- 18. What determines survival? Natural Selection traits that help individuals survive survive predators survive disease compete for food compete for territory traits that help individuals reproduce attracting a mate compete for nesting sites successfully raise young Survival & Reproduction of the Fittest Adaptations
- 19. Survival & Reproduction of the fittest not the strongestĄ not the bravestĄ not the fastestĄ not the biggestĄ Ą the fittest! the traits that help an organism fit the environment better to survive & reproduce Adaptations
- 20. Evolution explains Unity & Diversity Only evolution explains both unity of life similarities between all living things diversity of life wide variety of different creatures on Earth DNA
- 21. Survival & reproduction of the fittest bugĄ
- 22. 2006-2007 DonĄŊt be a DodoĄ Ask Questions !!
Editor's Notes
- #11: How to explain similarities bt organisms? how are related these organisms according to their similitude ? How did they acquire these characteristics? Some terminology was applied in an attempt to define these observed patterns
- #12: Macroevolution 10/07/11 G. Podgorski, Biol. 1010
- #13: Macroevolution 10/07/11 G. Podgorski, Biol. 1010
- #14: Macroevolution 10/07/11 G. Podgorski, Biol. 1010
- #18: `