BGP hijacks and leaks
- 1. BGP hijacks and leaks malicious or consensual Net::IP Meetup #12 Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 Pawe? Ma?achowski @pawmal80
- 2. whoami ? Currently: redGuardian DDoS mitigation tech lead (Atende Software sp. z o.o.) ? Previously: system engineer, IT operations lead, analyst, architect, project manager etc. (ATM SA, Netia SA) Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 2
- 4. Problem ? 2004.12: TT Net full table leak, massive outages ? 2008.02: Youtube rerouted to Pakistan Telecom via PCCW Global ? 2014: INEA SA + LG case (PL) ? 2017.04: financial institutions/credit card processors partially rerouted to PJSC Rostelekom ? 2017.12: high profile companies (FAG, Riot Games and others) announced by DV-LINK via Megafon via HE ? 2018.04: Amazon Route53 routed to malicious DNS server in eNET ? 2018.06: Telegram messenger partially routed to Iran Telecomunication Company ? 2018.07: Bitcanal ?hijack factoryĄą case ? 2018.11: Google traffic routed to MainOne via China Telecom via Trans Telecom ? Ą many more Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 4
- 5. Real life BGP routing decision factors 1. more specific preferred (originator decides) 2. higher local preference (layer 8 decides) 3. shorter AS_PATH (prepending) Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 5
- 6. BGP user types (simplified) ? multihomed network ? CDN (anycasting etc.) ? Eyeballs ? IP Transit: Tier 1, Tier n (paid vs. free peerings) ? IXP Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 6
- 7. BGP threats ? Prefix hijacking ? Route leaks (unintentional transit) ? AS path manipulation (e.g. shortening) Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 7
- 8. Reasons ? fat fingers, BGP optimizers and bad defaults ? prefix-lists and as-path filters not widely used ? blind chain of trust ? Internet barely works? Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 8
- 9. Howto ? Add victim AS to your official AS-SET in IRR ? Wait for upstream nightly filter updates ? Announce victimĄŊs IP address space ? Profit! Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 9
- 10. Howto, cont. ExaBGP route victim/24 next-hop self as-path [ foo ] community [ a:b ]; BIRD bgp_path.empty; bgp_path.prepend(foo); Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 10
- 11. Howto, cont. ?LINX has this peer configured as announcing the AS-SET AS-TTK. This set contains 984 entries of which 470+ are themselves AS-SETs. Many of these AS-SETs will themselves contain AS-SETs, and this patern repeats as you continue the AS-SET expansion. Ultimately, this large AS-SET expands to allow 886,051 prefixes from 16,608 origin ASNs.Ąą (2018.11) Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 11
- 12. Malicious, mistake or consensual? ? origin AS ? AS_PATH ? IRR validity (route object, ROA, etc.) ? mask length (more specific) ? end hosts reachability Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 12
- 13. BGP-based DDoS scrubbing center ? Hijacks customer IP address space ĻC global annoucement (BGP withdrawal issues) ĻC local/selective announcements ? Legal agreement, IRR and ROA valid ? Looks like on-demand optional IP transit Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 13
- 15. Detection ? Looking glasses/route views ? BGPmon (OpenDNS), BGPstream ? Radar (Qrator Labs) ? Resource Certification alerts (RIPE) ? Routing Information Service Live stream (RIPE) ? Routing History + BGP Play (RIPE) Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 15
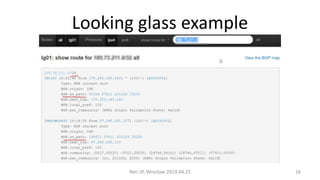
- 16. Looking glass example Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 16
- 17. BGPmon example Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 17
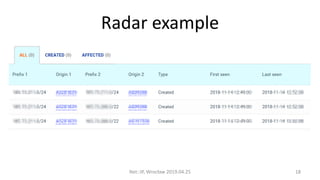
- 18. Radar example Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 18
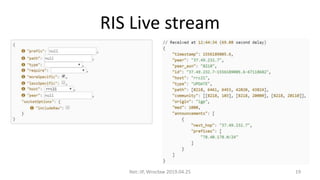
- 19. RIS Live stream Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 19
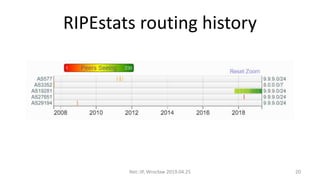
- 20. RIPEstats routing history Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 20
- 22. Prevention ? prefix deaggregation ? RPKI Route Announcement Validation ? BGPsec ? ASPA ? legal? Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 22
- 23. Prefix deaggregation ? split large subnet into multiple /24 prefixes ? limits hijacking ability (/25 are widely not accepted) ? not a final solution (RIB pollution) Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 23
- 24. RPKI ROA ? declare (origin AS, subnet, prefix range) tuples example: (AS x, 10.0.0.0/8, /8../16) ? operators validate before accepting ? lacks AS-PATH validation, origin AS easy to forge Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 24
- 25. RPKI (slow) adoption But: ?The AT&T/as7018 network is now dropping all RPKI- invalid route announcements that we receive from our peers.Ąą source: https://mailman.nanog.org/pipermail/nanog/2019-February/099501.html Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 25
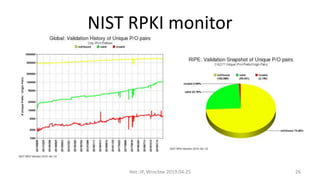
- 26. NIST RPKI monitor Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 26
- 27. IRR online tools Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 27 BGP he.net IRR Explorer
- 28. BGPsec ? BGP routers ĻC sign BGP updates: previous AS, next AS ĻC verify updates received ? IXP hack (no AS in AS-PATH) ? dead end (computation cost) Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 28
- 29. ASPA ? Autonomous System Provider Authorization ĻC declare your official peers ĻC operators validate AS_PATHs received ? currently RFC draft Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 29
- 31. Looking glasses (some of) ? CenturyLink: https://lookingglass.centurylink.com/ ? Cogent: http://www.cogentco.com/en/network/looking-glass ? GTT: http://www.as3257.net/lg/ (mtr only) ? HE: https://lg.he.net/ ? Liberty Global (UPC): sorry! ? KPN: https://lg2.eurorings.net/ ? NTT: https://www.us.ntt.net/support/looking-glass/ ? Open Transit (Orange): https://looking-glass.opentransit.net/ ? RETN: http://lg.retn.net/ ? TATA: http://lg.beta.as6453.net/ ? Telia: https://lg.telia.net/ Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 31
- 32. Looking glasses (some of), cont. ? NLNOG (aggregator): http://lg.ring.nlnog.net/ ? AMS-IX: sorry! (password) ? DE-CIX: https://lg.de-cix.net/ ? LINX: https://lg.linx.net/ ? GEANT: https://tools.geant.net/portal/links/lg/ Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 32
- 33. Important looking glasses (Poland) ? ATMAN + THINX: http://lg.atman.pl/ ? Exatel: http://lg.exatel.pl/ ? NASK (KOM+EDU): http://lg.nask.pl/ ? Netia: http://lg.netia.pl/ ? PLIX: http://lg.plix.pl/ ? Orange + TPIX: http://lg.tpnet.pl/, http://lg.tpix.pl/ ? Pionier (EDU), Vectra, etc.: sorry! Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 33
- 34. Other tools ? https://bgpmon.net/, https://bgpstream.com/, https://twitter.com/bgpmon, https://twitter.com/bgpstream ? https://radar.qrator.net/ ? https://bgp.he.net/ ? http://www.routeviews.org/ ? http://irrexplorer.nlnog.net/ ? https://ris-live.ripe.net/ ? https://stat.ripe.net/widget/routing-history ? https://rpki-monitor.antd.nist.gov/ Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 34
- 36. Sources ? https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BGP_hijacking ? https://blog.donatas.net/blog/2019/02/19/ebgp-requires-policy/ ? http://www.securerouting.net/ ? https://www.ripe.net/participate/policies/proposals/2019-03 ? https://www.arin.net/participate/policy/proposals/2019/ARIN_prop_266_v2/ ? ?PLNOG22 - Zmierzch tranzytu, sieci tier-1, czyli jak dzia?a internetĄą: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yfmEODv3m4k Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 36
- 37. Sources, cont. ? https://dyn.com/blog/internetwide-nearcatastrophela/ ? https://zaufanatrzeciastrona.pl/post/polski-operator-inea-wykorzystany-w-zaawansowanym-ataku- na-obce-sieci/ ? https://krebsonsecurity.com/2016/09/ddos-mitigation-firm-has-history-of-hijacks/ ? https://bgpmon.net/popular-destinations-rerouted-to-russia/ ? https://bgpmon.net/bgpstream-and-the-curious-case-of-as12389/ ? https://radar.qrator.net/blog/born-to-hijack (DV-LINK case) ? https://www.theregister.co.uk/2018/04/24/myetherwallet_dns_hijack/ ? https://dyn.com/blog/shutting-down-the-bgp-hijack-factory/ ? https://www.theregister.co.uk/2018/11/13/google_russia_routing/ ? https://medium.com/@qratorlabs/bad-news-everyone-new-hijack-attack-in-the-wild- 428ea761da89 ? https://blog.thousandeyes.com/amazon-route-53-dns-and-bgp-hijack/ Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 37
- 38. Sources, cont. ? https://rpki.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html ? https://bgpmon.net/securing-bgp-routing-with-rpki-and-roas/ ? https://blog.cloudflare.com/rpki-details/ ? https://www.ripe.net/manage-ips-and-asns/resource-management/certification/resource- certification-roa-management ? https://medium.com/@qratorlabs/eliminating-opportunities-for-traffic-hijacking- 153a39395778, https://ripe77.ripe.net/presentations/118-ripe77.azimov_v2.pdf ? https://www.de-cix.net/Files/11a60fcb156e443c98010211f498f5ae4439dab0/Matthias- Waehlisch---BGPSec---AS-path-validation.pdf ? https://rule11.tech/bgpsec-and-reality/ Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 38
- 39. LIVE DEMO Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 39
- 40. Live demo LetĄŊs hijack 3rd party prefix! ? Victim: AS v, foo/20 (foo/24 to be hijacked) ? Hijacker: AS h Preparation: ? Hijacker places AS v in his AS-SET (earlier) ? Open RIS Live session with ?foo/24Ąą filter Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 40
- 41. Live demo, cont. 1. Hijacker announces ?foo/24 origin AS hĄą 2. Local verification: BIRD show route foo/24 export upstream 1. Remote verification: NLNOG Looking Glass: foo/24 partially visible RIPE RIS Live: BGP hijacking updates received Disclaimer: AS v is our friendly customer. Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 41
- 42. Thank you! Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 42 https://netip.me https://twitter.com/pawmal80 /atendesoftware/presentations









![Howto, cont.
ExaBGP
route victim/24 next-hop self as-path [ foo ] community [ a:b ];
BIRD
bgp_path.empty;
bgp_path.prepend(foo);
Net::IP, Wroc?aw 2019.04.25 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bgphijackingnetipmeetupwroclaw201904-190427203313/85/BGP-hijacks-and-leaks-10-320.jpg)