Big Data_Big Data_Big Data-Big Data_Big Data
- 2. What is a Data? ŌĆó Data is any set of characters that has been gathered and translated for some purpose, usually analysis. ŌĆó It can be any character, including text and numbers, pictures, sound, or video.
- 3. What is Digital Data? ŌĆó Digital data are discrete, discontinuous representations of information or work. ŌĆó Digital data is a binary language.
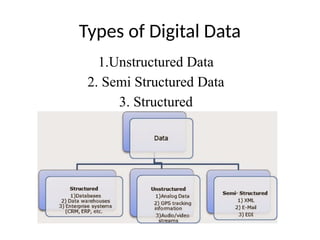
- 4. Types of Digital Data 1.Unstructured Data 2. Semi Structured Data 3. Structured
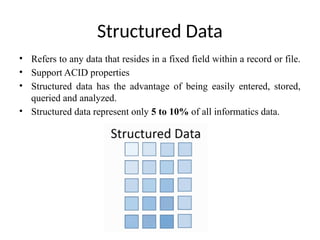
- 5. Structured Data ŌĆó Refers to any data that resides in a fixed field within a record or file. ŌĆó Support ACID properties ŌĆó Structured data has the advantage of being easily entered, stored, queried and analyzed. ŌĆó Structured data represent only 5 to 10% of all informatics data.
- 6. Unstructured Data ŌĆó Unstructured data is all those things that can't be so readily classified and fit into a neat box. ŌĆó Unstructured data represent around 80% of data. ŌĆó Techniques: Data mining-Association rule, Regression analysis, Text mining, NLP etc.,
- 7. Semi Structured Data ŌĆó Semi-structured data is a cross between the two. It is a type of structured data, but lacks the strict data model structure. ŌĆó Semi-structured data is information that doesnŌĆÖt reside in a relational database but that does have some organizational properties that make it easier to analyze.
- 8. Characteristic of Data ŌĆó Composition - What is the Structure, type and Nature of data? ŌĆó Condition - Can the data be used as it is or it needs to be cleansed? ŌĆó Context - Where this data is generated? Why? How sensitive this data? What are the events associated with this data?
- 9. What is Big Data? ŌĆó Collection of data sets so large and complex that it becomes difficult to process using on-hand database management tools or traditional data processing applications.
- 10. What is Big Data? Cont.. ŌĆó The data is too big, moves too fast, or doesnŌĆÖt fit the structures of your database architectures ŌĆó The scale, diversity, and complexity of the data require new architecture, techniques, algorithms, and analytics to manage it and extract value and hidden knowledge from it ŌĆó Big data is the realization of greater business intelligence by storing, processing, and analyzing data that was previously ignored due to the limitations of traditional data management technologies.
- 11. Why Big Data? & what makes Big Data? ŌĆó Key enablers for the growth of ŌĆ£Big DataŌĆØ are ŌĆó Every day we create 2.5 quintillion bytes of data. ŌĆó 90% of the data in the world today has been created in the last two years. Increase of storage capacities Increase of processing power Availability of data
- 12. Where does data come from? Data come from many quarters. ’āś Science ŌĆō Medical imaging, Sensor data, Genome sequencing, Weather data, Satellite feeds ’āś Industry - Financial, Pharmaceutical, Manufacturing, Insurance, Online, retail ’āś Legacy ŌĆō Sales data, customer behavior, product databases, accounting data etc., ’āś System data ŌĆō Log files, status feeds, activity stream, network messages, spam filters.
- 13. Where does data come from? Cont..
- 14. Characteristics Of 'Big Data' ŌĆó 5VŌĆÖs - Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity & Variability
- 15. CHALLENGES ŌĆó More data = more storage space ŌĆó Data coming faster ŌĆó Needs to handle various data structure ŌĆó Agile business requirement ŌĆó Securing big data ŌĆó Data consistency & quality
- 16. What is the importance of Big Data? ŌĆó The importance of big data is how you utilize the data which you own. Data can be fetched from any source and analyze it to solve that enable us in terms of 1) Cost reductions 2) Time reductions 3) New product development and optimized offerings, and 4) Smart decision making.
- 17. What is the importance of Big Data? Cont.. ŌĆó Combination of big data with high-powered analytics, you can have great impact on your business strategy such as: 1) Finding the root cause of failures, issues and defects in real time operations. 2) Generating coupons at the point of sale seeing the customerŌĆÖs habit of buying goods. 3) Recalculating entire risk portfolios in just minutes. 4) Detecting fraudulent behavior before it affects and risks your organization.
- 18. Who are the ones who use the Big Data Technology? ŌĆó Banking ŌĆó Government ŌĆó Education ŌĆó Health Care ŌĆó Manufacturing ŌĆó Retail
- 19. Storing Big Data ŌĆó Analyzing your data characteristics ’āś Selecting data sources for analysis ’āś Eliminating redundant data ’āś Establishing the role of NoSQL ŌĆó Overview of Big Data stores ’āś Data models: key value, graph, document, ’āś column-family ’āś Hadoop Distributed File System ’āś HBase ’āś Hive
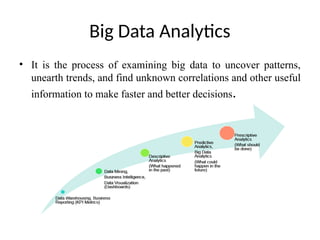
- 20. Big Data Analytics ŌĆó It is the process of examining big data to uncover patterns, unearth trends, and find unknown correlations and other useful information to make faster and better decisions.
- 21. Why is big data analytics important? ŌĆó Big data analytics helps organizations harness their data and use it to identify new opportunities. That, in turn, leads to smarter business moves, more efficient operations, higher profits and happier customers.
- 22. Types of Analytics ŌĆó Business Intelligence ŌĆó Descriptive Analysis ŌĆó Predictive Analysis
- 23. Business intelligence (BI) ŌĆó It is a technology-driven process for analyzing data and presenting actionable information to help executives, managers and other corporate end users make informed business decisions.
- 24. Descriptive Analysis ŌĆó Descriptive statistics is the term given to the analysis of data that helps describe, show or summarize data in a meaningful way such that, for example, patterns might emerge from the data.
- 25. Predictive Analysis ŌĆó Predictive analytics is the branch of data mining concerned with the prediction of future probabilities and trends. ŌĆó The central element of predictive analytics is the predictor, a variable that can be measured for an individual or other entity to predict future behavior.
- 26. Predictive Analysis ŌĆó There is 2 types of predictive analytics: ŌŚ” Supervised Supervised analytics is when we know the truth about something in the past Example: We have historical weather data. The temperature, humidity, cloud density and weather type (rain, cloudy, or sunny). Then we can predict today weather based on temp, humidity, and cloud density today ŌŚ” Unsupervised Unsupervised is when we donŌĆÖt know the truth about something in the past. The result is segment that we need to interpret Example: We want to do segmentation over the student based on the historical exam score, attendance, and late history.
- 27. Tools used in Big Data ŌĆó Where processing is hosted? Distributed Servers / Cloud (e.g. Amazon EC2) ŌĆó Where data is stored? Distributed Storage (e.g. Amazon S3) ŌĆó What is the programming model? Distributed Processing (e.g. MapReduce) ŌĆó How data is stored & indexed? High-performance schema-free databases (e.g. MongoDB) ŌĆó What operations are performed on data? Analytic / Semantic Processing
- 28. Top Big Data Technologies 1. Apache Hadoop ŌĆó Apache Hadoop is a java based free software framework that can effectively store large amount of data in a cluster. ŌĆó Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is the storage system of Hadoop which splits big data and distribute across many nodes in a cluster. ŌĆó This also replicates data in a cluster thus providing high availability. It uses Map Reducing algorithm for processing.
- 29. Top Big Data Technologies Cont.. 2. NoSQL ŌĆó NoSQL (Not Only SQL)is used to handle unstructured data. ŌĆó NoSQL databases store unstructured data with no particular schema. ŌĆó NoSQL gives better performance in storing massive amount of data. There are many open-source NoSQL DBs available to analyse big Data.
- 30. Top Big Data Technologies Cont.. 3. Apache Spark ŌĆó Apache Spark is part of the Hadoop ecosystem, but its use has become so widespread that it deserves a category of its own. ŌĆó It is an engine for processing big data within Hadoop, and it's up to one hundred times faster than the standard Hadoop engine, Map Reduce.
- 31. Top Big Data Technologies Cont.. 4. R ŌĆó R, another open source project, is a programming language and software environment designed for working with statistics. ŌĆó Many popular integrated development environments (IDEs), including Eclipse and Visual Studio, support the language.
- 32. Applications for Big Data Analytics
- 33. DATA SCIENTIST ŌĆó Data scientist/analyst is one of the trending and emerging job in the market
- 34. Thank You