bilirubin practicals for first year mbbs
- 1. M.B.B.S., MD., Fellowship in Diab., PGDEM CONSULTANT EMERGENCY PHYSICIAN DIABETOLOGIST TUTOR, BIOCHEMISTRY Exp No: Date: ESTIMATION OF BILIRUBIN Competency BI 11.12 Demonstrate the estimation of serum bilirubin
- 2. AIM & METHOD •AIM: • To determine the amount of total, direct and indirect bilirubin present in the given serum/ plasma sample. •METHOD: Modified DMSO/Diazo method
- 3. principle • Sulfanilic acid reacts with sodium nitrite to form diazotized sulfanilic acid. • Bilirubin reacts with diazotized sulfanilic acid in the presence of DMSO to form reddish purple Azobilirubin (Van Den Berg Reaction). • Water soluble, Conjugated bilirubin react very fast with Diazo reagent. • Whereas unconjugated bilirubin present in serum is complexed with albumin and reacts very slowly with Diazo reagent and it requires an activator, methanol (alcohol).
- 4. Indirect bilirubin is calculated as follows Concentration of Indirect bilirubin = Total bilirubin - Direct bilirubin For the estimation of total bilirubin serum is treated with diazo reagent and methanol. For the estimation of direct bilirubin serum is treated with only reagent.
- 5. Total bilirubin: Activator - Methanol Serum + diazotized sulfanilic acid Azobilirubin
- 6. Direct bilirubin: Serum + diazotized sulfanilic acid Azobilirubin
- 7. PROCEDURE
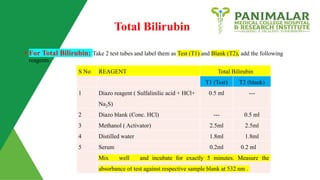
- 8. Total Bilirubin • For Total Bilirubin: Take 2 test tubes and label them as Test (T1) and Blank (T2), add the following reagents. S No REAGENT Total Bilirubin T1 (Test) T2 (blank) 1 Diazo reagent ( Sulfalinilic acid + HCl+ Na2S) 0.5 ml --- 2 Diazo blank (Conc. HCl) --- 0.5 ml 3 Methanol ( Activator) 2.5ml 2.5ml 4 Distilled water 1.8ml 1.8ml 5 Serum 0.2ml 0.2 ml Mix well and incubate for exactly 5 minutes. Measure the absorbance of test against respective sample blank at 532 nm .
- 9. Direct Bilirubin • For Direct Bilirubin: Take 2 test tubes and label them as Test (D1) and Blank (D2), add the following reagents. S No Reagent Direct Bilirubin D1 (Test) D2 (blank) 1 Diazo reagent ( Sulfanilic acid + HCl+ Na2S) 0.5 ml --- 2 Diazo blank (Conc. HCl) --- 0.5 ml 3 Methanol ( Activator) --- - 4 Distilled water 4.3ml 4.3ml 5 Serum 0.2 ml 0.2 ml Mix well and incubate for exactly 5 minutes. Measure the absorbance of test against respective sample blank at 532 nm .
- 10. CALCULATIONS: • Total Bilirubin = OD of test - OD of sample blank X Factor • Direct Bilirubin = OD of test - OD of sample blank X Factor • ( Note: factor will be provided by the kit manufacturer) • Indirect bilirubin = Total bilirubin - Direct bilirubin
- 11. RESULT: • The amount of total bilirubin in the given serum sample is __________mg/dl • The amount of direct bilirubin is _________mg/dl • The amount of indirect bilirubin is __________mg/dl.
- 12. NORMAL VALUES: • Total bilirubin: Adults : up to 1.2 mg/dl Infants : 0.2- 8 mg/dl • Direct bilirubin : 0 to 0.2 mg/dl. • Indirect bilirubin : 0.2 to 0.8 mg/dl
- 13. • CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE: • Causes of Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia: 1. Increased production of unconjugated bilirubin from heme  Hemolysis  Ineffective erythropoiesis  Rapid turnover of increased RBC mass 2. Decreased delivery of unconjugated bilirubin to hepatocyte  Right sided congenital heart failure  Post caval shunt
- 14. Causes of Unconjugated Hyperbilirubinemia: 3. Reduced uptake of conjugated bilirubin across hepatocyte membrane  Gilbert syndrome  Sepsis 4. Reduced storage in cytosol 5. Decreased biotransformation  Neonatal jaundice  Crigler Najjar syndrome  Hepato cellular dysfunction
- 15. • Causes of Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia: 1. Decreased secretion of conjugated bilirubin in to canalicular tract  Hepatocellular jaundice  Dubin Johnson and Rotor syndrome  Drug induced reaction 2. Decreased drainage  Extrahepatic obstructive stones, carcinoma, stenosis  Sclerosis cholangitis  Intrahepatic obstruction – granuloma, drugs, primary biliary cirrhosis, tumor.
- 16. Thank you