Bio.cnid.spong.review
- 1. * Biology class May 10th, 2012
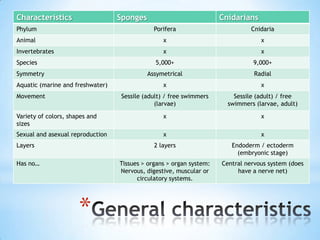
- 2. Characteristics Sponges Cnidarians Phylum Porifera Cnidaria Animal x x Invertebrates x x Species 5,000+ 9,000+ Symmetry Assymetrical Radial Aquatic (marine and freshwater) x x Movement Sessile (adult) / free swimmers Sessile (adult) / free (larvae) swimmers (larvae, adult) Variety of colors, shapes and x x sizes Sexual and asexual reproduction x x Layers 2 layers Endoderm / ectoderm (embryonic stage) Has noâĶ Tissues > organs > organ system: Central nervous system (does Nervous, digestive, muscular or have a nerve net) circulatory systems. *
- 3. * Sponges * Cnidarians Scyphozoa (jellyfish) Anthozoa (corals and sea anemone) Hydrozoa (hydra) Cubozoa (box * jellyfish)
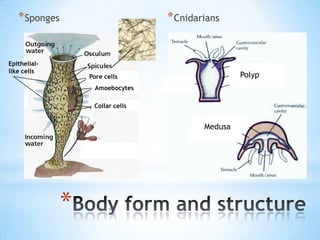
- 4. * Sponges * Cnidarians Epithelial- like cells Pore cells Polyp Amoebocytes Collar cells Medusa *
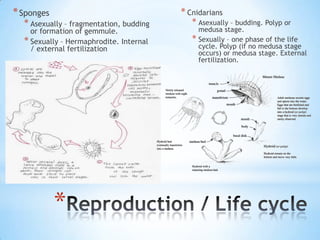
- 5. * Sponges * Cnidarians * Asexually â fragmentation, budding * Asexually â budding. Polyp or or formation of gemmule. medusa stage. * Sexually â Hermaphrodite. Internal * Sexually â one phase of the life / external fertilization cycle. Polyp (if no medusa stage occurs) or medusa stage. External fertilization. *
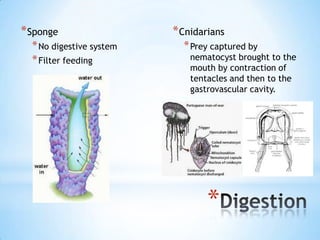
- 6. * Sponge * Cnidarians * No digestive system * Prey captured by * Filter feeding nematocyst brought to the mouth by contraction of tentacles and then to the gastrovascular cavity. *
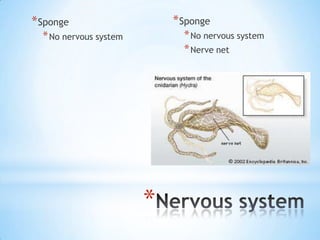
- 7. * Sponge * Sponge * No nervous system * No nervous system * Nerve net *