Biological science(cell)
- 1. Biological Science Cell By Ki Po Yi Veronica
- 2. Objective ïīTo find out the difference between human cell, plant cell and bacterial cell ïīTo identify the main parts of human cell ïīTo explain the function of parts of human cell
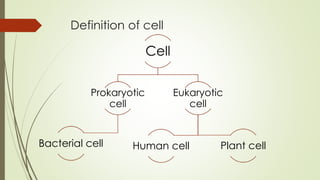
- 3. Definition of cell Cell Prokaryotic cell Bacterial cell Eukaryotic cell Plant cellHuman cell
- 4. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Bacterial cell Human cell Plant cell
- 5. Parts of the human cell
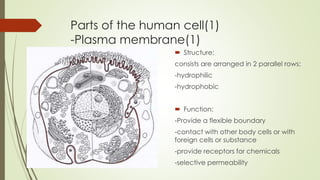
- 6. Parts of the human cell(1) -Plasma membrane(1) ïī Structure: consists are arranged in 2 parallel rows: -hydrophilic -hydrophobic ïī Function: -Provide a flexible boundary -contact with other body cells or with foreign cells or substance -provide receptors for chemicals -selective permeability
- 7. Parts of the human cell(1) -Plasma membrane(2)
- 8. Parts of the human cell(2) -Cytoplasm ïī Structure: -jelly-like substance ïī Function: -Provide support, shape, involved the movement of structure -Hold all the organelles -Chemical reaction are taken place -Transportation
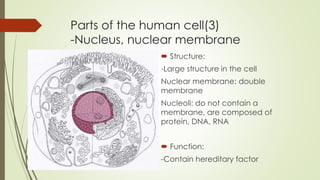
- 9. Parts of the human cell(3) -Nucleus, nuclear membrane ïī Structure: -Large structure in the cell Nuclear membrane: double membrane Nucleoli: do not contain a membrane, are composed of protein, DNA, RNA ïī Function: -Contain hereditary factor
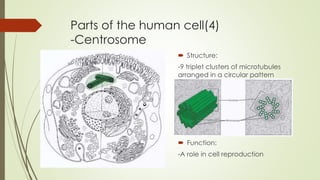
- 10. Parts of the human cell(4) -Centrosome ïī Structure: -9 triplet clusters of microtubules arranged in a circular pattern ïī Function: -A role in cell reproduction
- 11. Parts of the human cell (5) -Ribosome ïī Structure: -Compose of a type of RNA: ribosomal RNA and specific ribosomal protein -Free ribosome: no attachment to other parts of cell ïī Function: -Site of protein synthesis -Free ribosome -Other: attach to endoplasmic reticulum
- 12. Parts of the human cell(6) -Rough endoplasmic reticulum -Smooth endoplasmic reticulum ïī Structure: -Double membrane -Rough ER -Smooth ER ïī Function -contribution to mechanical support and distribution of the cytoplasm -involved in the intracellular exchange of materials with the cytoplasm -provide a surface area for chemical reactions -intracellular transportation system -Rough ER: protein synthesis -Smooth ER: lipid synthesis
- 13. Parts of the human cell(7) -Golgi complex ïī Structure: Cisternae: composed of stacks of membrane-bound structure ïī Function: -Process, package, deliver protein to various parts of the cell -associate with lipid secretion
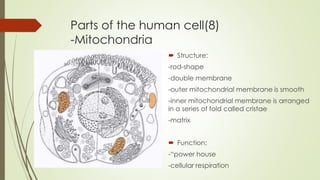
- 14. Parts of the human cell(8) -Mitochondria ïī Structure: -rod-shape -double membrane -outer mitochondrial membrane is smooth -inner mitochondrial membrane is arranged in a series of fold called cristae -matrix ïī Function: -âpower house -cellular respiration
- 15. Parts of the human cell(9) -Lysosome ïī Structure: -Formed from Golgi complex and have a single membrane -contain powerful digestive enzyme capable of breaking down many kinds of molecule ïī Function: -Digest the solid material contained in phagocytic vesicles -extracellular digestion -Autophagy
- 16. Parts of the human cell(10) -Peroxisomes ïī Structure: -similar in structure to lysosomes, but smaller ïī Function: -catalase: break down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen
- 17. Parts of the human cell(11) -Vacuole ïī Structure: -few small/ no vacuole ïī Function: -contain water and dissolved substance, food, enzyme
- 18. Reference: ïī Gerard J Tortora âThe cellular level of organizationâ,Principles of anatomy and Physiology, sixth edition(1990) ïī www.doabrown.info/page20/AQAAscibic21.htm ïī http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Nucleolus