BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 4
- 2. OUTCOME OF THE STUDIES State element in the cell List the chemical compounds in the cell Explain the importance of organic compounds in the cell Explain the importance of water in the cell 2
- 3. Chemical composition of the cell Elements Essential Elements: Carbon (C), Oxygen (O), Hydrogen (H) and Nitrogen (N) Calcium, Potassium, Phophorus, Sulphur, Sodium, Chlorine, Magnesium Trace Elements : Copper, Iodine, Iron Chemical compounds Organic compound Inorganic compound
- 4. 4 Major element (require in large quantity) Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen 96% of human body mass Minor element (require in smaller quantity) Calcium Phosphorus Potassium 4% of human body mass Trace element (require in the smallest quantity) Zinc Copper Iron 0.1% of human body mass 4
- 5. Compounds Organic compounds in cells Contains Carbon and Hydrogen Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic acid Inorganic compounds in cells Constitute non-living matter, and do not contain carbon Water
- 7. Formed by C,H and O Ratio C:H:0 is 1:2:1 Sub unit CH2O Formula (CH2O)n Organic compound Source of energy
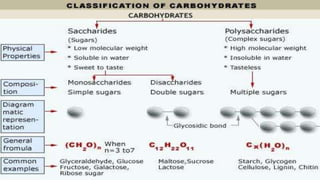
- 8. TYPES OF CARBOHYDRATES ŌĆó Maltose ŌĆó Sucrose ŌĆó Lactose ŌĆó Glycogen ŌĆó Starch ŌĆó Cellulose ŌĆó Glucose ŌĆó Fructose ŌĆó Galactose Monosaccharides Polysaccharides Disaccharides 8
- 10. Formation & breakdown of disaccharides glucose + condensation hydrolysis fructose sucrose H2O+
- 11. Formation & breakdown of disaccharides glucose + condensation hydrolysis glucose maltose H2O+
- 12. Formation & breakdown of disaccharides glucose + condensation hydrolysis galactose lactose H2O+
- 13. glucose glycogen Condensation reaction (-H2O) Hydrolysis (+ H2O) disaccharide Starch moleculeCondensation reaction (-H2O) Hydrolysis (+ H2O) cellulose Condensation reaction (-H2O) Hydrolysis (+ H2O)
- 14. The importance of carbohydrates 14 Energy storage Glycogen & starch Ribose sugar in DNA & RNA Support and structure Cellulose cell wall & chitin Energy production glucose Provide Immediate Fuel/energy so that cells can function
- 16. Elements in protein 16 Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur & phosphorus There are two types of amino acids : ŌĆó Essential ŌĆō cell need because body cannot produce ŌĆó Non-essential ŌĆō cell need but body can produce Basic unit: amino acids Amino acids are joined to each other in a particular sequence to form polypeptide chain or protein 01 02 03 04
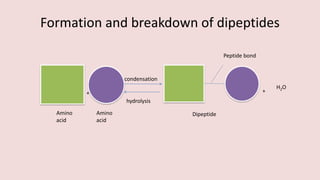
- 17. Formation and breakdown of dipeptides + condensation hydrolysis Peptide bond + H2O Amino acid Amino acid Dipeptide
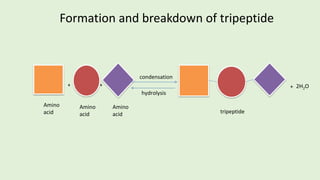
- 18. + condensation hydrolysis ++ 2H2O Amino acid Amino acid Amino acid tripeptide Formation and breakdown of tripeptide
- 19. condensation hydrolysis A polypeptide chain + 9H2O * 10 to 100 amino acids Formation and breakdown of polyptide
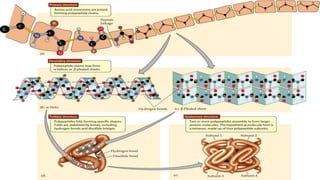
- 20. Protein Structures 3D protein structure is classified into 4 levels Primary structure Secondary structure Tertiary structure Quaternary structure Complete protein molecule is a simple unbranched chain of amino acids
- 22. Essential Amino acid that required for protein synthesis, but cannot be synthesized in the human body Obtained from food we eat Non essential Amino acid that is required for protein synthesis and can be synthesized by humans Essential amino acids & Non essential amino acids
- 24. 24 LIPIDS Glycerol & Fatty Acid01 0203 Fats ŌĆó Form the energy store of the body ŌĆó Two types: ŌĆó Compounds of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen. Some lipids contain nitrogen & phosphorus. ŌĆó Types of lipids are fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids and steroids ŌĆó Triglycerides are basic units of fats and oils. ŌĆó Glycerol ŌĆō colourless, oudourless, sweet-tasting and syrupy liquid ŌĆó Fatty acid - has long hydrogen tail with a carboxyl group at one end - have one or more double bond SATURATED FAT UNSATURATED FAT All single bond One or more double bond Less reactive More reactive In solid at room temp. In liquid at room temp. bad cholesterol Good cholesterol
- 25. Enzymes 25 Are protein molecules made by living cells, acting as catalysts Uses: Characteristics 1) Specific 2) Have active side 3) Speed up the rate of reactions 4) Are not destroy after the reaction 5) Can be help by confactor ŌĆō ferum & copper 6) Required in small amounts Intracellular & Extracellular Enzymes ’āś Intracellular ŌĆō produced in the cell ’āś Extracellular ŌĆō secreted out of the cell ŌĆó Enzyme action can be affected by the pH value of solution, the temperature of the medium of reaction, the concentration of the substrate and the concentration of enzyme. 01 02 0304 ŌĆó to tenderise meat ŌĆó Used in industry (detergent)
- 26. WATER 26 Inorganic compund Made up of hydorgen & oxygen Importance of water are Lorem Ipsum 01 02 03 I. Give support in plants and hydrostatic skeletons in worms II. Component of the protoplasm III. Solvent for solutes in the cells and blood plama IV. Medium for biochemical reaction V. Maintains the osmotic pressure in the tissue and blood plasma