Biology presentation on photosynthesis (by afr )
- 2. GROUP MEMBERS OF BIOLOGY ASSIGNMENT ARE : AFSHAN FAROOQ. RIMSHA ARSHAD AIMAN LIAQUAT AREEBA ISHTIAQ
- 3. Process by which plants and other autotrophs store the energy of sunlight into sugars. Requires sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Overall equation: 6 CO2 + 6 H20 ’āĀ C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Occurs in the leaves of plants in organelles called chloroplasts . photosynthesis in overview
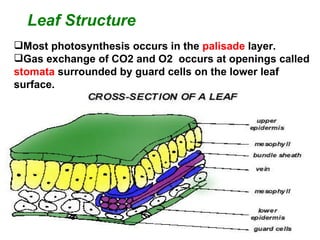
- 4. Most photosynthesis occurs in the palisade layer. Gas exchange of CO2 and O2 occurs at openings called stomata surrounded by guard cells on the lower leaf surface. Leaf Structure
- 5. LEAF STRUCTURE AND ITS FUNCTIONS ! INTRODUCTION AND EXPLANATION .
- 6. Chloroplast Structure Inner membrane called the thylakoid membrane. Thickened regions called thylakoids. A stack of thylakoids is called a granum. (Plural ŌĆō grana) Stroma is a liquid surrounding the thylakoids.
- 7. ╠²
- 8. Chlorophyll A is the most important photosynthetic pigment. Other pigments called antenna or accessory pigments are also present in the leaf. (orange / red) Xanthophylls (yellow Chlorophyll B Carotenoids / brown) These pigments are embedded in the membranes of the chloroplast in groups called photo systems. pigments
- 9. REQUIREMENTS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS : LIGHT CARBONDIOXIDE WATER LIMITING FACTOR TEMPERATURE PRODUCTS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS WILL BE EXPLAINED .
- 10. Q. What is a leaf structure and what is its function ? The structure of the leaf allows for maximum absorption of sunlight for photosynthesis. There are several levels of structure in studying a leaf. A leaf attached to the tree at a node. The stalk that attaches the leaf to the tree is the petiole which extends into the midrib of the leaf called the rachis. There may be a pair of extensions from the base of the petiole called stiplules. Many veins branch off the rachis. The flat part of the leaf is called the blade. There are many shapes of leaves and different margins. If we take a section of the leaf, we would find the following tissue layers from top to the bottom of the leaf: upper epidermis covered with a waxy cuticle, palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll in which the photosynthesis occurs, a lower epidermis perforated with numerous holes called stomata. The stomata are surrounded by guard cells that can open and close. The stomata allow gas exchange (carbon dioxide in and oxygen and water vapor out). There will be cross sections of veins as well. In the vein, there will be xylem carrying water and minerals at the top of the vein with phloem on the bottom of the vein .The structure of the leaf allows max. absorption of sunlight for photosynthesis ŌĆ”. EXTRAAAAAAA INFORMATION !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
- 11. LETS UNDERSTAND MORE DEEPLY !! ’üŖ FUNTIONS OF : blade vein midrib petiole node (will be explained)
- 12. let's make education value based !! By relating BIOLOGY with ALLAH !!!!
- 13. . ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” MS.ISMAT ! FOR MAKING US UNDERSTAND SO WELL ! THANKYOU.
- 14. THANKYOU !