Biomedical Waste Management.ppt
- 1. MEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT & It’s SOCIAL IMPACT Rajeshwari R ,B.E.,M.E.,(Ph.D).,MISTE., Faculty of Biomedical Engineering, KPR Institute of Engineering & Technology, Coimbatore. Ph:9597308485 Mail ID: rajeshwari.r@kpriet.ac.in
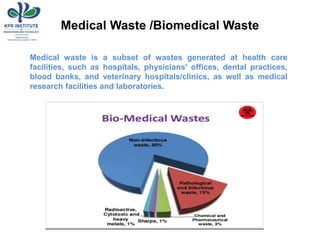
- 2. Medical Waste /Biomedical Waste Medical waste is a subset of wastes generated at health care facilities, such as hospitals, physicians' offices, dental practices, blood banks, and veterinary hospitals/clinics, as well as medical research facilities and laboratories.
- 3. SOURCES
- 13. WHO
- 14. Hazards to animals and birds •Plastic waste can choke animals, which scavenge on open dumps. •Injuries from sharps are common feature affecting animals. •Harmful chemicals such as dioxins and furans can cause serious health hazards to animals and birds. •Heavy metals can even affect the reproductive health of the animals. •Change in microbial ecology, spread of antibiotic resistance.
- 15. Environmental Impact Inadequate incineration results in •release of pollutants into the air and in the generation of ash residue. •Incinerated materials containing or treated with chlorine can generate dioxins and furans, which are human carcinogens and have been associated with a range of adverse health effects. •Incineration of heavy metals or materials with high metal content (in particular lead, mercury and cadmium) can lead to the spread of toxic metals in the environment. Only modern incinerators operating at 850-1100 °C and fitted with special gas- cleaning equipment are able to comply with the international emission standards for dioxins and furans.
- 16. The disposal of untreated health care wastes in landfills can lead to the contamination of drinking, surface, and ground waters if those landfills are not properly constructed.
- 17. When does the world starts noticing??
- 18. • In late 1980’s o Items such as used syringes were washed up on several East Coast beaches o Concern about HIV and HBV virus infection o Lead to development of biomedical waste management law in USA However in INDIA the seriousness about the management came into limelight only after 1990’s
- 23. HOSPITALS IN HOUSE SEGREGATION COMMON STORAGE POINT TRANSPORTATION UNLOADING AND TEMPERATURE STORAGE AT CBWTF TREATMENT DISPOSAL BMW MANAGEMENT PROCESS
- 24. Waste Transport by People
- 25. VEHICLE USED FOR TRANSPORTATION (Waste Trucks)
- 36. AWARENESS AND EDUCATION •Organizing seminars •Workshops •Practical demonstrations •Group discussions •Lectures