Bioreactor_on_Bioprocess_Engineering.ppt
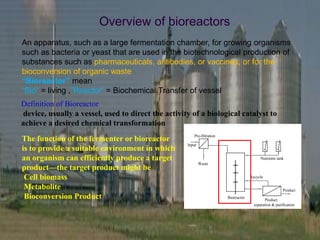
- 2. Definition of Bioreactor device, usually a vessel, used to direct the activity of a biological catalyst to achieve a desired chemical transformation ŌĆ£BioreactorŌĆØ mean ŌĆ£BioŌĆØ = living ,ŌĆØReactorŌĆØ = Biochemical Transfer of vessel An apparatus, such as a large fermentation chamber, for growing organisms such as bacteria or yeast that are used in the biotechnological production of substances such as pharmaceuticals, antibodies, or vaccines, or for the bioconversion of organic waste Product Bioreactor Recycle Product separation & purification Nutrients tank Waste Input Pre-filtration The function of the fermenter or bioreactor is to provide a suitable environment in which an organism can efficiently produce a target productŌĆöthe target product might be Cell biomass Metabolite Bioconversion Product
- 3. Requirements of Bioreactors The general requirements of the bioreactor are as follows: ’āśThe design and construction of bioreactors must keep sterility from the start point to end of the process. ’āśOptimal mixing with low, uniform shear. ’āśAdequate mass transfer, oxygen. ’āśClearly defined flow conditions. ’āśFeeding substrate with prevention of under or overdosing. ’āśSuspension of solids. ’āśGentle heat transfer. ’āśCompliance with design requirements such as: ability to be sterilized; simple construction; simple measuring, control, regulating techniques; scale-up; flexibility; long term stability; compatibility with up- downstream processes; antifoaming measures The basic points of consideration while designing a fermenters: ’ā╝ Productivity and yield ’ā╝ Fermenter operability and reliability ’ā╝ Product purification & Water management ’ā╝ Energy requirements & Waste treatment
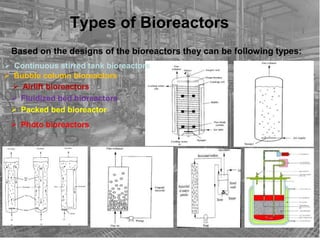
- 4. Types of Bioreactors Based on the designs of the bioreactors they can be following types: ’āś Photo bioreactors ’āś Packed bed bioreactor ’āś Fluidized bed bioreactors ’āś Airlift bioreactors ’āś Bubble column bioreactors ’āś Continuous stirred tank bioreactors
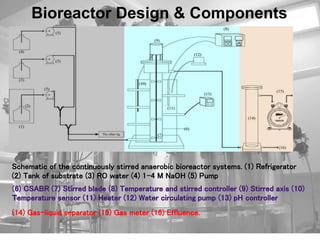
- 5. Bioreactor Design & Components Schematic of the continuously stirred anaerobic bioreactor systems. (1) Refrigerator (2) Tank of substrate (3) RO water (4) 1ŌĆō4 M NaOH (5) Pump (14) Gas-liquid separator (15) Gas meter (16) Effluence.
- 6. Bioreactor Components Bioreactors consist of ŌĆōVessel ŌĆōAgitator ŌĆōSparser ŌĆōBaffles ŌĆōProbes ’āśTemperature ’āśDissolved Oxygen ’āśpH ’āśPressure Gauge ŌĆōCooling Jacket ŌĆōPorts for input and output of material ŌĆōCondenser ŌĆōBack Pressure Valve ŌĆōInlet Filters and Exhaust Filters ŌĆōValves & Load Cell
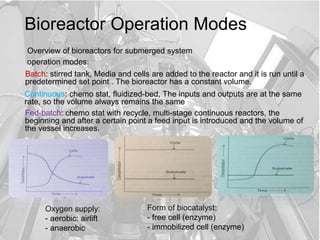
- 7. Bioreactor Operation Modes Overview of bioreactors for submerged system Fed-batch: chemo stat with recycle, multi-stage continuous reactors, the beginning and after a certain point a feed input is introduced and the volume of the vessel increases. operation modes: Oxygen supply: - aerobic: airlift - anaerobic Form of biocatalyst: - free cell (enzyme) - immobilized cell (enzyme) Batch: stirred tank, Media and cells are added to the reactor and it is run until a predetermined set point . The bioreactor has a constant volume. Continuous: chemo stat, fluidized-bed, The inputs and outputs are at the same rate, so the volume always remains the same
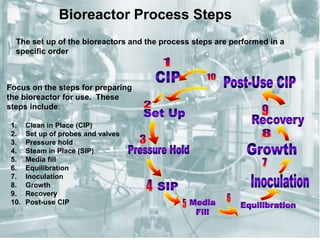
- 8. Bioreactor Process Steps The set up of the bioreactors and the process steps are performed in a specific order 1. Clean in Place (CIP) 2. Set up of probes and valves 3. Pressure hold 4. Steam in Place (SIP) 5. Media fill 6. Equilibration 7. Inoculation 8. Growth 9. Recovery 10. Post-use CIP Focus on the steps for preparing the bioreactor for use. These steps include:
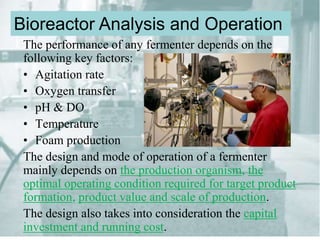
- 9. The performance of any fermenter depends on the following key factors: ŌĆó Agitation rate ŌĆó Oxygen transfer ŌĆó pH & DO ŌĆó Temperature ŌĆó Foam production The design and mode of operation of a fermenter mainly depends on the production organism, the optimal operating condition required for target product formation, product value and scale of production. The design also takes into consideration the capital investment and running cost. Bioreactor Analysis and Operation
- 10. I would like to thank our sir prof. N.K Brahma of our institution and my classmates for helping me to complete this project