Bitmessage
- 1. Bitmessage:An Analysis Vikram Reddy Pareddy CSc 8222 Department of Computer Science, Georgia State University
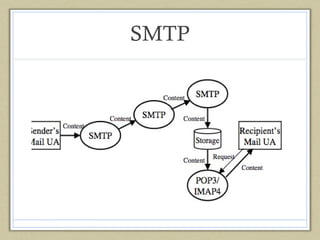
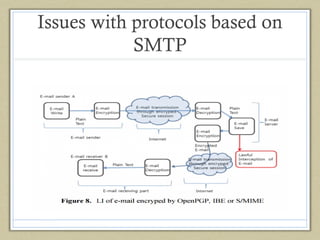
- 2. Email • SMTP – 1981 • Simple Protocol - designed mainly for academic and government use. • No data protection strategies included
- 3. SMTP
- 4. Improvements on SMTP • Sender Policy Framework(SPF) – It is an email validation system that tries to prevent spam by detecting spoofing, by verifying sender’s IP address. The domain administrators are expected to designate hosts in that domain that are legitimate hosts. • Domain Keys Identified Mail(DKIM) – It is a method of associating a domain name to the email message to make someone responsible for the email. This responsibility is set by using digital signatures.
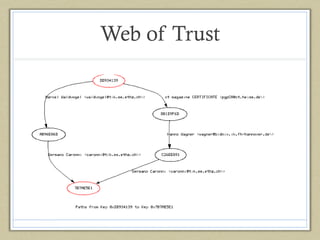
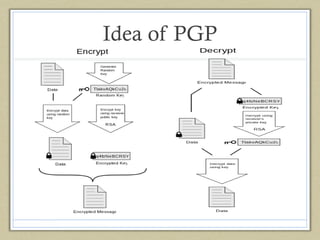
- 5. Secure Email • PGP – 1991 – Phil Zimmerman • It uses signing, encryption, certificates etc. to create secure environments – for email or for encrypted file systems etc. • Public key authentication – decentralized • Web of Trust
- 6. Web of Trust
- 7. Assumptions in Web of Trust • In order to verify the key, the assumption made is that everyone signs the key of others • Also everyone submits these signatures to the key servers.
- 8. Idea of PGP
- 9. Off the record messaging • Cryptographic protocol used to provide strong encryption for instant messaging and email • It uses a combination of AES symmetric key encryption, Diffie-Hellman key exchange, and SHA1 hash function.
- 10. Features of OTR systems • Encryption • Authentication • Deniable Encryption • Perfect Forward Secrecy
- 11. Invisible Internet Project • Provides a layer that serves secure communication/data transfer mechanism • Introduced in 2003 as a beta software • Not reviewed yet • No anonymity guaranteed
- 12. Issues with protocols based on SMTP
- 13. Bitcoin • Open source decentralized Peer to Peer currency • No central authority • Not designed for anonymity • Proof of work • Mining
- 14. Bitmessage • Based on Bitcoin, although it is designed to handle a different application • It differs from the protocols based on SMTP as it is based on the concept of EGE or “Everyone Gets Everything” • Using this concept, Bitmessage can not only mask the message body but also the metadata associated with the message i.e. the sender and receiver
- 15. EGE • No end points to a message • Encrypt the message and drop it into the block chain of messages • All the active users try to decrypt the message. • Only the intended recipient will be able to decrypt the message.
- 16. Other services of Bitmessage Broadcasting •Since Bitmessage is based on the concept of EGE, broadcasting a message comes naturally •The users have to get the password of the channel from some forum or word of mouth – and then they will be able to decrypt the messages using the password
- 17. Chans •Chans or channels are anonymous chat rooms •Users can simply encrypt using the public key of the chat room and post it •Completely anonymous
- 18. Perfect Forward Secrecy • An intruder can store all the encrypted conversations and later when he eventually breaks or somehow gets the private key, all the previously encrypted information is lost • This is a concern in almost all the PKI systems • In Bitmessage this concern is even more pronounced as anyone can store the block chains easily
- 19. • Bitmessage doesn’t provide PFS • However, this can be supported in Bitmessage using and implementation of key rotation • Every message that is sent has to be sent using a new key. These are called ephemeral keys
- 20. Message Retention • In Bitmessage, the messages are retained for two days before they are deleted • The sender expects an acknowledgement from the receiver which confirms the delivery of the message • If the receiver doesn’t check his mailbox in two days that the message was sent, the messae is lost and the sender has to send it again This concept is being improved using the Time-to-live concept
- 21. Streams • According to Prof. Tom Rodden of Univ of Nottingham, 2.8 million mails are being sent per second across the world. • If Bitmessage is expected to store all these messages, it has to implement some concept compared to the normal block chain used by bitcoin • For this, Bitmessage uses Streams. • Streams are a way to self-segregate the messages when the volume of the messages is too high
- 22. • When the volume of messages become too high, the client can divide the block chain into child streams • Problem: Inter stream messaging is not possible in Bitmessage. • If the receiver of the message is in a different stream, the sender has to create an address in that other stream in order to send the message.
- 23. Conclusion • Bitmessage completely redesigns the email system • It is completely anonymous • There are a few issues that still exist such as Perfect Forward Secrecy and the question of scalability
- 24. Future Work • An MIT graduate has developed a new protocol based on Bitmessage • This message is called Bitmask or Bitmessage 2.0. This protocol uses bandwidth based metrics instead of proof of work • A protocol called LibertyMail is being developed which is again based on Bitmessage system
- 25. Idea • Currently, Bitmessage, like bitcoin in the beginning has only one client, Bitmessage-Qt • This is a standalone client in the system which is used independent of any mail client • The problem with this kind of client is that it downloads all the block chain into the individual system • While this is a hindrance only when downloading the client for the first time, it is still a hindrance
- 26. • Bitcoin overcomes this hindrance by using a thin client based architecture • Electrum is an example • Electrum has its multiple servers located across the world. • A person who wants to use a bitcoin client can generate the keys on his local machine and send it to the electrum server which posts it onto the block chain
- 27. • Electrum uses passphrase based electrum client that creates deterministic addresses based on the seed value. • The idea of my project is to use a similar architecture in Bitmessage. • Using this architecture, we can still mask the metadata
- 28. References