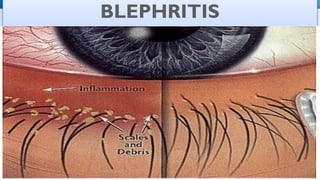
Blepharitis is a common eye condition that causes inflammation of the eyelids.
- 3. BLEPHRITIS
- 4. INTRODUCTION Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. They may appear red, swollen , or feel like they are burning or sore. flakes or oily particles (crusts) wrapped at the base of eyelashes too. Blepharitis is very common, especially among people who have oily skin, dandruff. Greek blepharon ŌĆśeyelidŌĆÖ + -itis.
- 5. DEFINITION Blepharitis is a subacute (or) chronic inflammation of the lid margins. Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. Blepharitis usually affects both eyes along the edges of the eyelids. Blepharitis commonly occurs when tiny oil glands near the base of the eyelashes become clogged, causing irritation and redness.
- 6. ŌĆó Anatomy of lid margin:- - It is about 2mm broad & is divided into 2 parts by the punctum(Medial & lateral) Lacrimal portion(medial) :- It is devoid of lashes & glands Ciliary portion ( lateral) :- It consists of rounded antr.boder Sharp post.border & an intermarginal strip (b/w the two borders) ŌĆó The grey line divides the intermarginal strip into a)Anterior strip bearing 2-3 rows of lashes b)Posterior strip on which openings of meibomian glands are arranged in a row ŌĆó Importance ŌĆō the splitting of eyelids when required in operations is done at the level of grey line
- 8. TYPES OF BLEPHARITIS A.Bacterial blepharitis B.Seborrhoeic or Squamous blepharitis C.Mixed staphylococcal with seborrhoeic blepharitis D. Posterior blepharitis or Meibomitis E.Parasitic blepharitis
- 10. ŌĆó Also known as -Chronic antr.blepharitis -Staphylococcal blepharitis -Ulcerative blepharitis ŌĆó It is a chronic infection of the anterior part of lid margin ŌĆó It is a common cause for occular & discomfort and irritation ŌĆó It is usually starts in childhood & may continue throught out the life
- 11. ETIOLOGY :- ’āś Causative organisms ŌĆō - (M/C) cogulase +ve staphylococci -Rarely streptococci , propionibacterium acnes & moraxella may be involved PREDISPOSING FACTORS :- Rarely includes chronic conjuctivitis and dacrocystitis
- 12. CLINICAL FEATURES:- Symptoms :- Chronic irritation Itching Mild lacrimation Gluing of cilia Mild photophobia Symptoms are worse in the morning Remissions and exacerbations in symptoms are quite common
- 13. ŌĆó SIGNS :- - Yellow crusts - Small ulcers on removing crusts - Hyperemia ŌĆó Mild papillary conjuctivitis and conjuctiva hyperemia are common assosciations
- 15. - Tylosis - Epiphora - Eczema of skin & ectropion - Recurrent styes - Marginal keratitis - Tear film instabillity ŌåÆ dry eye
- 16. Treatment a) Lid hyegine(twice daily) - includes - Warm compress - Crust removal (3% sodium bicarbonate) - Avoid rubbing of eyes b) Antibioics - Eye ointment - Eye drops - Oral antibiotics (erythromycin,doxicycline) c) Topical steroids (Fluoromethalone) d) Occular lubricants
- 17. ŌĆó It is primarily anterior blepharitis with some spill over posteriorly ŌĆó ETIOLOGY :- - Assosciated with seborrhoea of scalp(dandruff) - Glands of zeis secrete abnormal excessive neutral lipids - whitish material at the lid margins - Mild discomfort - Irritation - occasional watering - Falling of eyelashes Corynebacterium acne Neutral lipis ŌĆó Symptoms :- Irritating free fatty acids Seborrhoea of scalp
- 18. ŌĆó Signs :- - Accumulation of white dandruff like scales among lashes - Underlying surface hyperaemic with out ulcers - Lashes fall out easily - Lid margin is thickened ŌĆó Complications : -similar to bacterial blepharitis ŌĆó Treatment :- - General improvement of health & diet - Seborrhoea of scalp should treated - Removal of scales with luke warm sol. (3% NaHco /baby samphoo) 3 - Antibiotics (erythromycin/doxicycline) Madarosis & Lid oedema
- 19. ŌĆó It is inflammation of Meibomian glands ŌĆó Two forms as Chronic & acute ŌĆó Chronic type :- - Due to meibommian gland dysfunction - Common in middle aged people - Due to action of bacterial lipases ŌĆó Clinical features :- a) Symptoms :- Chronic irritation Burning Mild lacrimation Symptoms are more worse in morning
- 20. Signs :- a) Lid margins ŌĆō shows foam like secretions b) Meibommian glands -openings are prominent with secretions expressed by pressure on lids with toothpaste appearance -Orifice shows capping with oil globules,plugging c)Vertical yellowish streaks shining through conjuctiva d) Hyperemia and telangectisia of post. Lid margin e) Secondary changes - papillary conjuctivitis - inferior corneal punctate epithelial erosions Thickened posterior lid margin Capping of meibimian gland orifice by oil globules
- 21. ŌĆó Acute Meibomitis :- - It is due to staphylococcal infection Characteristic features :- - Painful swelling around the involved gland -Pressure results in expression of pus ŌåÆ serosanguinous discharge ŌĆó Treatment :- - Lid hygiene(warm compress , massage) - Topical antibiotics (immediately after massage) - Systemic tetracyclines (doxycycline) - Ocular lubricants - Topical steroids (fluoromethalon-for papillary conjuctivitis)
- 22. ŌĆó It is associated infestation of lashes by lice ŌĆó Common in people living in poor hygienic conditions ŌĆó Clinical features :- Infestation with lice causes chronic blepharitis & chronic follicular comjuctivitis ŌĆó Symptoms :- - Chronic irritation - Itching - Burning -Mild lacrimation Phthiriasis palpebrum Pediculosis Due to infestation by phthiriasis pubis(crab louse) Due to infestation by pediculus humanus corporis / capitis Common in adults & mainly acquired as sexually transmitted disease Infested lice spreads to involve lashes
- 23. ŌĆó Signs :- a)Lid margin ŌĆō red & inflammed b)Slit lamp examination ŌĆō Lice anchoring lashes with claws c)Nits ŌĆō seen as opalescent pearls adherent to base of cilia d)Conjuctiva congestion on land standing cases ŌĆó Treatment :- - Mechanical removal of lashes with forceps -Application of antibiotic ointment & yellow mercuric oxide 1% to lid margins and lashes - Delousing of patient
- 24. TREATMENT Warm compresses Wet a clean washcloth with warm water and wring it out until somewhat dry. Place the washcloth over closed eyes for at least 1 minute.Wet the washcloth as often as needed so it stays warm.This will help loosen the flakes sticking around eyelashes. It also helps keep nearby oil glands from clogging ( Blocking) ThereŌĆÖs also an electronic device that uses heat and massage to unclog the oil glands in your eyelids.The treatments are done in the office by ophthalmologist. Eyelid scrubs Soak a clean washcloth, cotton swab (Q-tip) applicator, or lint-free pad in baby shampoo diluted in warm water.Then use it to gently scrub the base of eyelashes. Scrub for about 15 seconds.
- 25. Antibiotics ophthalmologist may have use an antibiotic ointment on eyes. Put a small amount of ointment on a clean fingertip or a cotton swab (Q-tip). Gently apply the ointment to the base of eyelashes. Do this just before bedtime, or as doctor recommends. Doctor might also prescribe an antibiotic medicine for to take by mouth. Eye drops Artificial tears or steroid eye drops may reduce redness, swelling and dry eye. Ophthalmologist might prescribe an antibiotic eye drop to help the oil glands work better. Skin and eyelid hygiene It is very important to keep eyelids , skin and hair clean.This keeps blepharitis symptoms under control. Carefully wash eyelashes every day with baby shampoo diluted in warm water.Also, wash hair, scalp and eyebrows with an antibacterial shampoo.There are some new antiseptic sprays ,can use on the skin that keep bacteria from growing too much.
- 26. Complications ŌĆóConjunctivitis ŌĆóKeratitis. ŌĆóCorneal infiltration. ŌĆóCorneal ulcer. ŌĆó Trichiasis. ŌĆó Eyelid notching. ŌĆóEntropion. ŌĆóEctropion.