Block chain
- 1. Blockchain
- 2. • What’s a blockchain? • How do they work, what problems do they solve and how can they be used?
- 3. • Everyone is talking about blockchains and cryptocurrencies these days. But what is this blockchain thing? • A blockchain is a way of storing data so that cannot be changed anymore. This is called immutability and a very useful feature when dealing with very important data like bank records or transactions.
- 4. • Like the name indicates, A blockchain is a chain of blocks that contains information. • This technique was originally described in in 1991 by a group of researchers (Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta) and was originally intended to timestamp digital documents so that it’s not possible to backdate them or to tamper with them.
- 5. How do they work?
- 6. 1- The data that inserted inside a block it depends on the type of blockchain. The Bitcoin blockchain for example stores the details about the transaction in here, such as the sender, receiver and amount of coins. Data
- 7. You can compare a hash to fingerprint. It identifies a block and all of it’s contents and it’s always unique like a fingerprint. Once a block is created, it’s hash is being calculated Hash
- 8. • Changes something inside the block will cause the hash to change • Hashes is very useful when you want to detect changes to block • If the fingerprint of a block changes, it no longer the same is the same block Detect changes
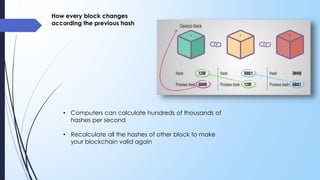
- 9. Hash of previous block • The third elements inside each block the hash of the previous block • This effectively creates a chain of blocks and it’s this technique that makes a blockchain so secure
- 10. • Computers can calculate hundreds of thousands of hashes per second • Recalculate all the hashes of other block to make your blockchain valid again How every block changes according the previous hash
- 11. Proof of work It’s a mechanism that slows down the creation of new blocks the proof-of-work difficulty is determined by a moving average targeting an average number of blocks per hour. If they're generated too fast, the difficulty increases.
- 12. Example • In bitcoins case: it takes 10 minutes to calculate the proof-of- work and add new block to the chain • This mechanism makes it very hard to tamper with the blocks, because you tamper with 1 block, you need to calculate all the following blocks • so the security of a blockchain comes from its creative use of hashing and the proof-of-work mechanism
- 13. Peer-to-peer (p2p) • Instead of using central entity to manage the chain, blockchain use peer-to-peer network and every one is allow to join • Files can be shared directly between systems on the network without the need of a central server • The only requirements for a computer to join a peer-to- peer network are an Internet connection and P2P software • When someone join the networks, he gets full copy of the blockchain
- 14. Create new block • Each node then verifies the block to make sure that it hasn’t been tampered with • If everything checks out, each node add this block to there own block
- 15. nodes • They agree about what blocks are valid and which aren’t • Blocks that tamper with will be rejected by other nodes in the network • So to successfully tamper with a chain you will need to tamper with all the blocks on the chain
- 16. • Blockchain are also constantly evolving • One of the more recent developments is the creation of smart contract • This contract are simple programs that are stored on blockchain and can be used to automatically exchange coins based on certain conditions