Blood
- 1. BLOOD PREPARED BY- KAMAL JEET BHATTI PGT BIOLOGY JNV KARNAL
- 2. âĒ Blood is a body fluid in humans and other animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. âĒ Blood is a fluid connective tissue composed of a fluid matrix, plasma and the blood corpuscles. It forms about 30-35% of the extracellular fluid. It is slightly alkaline fluid having pH7.4. âĒ Blood is special type of connective tissue in which extracellular matrix is fluidy in nature that is Plasma.
- 3. BODY FLUIDS
- 4. Body fluid percentage TOTAL BODY WEIGHT 60% BODY FLUID(WATER) 40% INTRACELLULAR FLUID 20% EXTRACELLULAR FLUID INTERSTIAL FLUID 75% PLASMA 25% 40% DRY WEIGHT
- 5. COMPOSITION OF BLOOD âĒ Blood is a fluid connective tissue composed of 55% plasma and 45% formed elements including WBCs, RBCs, and platelets. âĒ Since these living cells are suspended in plasma, blood is known as a fluid connective tissue and not just fluid. âĒ An average person carries about 5 to 6 litres of the blood.
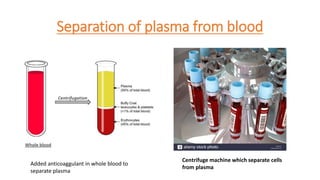
- 6. Separation of plasma from blood Centrifuge machine which separate cells from plasma Added anticoaggulant in whole blood to separate plasma
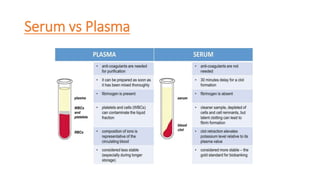
- 7. Plasma âĒ Plasma is straw coloured viscous fluid that constitutes 55% of blood volume. It consists of 90-92% water, 6-8% protein (fibrinogens, albumins and globulins), glucose, amino acids and small amount of minerals like Na+, Ca++, Cl- etc. âĒ Plasma carries the fibrinogen protein which helps in blood clotting. âĒ Serum is the supernatant of the coaggulated blood.
- 9. Composition of the plasma
- 10. Protein in the plasma and their role Small fraction of the globulin called gamma globuln act as antibodies in the blood helps in immune response.This fraction is also called immunoglobulin(Ig).
- 11. Formed elements( Blood cells)
- 12. Continue âĒ Mainly three types of cells are present in the blood. 1. Red blood corpuscle (Erythrocytes) 2. White blood corpuscles (Leucocytes) 3. Platelets ( Thrombocytes) Hematopisis is the process of blood cell synthesis which occurs in the Red bone marrow ( Inner part of the bones). Yellow bone marrow is the inactive part of the bone which mainly cantains the fat cells but no hematopoisis occurs in this part. Red bone marrow cantains the Haematopitic stem cells which regularly divides to produce the blood cells.
- 13. Hematopoisis âĒ Hematopoisis is the synthesis of the blood cells in the red bone marrow. âĒ In the fetal life (before birth) the hematopoisis occurs in different parts of the fetus- Upto 3 week- Liver Upto 3 months - Spleen and the lymph nodes. At the time of birth- Allmost all bones Adult age - Red bone marrow part of some bones like sternum, ribs,femur, humerus,pelvicbones etc. âĒ Red bone marrow cantains the special type of cells which divides continuesly throughout life to produce different type of blood cells.These cells are called Hemopoitic Stem cells which are multipotent stem cells.
- 14. Hemopoitic stem cells âĒ Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis.This process occurs in the red bone marrow, in the core of most bones. âĒ Stem cells are special type of cells which have ability to divide for long time and they also keep their number constant.
- 16. Erythrocytes or Red blood corpuscles âĒ They are the most common type of cells present in the blood. âĒ They are produced by the myeloid linage of the Hemopoitic stem cell (HSC) division. âĒ They are enucleated when matured but their progenitor cells contains nucleus. âĒ They are biconcave in shape.This shape helps it to move in narrow cappilaries in the body. âĒ The 33% cytoplasm of the RBC is filled with the Haemoglobin which mainly helps in oxygen transportation.The normal size of the RBC is approximately 7-8 micrometer and the volume id about 90 femtometer. âĒ One RBC cantains about 30picogram of haemoglobin.
- 17. Erythrocytes or Red blood corpuscles--- âĒ Vitamin B12 and the folic acid is necessary for the cell division of the erythroblast(progenitor cell) to produce the RBC. âĒ Iron is necessary for the production of the hemoglobin.Oxygen temporarily binds with the iron in the hemoglobin during its transportation in the blood. âĒ The deficiecny of vitamin b12, folic acid,and iron will couse different type of anemia (Deficiency of blood). âĒ 1ml of blood cantains approximately 5 million of RBC. âĒ The normal life span of the RBC is about 120 days. âĒ Reticulocytes are the freshly formed RBC in the blood. âĒ RBC helps in the transportation of the oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
- 18. Leucocytes or White blood cells âĒ Leuco mean white and cyte means cell so they are also called as the white blood cell. âĒ There are different types of leucocytes based on their structure, nucleus shape, presence and absence of the granulocytes in their cytoplasm and their fuction. âĒ They mainly function in the immune system of the body and protects us from variuos types of infectious diseases and the invaders. âĒ They comes from both the linage that is myeloid and lymphoid in the bone marrow. âĒ Their production is called as the leucopoisis.
- 19. Leucocytes or White blood cells------- âĒ 1ml of the blood cantains about 4000-11000 cell in normal condition. âĒ The increased number in the blood may indicates the infection in any part of the body. âĒ The less number of WBC than the normal value is called leucopenia. âĒ They are present in blood, lymph,lymph nodes even in the different organs as their permanent resident. âĒ Their life span varies from cell to cell.some white blood cells have life span of 7-10 days but some memory lymphocyes have very long life span. âĒ WBC are the worrier cells of the body. They helps in the innate immunity as well aquired immunity.
- 20. Types of the WBC âĒ Neutrophls âĒ basophils âĒ Eosinophils âĒ Monocytes âĒ Natural killer cells âĒ T cell âĒ B cell âĒ Dendrite cell âĒ Mast cells âĒ Macrophages
- 21. Platelets or Thrombocytes âĒ Platelets are not the cells but they are the fragments of the cells which are produced by the Megakaryocyte in the bone marrow. âĒ The production of thrombocytes is called thrombopoisis. âĒ They have no nucleus so they are short lived. âĒ The normal life span of the platlet is 8- 9 days. The old platlets are destroyed by the phogocytic cells in the spleen and lymph nodes. âĒ Platlets helps in the hemostatis. Hemostatis is the process to prevent and stop bleeding, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel (the opposite of hemostasis is hemorrhage) âĒ Platlets makes the plug or clot at the site of bleeding or pucture in the blood vessel and stop the blood loss.
- 23. Platelets or Thrombocytes âĒ Sometime platlets makes clumps in the blood vessels and circulates in the vessels which is called thrombosis.It obstruct the small vessels in the ciculatory system and it is a major cause of heart attack or brain strock. âĒ Normal person caries 150000 - 450000 platlets in 1cc blood. âĒ less platlets in blood is called thrombocytopenia.
- 24. Lymph âĒ Lymph is the fluid which squeezed from the blood capillaries and become the interstitial fluid. This interstitial fluid collected in the lymphatic vessels and again go to the larger vein to main circulation. âĒ Its composition is about about same as the plasma in the blood but it cantain the waistmaterial released by the cells. âĒ Lymph cantains certain cell mainly in the lymph nodes like T- lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes and many others. âĒ Its main fuction is to drain the fluid coming from the blood back to the blood vessels.
- 25. Lymph production âĒ Lymph helps in the immune system of the body. âĒ It also helps in the absorption of the fats in the intestine via small vessels called Lacteals.
- 26. Blood vs Lymph
- 27. THANKS