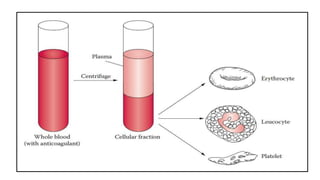
Blood analysis (Forensic Serology)
- 1. Analysis of Bl d Dr.Archana Mahakalkar Department of Forensic Biology Government Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur
- 5. Colorimetric Assays 1. Phenolphthalin Assay The phenolphthalin assay is also known as the Kastle-Meyer test. Oxidation©Creduction reaction as basis for presumptive assays for blood identification. AH2 = substrate. A = oxidized substrate. Phenolphthalein(1g) dissolved in acetic acid (100ml). Sodium perborate (1.4g) is dissolved in the solution Apply on to stain
- 6. 2. Leucomalachite Green reaction: The reagent is prepared by dissolving leucomalachite green (0.1g), sodium perborate (0.3g) in 65% glacial acetic acid. The reagent is applied to thestain. Intense green color indicates blood.
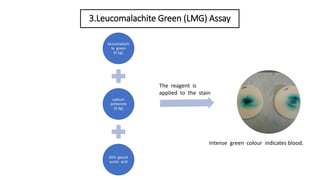
- 7. 3.Leucomalachite Green (LMG) Assay leucomalachi te green (0.1g), sodium perborate (0.3g) 65% glacial acetic acid The reagent is applied to the stain Intense green colour indicates blood.
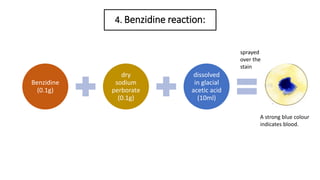
- 8. 4. Benzidine reaction: Benzidine (0.1g) dry sodium perborate (0.1g) dissolved in glacial acetic acid (10ml) A strong blue colour indicates blood. sprayed over the stain
- 9. 5. Luminol (3-aminophthalhydrazide) The oxidation products of Luminol have chemiluminescent properties. Oxidation of Luminol catalyzed by heme produces an intense light . The light emitted from a positive reaction can only be observed in a dark environment and this limits the applications of Luminol. Chemical reaction of Luminol
- 10. 6. Fluorescin When oxidized and catalyzed by heme, it demonstrates fluorescent properties. Usually, fluorescin-sprayed stains are exposed to light in the range of 425 to 485 nm using an alternate light source device. In a positive reaction, the oxidized fluorescin will emit an intense yellowish-green fluorescent light and therefore indicate the presence of a blood stain. Chemical structure of fluorescein.
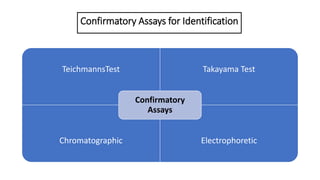
- 11. Confirmatory Assays for Identification TeichmannsTest Takayama Test Chromatographic Electrophoretic Confirmatory Assays
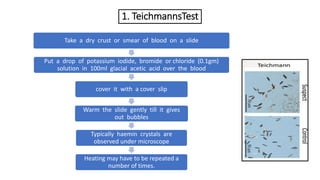
- 12. 1. TeichmannsTest Take a dry crust or smear of blood on a slide Put a drop of potassium iodide, bromide or chloride (0.1gm) solution in 100ml glacial acetic acid over the blood cover it with a cover slip Warm the slide gently till it gives out bubbles Typically haemin crystals are observed under microscope Heating may have to be repeated a number of times.
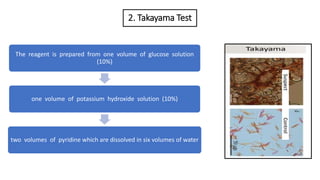
- 13. 2. Takayama Test The reagent is prepared from one volume of glucose solution (10%) one volume of potassium hydroxide solution (10%) two volumes of pyridine which are dissolved in six volumes of water
- 14. 3. Identification of Human Hemoglobin Protein Immunochromatographic assays for the identification of Hb in human blood. (a) In a sample well, Hb in a blood sample is mixed with a labeled anti-Hb Ab. (b) The Hb binds to the labeled anti-Hb Ab to form a labeled Ab©CHb complex. The complex diffuses toward the test zone. (c) At the test zone, the labeled Ab©CHb complex binds to an immobilized anti-Hb Ab to form a labeled Ab©CHb©CAb sandwich. (d) At the control zone, the labeled anti-Hb Ab binds to an immobilized antiglobulin and is captured. Ab and Hb represent the antibody and hemoglobin, respectively. (? Richard C. Li.)
- 15. 4. Human Glycophorin A protein Immunochromatographic assays for the identification of GPA in human blood. (a) In a sample well, GPA in a blood sample is mixed with a labeled anti-GPA Ab. (b) The GPA binds to the labeled anti-GPA Ab to form a labeled Ab©CGPA complex. (c) At the test zone, the labeled Ab©CGPA complex binds to an immobilized anti-GPA Ab to form a labeled Ab©CGPA©CAb sandwich. (d) At the control zone, the labeled anti-GPA Ab binds to an immobilized antiglobulin and is captured. Ab and GPA represent the antibody and GPA protein, respectively. (? Richard C. Li.)
- 17. Thank you