Blood typing-analysispdf
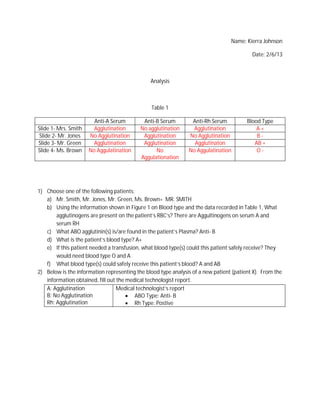
- 1. Name: Kierra Johnson Date: 2/6/13 Analysis Table 1 Anti-A Serum Anti-B Serum Anti-Rh Serum Blood Type şÝşÝߣ 1- Mrs. Smith Agglutination No agglutination Agglutination A+ şÝşÝߣ 2- Mr. Jones No Agglutination Agglutination No Agglutination B- şÝşÝߣ 3- Mr. Green Agglutination Agglutination Agglutinaton AB + şÝşÝߣ 4- Ms. Brown No Aggulatination No No Aggulatination O- Aggulationation 1) Choose one of the following patients: a) Mr. Smith, Mr. Jones, Mr. Green, Ms. Brown= MR. SMITH b) Using the information shown in Figure 1 on Blood type and the data recorded in Table 1, What agglutinogens are present on the patient’s RBC’s? There are Aggultinogens on serum A and serum RH c) What ABO agglutinin(s) is/are found in the patient’s Plasma? Anti- B d) What is the patient’s blood type? A+ e) If this patient needed a transfusion, what blood type(s) could this patient safely receive? They would need blood type O and A f) What blood type(s) could safely receive this patient’s blood? A and AB 2) Below is the information representing the blood type analysis of a new patient (patient X). From the information obtained, fill out the medical technologist report. A: Agglutination Medical technologist’s report B: No Agglutination ď‚· ABO Type: Anti- B Rh: Agglutination ď‚· Rh Type: Postive
- 2. 3) Compare and Contrast agglutinogens and agglutinins. In the diagram show at least 2 similarities and 2 differences. Agglutinogens Agglutinins Differences Similarities Differences Agglutinogens are found on the When the immune system Agglutinins are antibodies surface of erythrocytes. Any cause cross linking of cells or found in the Plasma. substance that, acting as an particles an agglutination antigen, stimulates the reaction occurs and the responsible antibody is an production of agglutinin. The agglutinin particulate antigen used in conducting agglutination tests. 4) Pretend you went with your class on a medical career field trip to a local hospital. One of the stops on the visit was to the hospital’s blood lab. The medical technologist at this stop gave a demonstration of how blood types are determined. Your job is to write a paragraph for the school newspaper on the visit to the blood lab, summarizing what you’ve learned about how ABO/Rh blood groups are determined. Write a paragraph and include the title. On my visit to the hopital’s blood lab, I learned how to determine ABO/Rh blood groups. They are determined by antigen/ antibody interactions. Antigens are the markers on your cells that determine your blood type. Antibodies are produced by the immune system. They attach to antigens and mark the antigen for destruction by the immune system. Red blood cells are mixed with a solution that contains antibodies (Anti- A and Anti- B) If a person has A on their cells, the anti- A will bind to the cells causing agglutination (clumping). Same thing when they have B on their cells. If they have type AB blood, both anti- A and anti- B will agglutinate their cells and if they have type O blood, neither of them will agglutinate their cells. 5) List at least 3 situations where blood typing could be used. a) Paternity Test b) DNA Analysis c) Blood Transfusions 6) Define Erythroblastosis Fetalis. Erythroblastosis Fetalis is a blood disorder in a fetus or newborn infant. In some infants, it can be life threatening. a) Describe the sequence of events that lead to this condition. HDN can develop when the mother and her unborn baby have different blood types (called, “incompatibility). The mother then produces antibodies that attack the developing baby’s red blood cells. b) What might be some benefits if the medical profession developed a shot or vaccination that could desensitize an Rh+ situation? Tranfusions or death could be avoided or not needed during birth if they had an advanced drug to prevent this disease from happening. 7) You are a type A eryhthorocyte placing an ad in the personals and you are seeking a compatible mate for a long lasting transfusion. Create an ad to be submitted to the newspaper.
- 3. Just a go-with-the-flow type A personality eryhthorocyte looking for a type O or A eryhthorocyte to spend all my life with flowing down capillaries just happily delivering oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from the body. 8) Another important diagnostic tool used by medical technologist is determining a patient’s blood cell count, for both red blood cells and white blood cells. When this procedure is performed, one technique used is to take multiple samples and calculate the average. This method of multiple sampling is a standard procedure in scientific and medical investigations. Discuss why this method is important in blood typing. This is how they know whether or not the person’s blood has the average or normal red blood cell and white blood cell count. If there is any abnormalities then they will know whether or not you may have a health condition before transfusions. If you have a low count in RBC’s this causes anameia due to iron deficiency. WBC’s show the bodies response to infection or possible Leukaemia. 9) Each year thousands of people contract blood borne diseases. What could be done in a clinical blood lab to minimize the risk of obtaining or spreading a blood borne disease? Always wear safety gear such as, mask, gloves, protective shoe covers, and protective full- body aprons. It is always important to disinfect/ sterilize equipment and wash hands before performing work and after perfomring work. Saftey precautions and protocol always need to be made/ followed to avoid any blood bourne diseases. 10) In a short paragraph, identify what you think may be the next important breakthrough, milestone or discovery in the study of blood and blood diseases and explain why. In a article I read, it explains that scientists have discovered certain rare blood types which can make individuals more or less vulnerable to HIV infection. People with Fabry disease—caused by a missing fat-metabolizing enzyme that can lead to eye, kidney and heart problems—who accumulate higher levels of Pk also have fewer body-wide infections. A team from University of Toronto to examine whether blood Pk levels could influence whether or not someone became infected with HIV. The group studied the blood of three groups of people: those with high levels of Pk, those with normal levels and those whose cells don’t express any Pk at all. They found that the cells of people who express high levels of Pk, a rare group representing about one in a million people, were resistant to HIV infection. Conversely, the cells of those who express no Pk at all, representing about five in a million people, were particularly susceptible to HIV infection. This research doesn’t mean that certain blood types doesn’t determine whether you will get HIV or not. However, this could suggest that individuals who are exposed to the virus can have more of an ability to fight against it.