boolean-algebra.pdf
- 1. Boolean algebra By P. THRIVENI, M.Tech Assistant professor
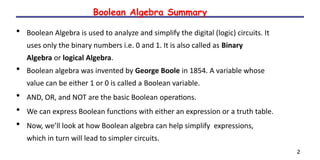
- 3. 2 Boolean Algebra Summary âĒ Boolean Algebra is used to analyze and simplify the digital (logic) circuits. It uses only the binary numbers i.e. 0 and 1. It is also called as Binary Algebra or logical Algebra. âĒ Boolean algebra was invented by George Boole in 1854. A variable whose value can be either 1 or 0 is called a Boolean variable. âĒ AND, OR, and NOT are the basic Boolean operations. âĒ We can express Boolean functions with either an expression or a truth table. âĒ Now, weâll look at how Boolean algebra can help simplify expressions, which in turn will lead to simpler circuits.
- 4. Rules in Boolean Algebra Following are the important rules used in Boolean algebra. 1. Variable used can have only two values. Binary 1 for HIGH and Binary 0 for LOW. 2. Complement of a variable is represented by an over bar (-). Thus, complement of variable B is represented as . Thus if B = 0 then = 1 and B = 1 then = 0. 3. OR ing of the variables is represented by a plus (+) sign between them. For example OR ing of A, B, C is represented as A + B + C. 4. Logical AND ing of the two or more variable is represented by writing a dot between them such as A.B.C. Sometime the dot may be omitted like ABC.
- 5. Boolean Algebra Summary âĒ Recall that the two binary values have different names: â True/False â On/Off â Yes/No â 1/0 âĒ We use 1 and 0 to denote the two values. âĒ The three basic logical operations are: â AND â OR â NOT âĒ AND is denoted by a dot (·). âĒ OR is denoted by a plus (+). âĒ NOT is denoted by an overbar ( ÂŊ ), a single quote mark (') after
- 6. Boolean Laws There are six types of Boolean Laws. Commutative law âĒ Any binary operation which satisfies the following expression is referred to as commutative operation. âĒ Commutative law states that changing the sequence of the variables does not have any effect on the output of a logic circuit.
- 7. Associative law âĒThis law states that the order in which the logic operations are performed is irrelevant as their effect is the same. Distributive law âĒDistributive law states the following condition. Boolean Laws
- 8. AND law âĒThese laws use the AND operation. Therefore they are called as AND laws. OR law âĒThese laws use the OR operation. Therefore they are called as OR laws. Boolean Laws
- 9. INVERSION law âĒThis law uses the NOT operation. The inversion law states that double inversion of a variable results in the original variable itself. Boolean Laws
- 10. Proofs A 0 A.0=0 0 0 0 1 0 0 AND law 1. A.0=0 A 1 A.1=A 0 1 0 1 1 1 2. A.1=A A A A.A=A 0 0 0 1 1 1 3. A.A=A A A A.A=0 0 1 0 1 0 0 4. A.A=0
- 11. Proofs A 0 A+0=A 0 0 0 1 0 1 OR law 1. A+0=A A 1 A+1=1 0 1 1 1 1 1 2. A+1=1 A A A+A=A 0 0 0 1 1 1 3. A+A=A A A A+A=1 0 1 1 1 0 1 4. A+A=1
- 12. Proofs Inversion law 1. A=A A A A=A 0 1 0 1 0 1
- 13. âĒLogic gates are the basic building blocks of any digital system. âĒ It is an electronic circuit having one or more than one input and only one output. âĒThe relationship between the input and the output is based on a certain logic. Based on this, logic gates are named as AND gate, OR gate, NOT gate etc. Logic gates AND Gate A circuit which performs an AND operation is shown in figure. It has n input (n >= 2) and one output.
- 14. AND gate Truth Table Logic diagram
- 15. OR Gate A circuit which performs an OR operation is shown in figure. It has n input (n >= 2) and one output. Logic diagram Truth Table
- 16. NOT Gate NOT gate is also known as Inverter. It has one input A and one output Y. Logic diagram Truth Table
- 17. NAND Gate A NOT-AND operation is known as NAND operation. It has n input (n >= 2) and one output. Logic diagram Truth Table
- 18. NOR Gate A NOT-OR operation is known as NOR operation. It has n input (n >= 2) and one output. Logic diagram Truth Table
- 19. XOR Gate XOR or Ex-OR gate is a special type of gate. It can be used in the half adder, full adder and subtractor. The exclusive-OR gate is abbreviated as EX-OR gate or sometime as X-OR gate. It has n input (n >= 2) and one output. Logic diagram Truth Table
- 20. XNOR Gate XNOR gate is a special type of gate. It can be used in the half adder, full adder and subtractor. The exclusive-NOR gate is abbreviated as EX-NOR gate or sometime as X-NOR gate. It has n input (n >= 2) and one output. Logic diagram Truth Table
- 21. De Morgan's Theorems De Morgan has suggested two theorems which are extremely useful in Boolean Algebra. The two theorems are discussed below. Theorem 1 âĒ The left hand side (LHS) of this theorem represents a NAND gate with inputs A and B, whereas the right hand side (RHS) of the theorem represents an OR gate with inverted inputs. âĒ This OR gate is called as Bubbled OR.
- 23. Table showing verification of the De Morgan's first theorem â
- 24. Theorem 2 âĒThe LHS of this theorem represents a NOR gate with inputs A and B, whereas the RHS represents an AND gate with inverted inputs. âĒThis AND gate is called as Bubbled AND.
- 26. Table showing verification of the De Morgan's second theorem â
- 27. âĒThis theorem states that the dual of the Boolean function is obtained by interchanging the logical AND operator with logical OR operator and zeros with ones. âĒFor every Boolean function, there will be a corresponding Dual function. Duality principle
- 28. Group1 Group2 x + 0 = x x.1 = x x + 1 = 1 x.0 = 0 x + x = x x.x = x x + xâ = 1 x.xâ = 0 x + y = y + x x.y = y.x x + y+zy+z = x+yx+y + z x.y.zy.z = x.yx.y.z x.y+zy+z = x.y + x.z x + y.zy.z = x+yx+y.x+z In each row, there are two Boolean equations and they are dual to each other. We can verify all these Boolean equations of Group1 and Group2 by using duality theorem. Duality principle
- 29. Consensus Theorem Theorem1. AB+ AâC + BC = AB + AâC Theorem2. (A+B). (Aâ+C).(B+C) =(A+B).( Aâ+C) âĒThe BC term is called the consensus term and is redundant. âĒThe consensus term is formed from a PAIR OF TERMS in which a variable (A) and its complement (Aâ) are present; âĒthe consensus term is formed by multiplying the two terms and leaving out the selected variable and its complement
- 30. Consensus Theorem1 Proof: AB+AâC+BC=AB+AâC+(A+Aâ)BC =AB+AâC+ABC+AâBC =AB(1+C)+AâC(1+B) = AB+ AâC
- 31. Minimization of Boolean functions By P. THRIVENI, M.Tech Assistant professor
- 32. Algebraic Manipulation (Minimization of Boolean function) âĒBoolean algebra is a useful tool for simplifying digital circuits. âĒWhy do it? Simpler can mean cheaper, smaller, faster. Example: Simplify F = xâyz + xâyzâ + xz. = xây(z + zâ) + xz (Z+Zâ=1) = xâyâĒ1 + xz = xây + xz
- 35. Example: Prove xâyâzâ + xâyzâ + xyzâ = xâzâ + yzâ Proof: xâyâzâ+ xâyzâ+ xyzâ = xâyâzâ + xâyzâ + xâyzâ + xyzâ = xâzâ(yâ+y) + yzâ(xâ+x) y+yâ=1, x+xâ=1 = xâzââĒ1 + yzââĒ1 = xâzâ + yzâ
- 36. Problem Minimize the following Boolean expression using Boolean identities â F(A,B,C)=AâēB+BCâē+BC+ABâēCâē Given F(A,B,C)=AâēB+BCâē+BC+ABâēCâē F(A,B,C)=AâēB+B(Câē+C)+ABâēCâē F(A,B,C)=AâB+B.1+ABâCâ = AâB+B+ABâCâ [B.1=B] = B(Aâ+1)+ABâCâ [Aâ+1=1] = B+ABâCâ [Apply distributive law A+BC=(A+B)(A+C)] = (B+Bâ)(B+ACâ) [B+Bâ=1] = B+ACâ
- 37. Problem Minimize the following Boolean expression using Boolean identities â F(A,B,C)=(A+B)(A+C) Given, F(A,B,C)=(A+B)(A+C) F(A,B,C)=A.A+A.C+B.A+B.C =A+AC+AB+BC [A.A=A] = A(1+C+B)+BC [1+Anything=1] = A+BC
- 39. âĒ Boolean algebra deals with binary variables and logic operation. A Boolean Function is described by an algebraic expression called Boolean expression which consists of binary variables, the constants 0 and 1, and the logic operation symbols. Consider the following example. Here the left side of the equation represents the output Y. So we can state equation no. 1 Boolean Expression â Function
- 40. âĒA truth table represents a table having all combinations of inputs and their corresponding result. âĒIt is possible to convert the switching equation into a truth table. For example, consider the following switching equation. âĒThe output will be high (1) if A = 1 or BC = 1 or both are 1. The truth table for this equation is shown by Table (a). The number of rows in the truth table is 2n where n is the number of input variables (n=3 for the given equation). Hence there are 23 = 8 possible input combination of inputs. Truth Table Formation
- 42. âĒIt is in the form of sum of three terms AB, AC, BC with each individual term is a product of two variables. Say A.B or A.C etc. Therefore such expressions are known as expression in SOP form. âĒThe sum and products in SOP form are not the actual additions or multiplications. In fact they are the OR and AND functions. âĒIn SOP form, 0 represents a bar and 1 represents an unbar. SOP form is represented by Given below is an example of SOP. Sum of Products (SOP) Form


































![Problem
Minimize the following Boolean expression using Boolean identities â
F(A,B,C)=AâēB+BCâē+BC+ABâēCâē
Given F(A,B,C)=AâēB+BCâē+BC+ABâēCâē
F(A,B,C)=AâēB+B(Câē+C)+ABâēCâē
F(A,B,C)=AâB+B.1+ABâCâ
= AâB+B+ABâCâ [B.1=B]
= B(Aâ+1)+ABâCâ [Aâ+1=1]
= B+ABâCâ [Apply distributive law A+BC=(A+B)(A+C)]
= (B+Bâ)(B+ACâ) [B+Bâ=1]
= B+ACâ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/boolean-algebra-230110163159-1813a68f/85/boolean-algebra-pdf-36-320.jpg)
![Problem
Minimize the following Boolean expression using Boolean identities â
F(A,B,C)=(A+B)(A+C)
Given, F(A,B,C)=(A+B)(A+C)
F(A,B,C)=A.A+A.C+B.A+B.C
=A+AC+AB+BC [A.A=A]
= A(1+C+B)+BC [1+Anything=1]
= A+BC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/boolean-algebra-230110163159-1813a68f/85/boolean-algebra-pdf-37-320.jpg)