Breech presentation, types and its management
- 1. Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first.
- 2. ŌĆó The lie is longitudinal with the sacrum as denominator
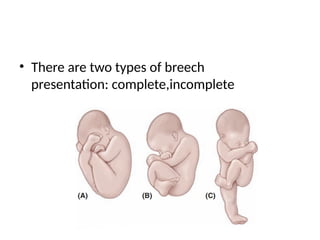
- 3. ŌĆó There are two types of breech presentation: complete,incomplete
- 4. Types of Breech ŌĆó Incomplete breech presentation, there is incomplete flexion with extension at 1 or 2 joint. FRANK BREECH KNEE PRESENTATION FOOTLING PRESENTATION
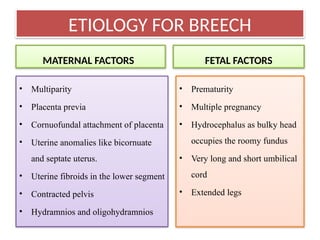
- 6. ETIOLOGY FOR BREECH MATERNAL FACTORS ŌĆó Multiparity ŌĆó Placenta previa ŌĆó Cornuofundal attachment of placenta ŌĆó Uterine anomalies like bicornuate and septate uterus. ŌĆó Uterine fibroids in the lower segment ŌĆó Contracted pelvis ŌĆó Hydramnios and oligohydramnios FETAL FACTORS ŌĆó Prematurity ŌĆó Multiple pregnancy ŌĆó Hydrocephalus as bulky head occupies the roomy fundus ŌĆó Very long and short umbilical cord ŌĆó Extended legs
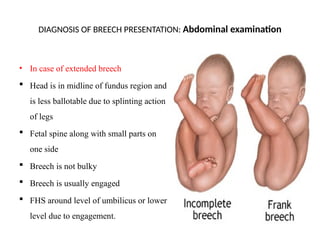
- 7. DIAGNOSIS OF BREECH PRESENTATION: Abdominal examination ŌĆó In case of complete breech ’é¦ Head on fundus region ’é¦ Fetal spine on one side ’é¦ Breech is bulky ’é¦ Breech is not engaged ’é¦ FHS above level of umbilicus
- 8. DIAGNOSIS OF BREECH PRESENTATION: Abdominal examination ŌĆó In case of extended breech ’é¦ Head is in midline of fundus region and is less ballotable due to splinting action of legs ’é¦ Fetal spine along with small parts on one side ’é¦ Breech is not bulky ’é¦ Breech is usually engaged ’é¦ FHS around level of umbilicus or lower level due to engagement.
- 9. DIAGNOSIS OF BREECH PRESENTATION: Vaginal examination ’é¦ Conical bag of membranes ’é¦ Presenting part is high up. ’é¦ Both ischial tuberosity, anus, sacrum, buttocks and feet are palpated-in complete breech. ’é¦ In extended breech,feets not palpated. ’é¦ In footling presentation, feets are presenting part.
- 10. DIAGNOSIS OF BREECH PRESENTATION: Ultrasonography ’é¦ Very useful method: ’é¦ Confirms the breech ’é¦ Type of breech ’é¦ To rule out any fetal anomalies and uterine anomalies. ’é¦ Fetal biometry, EFW ’é¦ Localization of placenta previa
- 11. ŌĆó Delivery of Buttocks ŌĆó Engagement : intertrochanteric diameter lies in the inlet. It can be either RSA or LSA ŌĆó Descent: Breech is very less efficient dilator than the head, so descent will be slow ŌĆó Internal rotation: ŌĆó More descent with lateral flexion. ŌĆó Birth of buttocks:- The anterior hip will come first at vulva by lateral flexion and posterior hip distends the perineum and then delivered. NORMAL LABOUR METHODS- BREECH
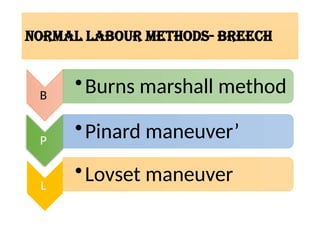
- 13. NORMAL LABOUR METHODS- BREECH B ŌĆóBurns marshall method P ŌĆóPinard maneuverŌĆÖ L ŌĆóLovset maneuver
- 14. NORMAL BREECH LABOUR METHODS The BurnsŌĆōMarshall method involves allowing the breech to 'hang' by its weight until the nape of the neck (or the 'hair-line') is visible. This is followed by holding both feet and the fetus on to the maternal abdomen to deliver the fetal head.
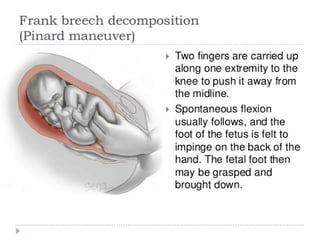
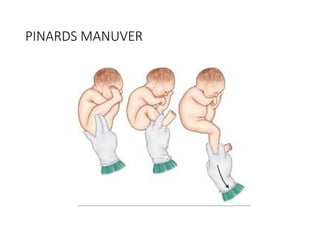
- 17. PINARDS MANUVER
- 18. LOVSET MANUVER
- 19. Antenatal Management ŌĆó Antenatal management involves the following: ŌĆó Screening high risk factors ŌĆó ECV in suitable cases ŌĆó Decision about mode of delivery
- 20. MODE OF DELIVERY ŌĆó Elective caesarean delivery: ŌĆó All complicated breech like pre eclampsia, Contracted pelvis, placenta previa ŌĆó Large baby more than 3500 gm/ BPD>9.5cm ŌĆó Previous C.S ŌĆó Non availability of skilled obstetrician ŌĆó IUGR
- 21. MODE OF DELIVERY Vaginal delivery: