Brillouin zone and wigner seitz cell
- 1. Brillouin Zone and Wigner- Seitz Cell NAME ŌĆō VINOD KUMAR ROLL NO: 2662
- 2. Introduction: Wigner-Seitz Cell named after Eugene Wigner and Frederick Seitz is a type of voronoi cell used in the study of crystalline material in solid state physics. The concept of brillouin zone was developed by French physicist Leon Brillouin
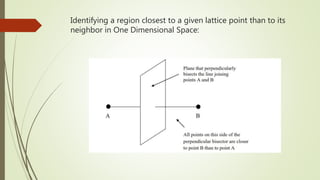
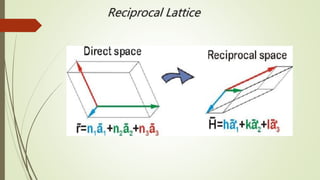
- 3. Wigner-Seitz cell The WignerŌĆōSeitz cell around a lattice point is defined as the locus of points in space that are closer to that lattice point than to any of the other lattice points. It can be shown mathematically that a WignerŌĆōSeitz cell is a primitive cell spanning the entire direct space without leaving any gaps or holes. The WignerŌĆōSeitz cell in the reciprocal space is known as the first Brillouin zone. It is made by drawing planes normal to the segments joining nearest lattice points to a particular lattice point, through the midpoints of such segments.
- 4. Identifying a region closest to a given lattice point than to its neighbor in One Dimensional Space:
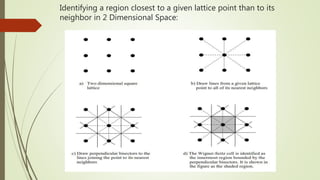
- 5. Identifying a region closest to a given lattice point than to its neighbor in 2 Dimensional Space:
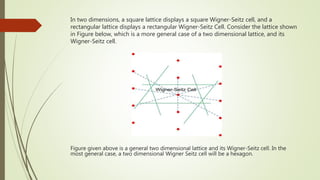
- 6. In two dimensions, a square lattice displays a square Wigner-Seitz cell, and a rectangular lattice displays a rectangular Wigner-Seitz Cell. Consider the lattice shown in Figure below, which is a more general case of a two dimensional lattice, and its Wigner-Seitz cell. Figure given above is a general two dimensional lattice and its Wigner-Seitz cell. In the most general case, a two dimensional Wigner Seitz cell will be a hexagon.
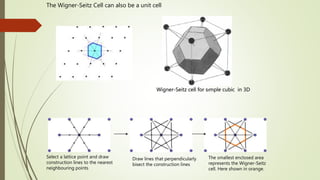
- 7. The Wigner-Seitz Cell can also be a unit cell Wigner-Seitz cell for s─▒mple cubic in 3D Select a lattice point and draw construction lines to the nearest neighbouring points Draw lines that perpendicularly bisect the construction lines The smallest enclosed area represents the Wigner-Seitz cell. Here shown in orange.
- 8. Brillouin zone A Brillouin Zone is defined as a Wigner-Seitz primitive cell in the reciprocal lattice. What is primitive cell ? The primitive cell is defined as unit cell which contains lattice points at corner only
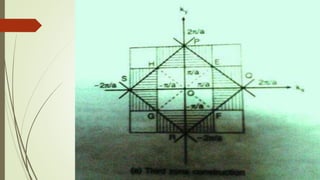
- 10. Construction of brillouin zones ’é┤ The brillouin zones are constructed from the planes which are the perpendicular or bisectors of all reciprocal lattice vectors ’é┤ The first zones is the smallest volume about the origin enclosed by these planes ’é┤ The second zone is the volume between the first zone and next set of planes
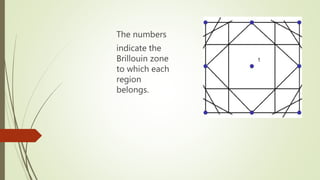
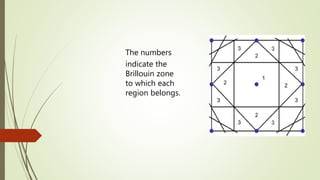
- 13. The numbers indicate the Brillouin zone to which each region belongs.
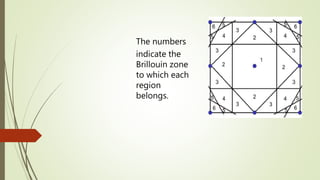
- 14. The numbers indicate the Brillouin zone to which each region belongs.
- 15. The numbers indicate the Brillouin zone to which each region belongs.
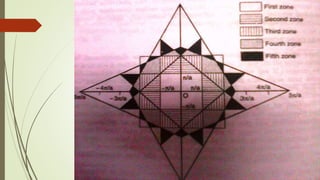
- 16. Identification of the first and higher order Brillouin Zones for a two dimensional from above figures 1. Only the first Brillouin Zone is identified; in 2. First, second and third Brillouin zones are identified; and in 3. First second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth Brillouin zones have been identified. All the zones identified are only within the context of the figure drawn, i.e. there are other regions which will correspond to the fourth, fifth, and sixth Brillouin zones, which do not show up in the region shown above.
- 17. Thank You