Brochiectasis
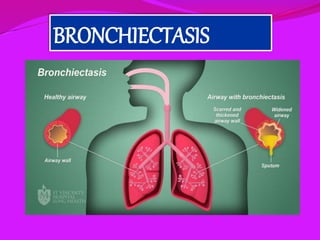
- 2. Bronchiectasis is defined as a permanent dilation of the bronchi. It seems to be a consequence of previous lung diseases, especially lung infections that were not treated sufficiently. Clinically, the disease manifests as recurrent episodes of respiratory tract infections together with an enduring cough and continuous production of sputum. The treatment of bronchiectasis remains a challenge due to the multiple causes and facts of the disease. pharmacological therapy is aimed at the reduction of microbial invasion with antibiotics, Effective prevention measures such as smoking cessation and vaccines may prevent disease exacerbations. introduction
- 4. 2) Bronchiectasis is a chronic, irreversible dilation of the bronchi and bronchioles OR Bronchiectasis is characterized by permanent, abnormal dilation of one or more large bronchi 3) Bronchiectasis is a condition anatomically defined by chronic, irreversible dilation and distortion of the bronchi caused by inflammatory destruction of the muscular and elastic components the bronchial walls. 4) It connection with inflammation of the bronchi , particularly when this leads to weakness of the walls with the accumulation of secretion. SIR WILLIAM OSLER CONT :
- 5. NORMAL BRONCHUS TO BRONCHIECTASIS
- 8. CONT:
- 9. CONT:
- 10. CONT:
- 11. CONT:
- 13. CONT:
- 14. PATHOLOGY
- 15. CLINICAL PICTURE
- 16. CONT :
- 17. CONT :
- 18. CONT :
- 20. VIEW OF LEFT LUNG BRONCHIECTSIS VIEW OF BRONCHOSCOPY VIEW OF CT SCAN VIEW OF SPUTUM CULTURE-GRAM NEGATIVE STAIN
- 21. TREATMENT GOAL: 1)eliminate cause 2)improve tracheo bronchial clearance 3)control infection 4)reverse airflow obstruction TREATMENT
- 22. 1) ANTIBIOTICS-Initially during the acute phase amoxicillin,TMP or Levofloxacin should be Started And later proper antibiotic should be chosen accordingly to the sputum culture and Gramâs stain. When pseudomonas is the organism oral Quinolone or parentral therapy with aminoglycosides , carbapenam or third generation cephalosporins should be given. 2) AEROSOLIZED ANTIBIOTICS-It is beneficial in treating Pseudomonas infection, Currently the inhaled Tobramycin is most widely used. Gentamycin and Colistin have also been used . 3) BROCHIAL HYGIENE- 1.postural drainage with percussion and vibration helps in effective clearance. 2.devices like flutter device,intrapulmonic percussive ventilation device and incentive spirometry are available. 3.proper mechanical and devices with proper positioning of the patient can help the patients with copious secretions MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
- 23. 4)USE OF MUCOLYTICS can help thinning out the thick mucous secretion.Use of recombinent DNAese which help in the destruction of the DNA released by the neutrophiles has shown improvement in the PF in case of CF. 5)BRONCHODILATORS help in the obstruction and clearance of the bronchus.Use of nebulization concentrated with 7%NACL have shown beneficial in CF-related bronchiectasis. 6)ANTI-INFLAMMATORY THERAPY- reduce the inflammation caused by the organisms and subsequently reduce the tissue damage. EX: inhaled corticosteroids,leucotriene inhibitors and NSAID can be given. CONT:
- 24. POSITIONAL DRAINAGE AND PHYSIOTHERAPY
- 31. Nursing mangement depends upon the stages of bronchiectasis.The goal of nursing management is to minimize the complication and preserve the health of the child. 1)Assess the general condition ,vitals, respiratory status and ABG analysis. 2)Provide comfortable position ,warm and humid environment and propped up position with extra pillows or by providing special bed 3)Administration of oxygen therapy to relieve dyspnea 4)Make airway clearance by suction or removal of secretions by steam inhalation and physiotherapy 5)Provide extra fluid intake 6)Maintain calm,airy,warm and humid environment 7)Well balanced diet to provide extra calories. 8)Assist the chid in breathing exercise and postural drainage 9)Elevate anxiety by providing toys according to age 10)Educate parents regarding disease process,treatment and care NURSING MANAGEMENT
- 32. NURSING DIAGNOSIS 1)Impaired gas exchange related to ventilation perfusion inequality as evidenced by decreased level of spo2 GOAL-Improve in gas exchange. NURSING INTERVENTION 1.Administer bronchodilators as prescribed.(inhalation is the preferred route). 2.Instruct and encourage patient in diaphragmatic breathing and effective coughing. 3.Administer antibiotics as prescribed. 4. Educate regarding types of indoor and outdoor air pollution.
- 33. 2)Ineffective airway clearance related to incresed mucus production , ineffective cough , bronchopulmonary infection, and other complications. GOAL-Achievement of airway clearance. NURSING INTERVENTION 1)Adequately hydrate the patient. 2)Use of diaphragmatic breathing and coughing techniques. 3)Assist in administering nebulizer. 4)Avoid bronchial irritants such as cigarette smoke, aerosal and fumes. 5)Administer antibiotics as prescribed. CONT:
- 34. COMPLICATIONOF BRONCHIECTASIS 1)Bronchopneumonia 2)Cerebral abscess due to septic purulent emboli may travel from lungs into the arteries to the brain cause cerebral abcess. 3)Pneumonia 4)Hemoptysis 5)Atelectasis 6)Pulmonary hypertension 7)Empyema 8)Septicemia 9)Recurrent pleurisy 10)Respiratory failure