Bsc Civil Engineering course CE200_Pointing
- 1. 1 POINTING
- 2. 2 POINTING The term pointing is applied to the finishing of mortar joints in masonry. In exposed masonry, joints are considered to be weakest and most vulnerable spots from which rain water or dampness can enter. Pointing consists of raking the joints to a depth of 10 to 20 mm and filling it with better quality of mortar in desired shape. Pointing is completed with the following mortar mixes: Lime mortar: 1:2 mix Cement mortar: 1:3 mix
- 3. 3 New work: All the joints are raked down to a depth of 20 mm while the mortar in the joint is still soft. The surface of the joints are then cleaned and thoroughly wetted. Old work: All loose pointing and superfluous mortar on the surface and in the joints are removed. The joints and surface are cleaned and then thoroughly wetted. POINTING Preparation of surface
- 4. 4 ’üČ Flush pointing ’üČ Recessed pointing ’üČ Rubbed, keyed or grooved pointing ’üČ Beaded pointing ’üČ Struck pointing ’üČ Tuck pointing ’üČ V pointing ’üČ Weathered pointing Types of pointing POINTING
- 5. 5 This type of pointing is formed by pressing mortar in the raked joint and by finishing off flush with the edges of masonry units. The edges are neatly trimmed with trowel and straight edge. POINTING Flush pointing
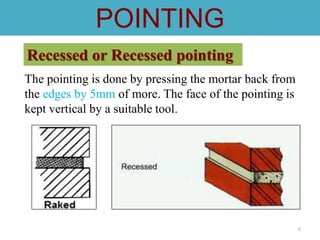
- 6. 6 The pointing is done by pressing the mortar back from the edges by 5mm of more. The face of the pointing is kept vertical by a suitable tool. POINTING Recessed or Recessed pointing
- 7. 7 This is a modification of flush pointing by forming a groove at its mid height, by a pointing tool. POINTING Rubbed, keyed or grooved pointing This is special type of pointing formed by steel or ironed with a concave edge. It gives good appearance, but is liable to damage easily. Beaded pointing
- 8. 8 This is a modification of flush pointing in which the face of the pointing is kept inclined, with its upper edge pressed inside the face by 10mm. This pointing drains water easily POINTING Struck or Weathered pointing
- 9. 9 It is formed by first pressing the mortar in the raked joint and finishing flush with the face while the pressed mortar is green. Groove having 5mm width and 3mm depth is cut in the centre of the groove. This groove is then filled in or tucked in with white cement putty, kept projecting beyond the face of the joint by 3mm. POINTING Tuck pointing
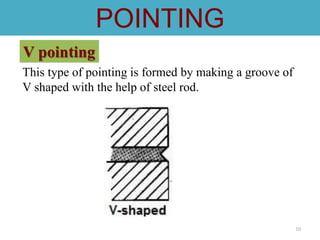
- 10. 10 This type of pointing is formed by making a groove of V shaped with the help of steel rod. POINTING V pointing