Building Airtightness-
- 2. ïĄ Overview ïĄ Terminologies. ïĄ Benefits of AirTight Buildings ïĄ Airtightness consequences. ïĄ Improving Airtightness ïĄ Air tightness test.
- 3. ïĄ Controlling air leakage is an important factor effecting: ï§ Building's energy efficiency. ï§ Occupants comfort. ïĄ Uncontrolled Infiltration of air could have drawbacks such as ï§ Increasing energy consumption. ï§ Health and safety of the buildingâs occupants. ï§ Accelerate deterioration of building materials. ⊠Such as concrete corrosion, mold, wet insulationâĶetc.
- 4. ïĄ Airtightness Resistance of infiltration/exfiltration of conditioned air through gaps, cracks, openings in the building envelop. ïĄ Causes of air leaks ï§ Pressures difference across the building envelope. ï§ Temperature difference across the building envelope.
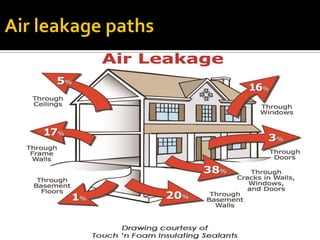
- 5. ïĄ Air Leakage Air leakage refers to the unplanned, unpredictable and unintentional airflow in the buildings (Infiltration) or out of the buildings (exfiltration) through buildingâs envelope. ïĄ Building Envelope The building envelope includes all the building components that separate the indoors from the outdoors. It includes o Foundation o Roof o Windows o Exterior walls o doors.
- 6. ïĄ Infiltration is the movement of air through leaks, cracks, or other adventitious openings INTO the building. Exfiltration is the movement of air through leaks, cracks, or other adventitious openings OUTSIDE the building. ïĄ Wind Washing Air movement that occurs due to wind entering a building envelop and passing through the thermal insulation and significantly impacting the thermal and moisture performance of those assemblies.
- 7. ïĄ Stack Effect Stack effect is a temperature-driven phenomenon, which is especially noticeable in cold weather, when warmer indoor air, which is lighter than the colder outdoor air, tends to rise in the building. It is influenced by: ⊠Temperature differential between indoors and outdoors. ⊠Size and location of the opening in the building enclosure.
- 9. ïĄ Air-tight buildings waste less energy, and cause less CO2 ïĄ Enables right-sizing of HVAC system. ïĄ Reduced Energy Costs. ïĄ Vital to achieving âpassiveâ builds ïĄ Reduced Interstitial Condensation ïĄ More Comfort for Occupants. ïĄ Opportunity for Owners to give their buildings an advantage.
- 13. ïĄ Design a tight building. ï§ Material type. ï§ Building orientation. ï§ Opening sizes. ï§ Install airtight layer. ï§ Pressurization. ïĄ Construct a tight building. ï§ Pipe and duct penetrations. ï§ Openingâs sealant. ï§ Wallâs joints. ï§ Use sealant for openings and penetrations.
- 14. AirtightnessTest ïĄ Smoke pencil ïĄ Theatrical fog ïĄ Infrared thermography
- 15. AirtightnessTest
- 16. Identification of leakage pathways using theatrical fog
- 17. Infrared thermography Exterior infrared thermography is conducted early morning or late evening when inside and outside temperature differences are greatest.
- 18. Discussion
- 19. ïĄ Passive House Is the house which is built to be extremely energy efficient, and has a comfortable interior climate maintained without a traditional heating system - or active cooling.
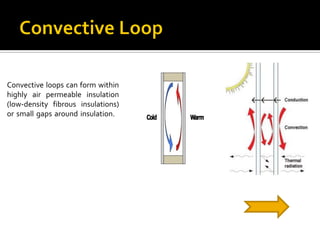
- 20. Convective loops can form within highly air permeable insulation (low-density fibrous insulations) or small gaps around insulation.