Burns.pptx it's management is absolutely
- 1. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 1 BURNS ZERA COLLEGE / HARVEST UNIVERSITY
- 2. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 2 OUTLINE ŌĆó Definion ŌĆó Types ŌĆó Anatomy ŌĆó Classification ŌĆó Pathophysiology ŌĆó Assessment ŌĆó Management ŌĆó Complications
- 3. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 3 Definition & Types ŌĆó Definition ŌĆó A burn is a thermal injury caused by biological, chemical, electrical and physical agents with local and systemic effects ŌĆó Etiology ŌĆó Thermal injury ŌĆó Chemical burns ŌĆó Cold injury ŌĆó Ionising radiation ŌĆó Sun burns
- 4. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 4 Anatomy Skin layers
- 5. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 5 Classification ŌĆó Superficial (first degree) ŌĆó Partial thickness (second degree) ŌĆó 1) Superficial partial ŌĆó 2) Deep partial ŌĆó Full thickness (third degree)
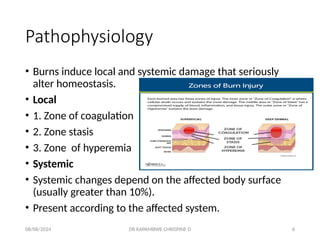
- 6. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 6 Pathophysiology ŌĆó Burns induce local and systemic damage that seriously alter homeostasis. ŌĆó Local ŌĆó 1. Zone of coagulation ŌĆó 2. Zone stasis ŌĆó 3. Zone of hyperemia ŌĆó Systemic ŌĆó Systemic changes depend on the affected body surface (usually greater than 10%). ŌĆó Present according to the affected system.
- 7. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 7 Assesment ŌĆó History ŌĆó Causative agent, duration, intervention and circumstance ŌĆó Examination ŌĆó TBSA estimation ŌĆó 1) Wallace rule ŌĆó 2) Rule of palms ŌĆó 3) Lund and browder chart
- 8. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 8 TBSA ESTIMATION
- 9. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 9
- 10. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 10 MANAGEMENT 1 Burn management is conducted by members of a multidisciplinary burn team which include medical, surgical, intensive care, nursing, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, diatetics, social work, psychiatry, , speech therapy, . Serious burn requiring hospitalization ’ü▒Greater than 15% burns in an adult ’ü▒Greater than 10% burns in a child ’ü▒Any burn in the very young, the elderly or the infirm ’ü▒Any full thickness burn ’ü▒Burns of special regions: face, hands, feet, perineum ’ü▒Circumferential burns ’ü▒Inhalation injury - Associated trauma or significant pre-burn illness: e.g. diabetes
- 11. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 11 Management 2 ŌĆó 1) First aid ŌĆó Stop the burning process ŌĆó Cool the area with tap water
- 12. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 12 Management cont... ŌĆó 2)Definitive ŌĆó Admit the patient. ŌĆó Do ABCDE ŌĆó Determine percentage, degree and type of burn ŌĆó IV access and early fluid replacement. ŌĆó Investigations ŌĆó Medication ŌĆó Other care
- 13. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 13 Management cont... ŌĆó Fluid replacements ŌĆó a) Barclay & Muir formula or Leads formula: Body wt. x TBSA%/2 = Xmls ŌĆó b) Parkland formula: Body wt x TBSA% x (1-4mls) = X mls
- 14. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 14 Parkland formula: ŌĆó Body wt x TBSA% x (1-4mls) = X mls ŌĆó -1st give half of Xmls in the 1st 8hrs from time of burns event ŌĆó -2nd give next half of Xmls in the next 16hrs ŌĆó The fluids used are Crystalloids, N-saline, RingerŌĆÖs lactate or HartmannŌĆÖs ŌĆó solution ŌĆó ŌĆó TBSA>15%: blood transfusion after 24 hours (pediatrics) ŌĆó ŌĆó TBSA>20%: blood transfusion (adults)
- 15. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 15 Management cont... ŌĆó Investigations ŌĆó Full Blood Count and Differential count. ŌĆó Wound swab for Microscopy Culture and Sensitivity ŌĆó Biochemistry ŌĆó ESR
- 16. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 16 Management cont... ŌĆó Medications ŌĆó Tetanus toxoid 0.5mls IM-single dose ŌĆó Topical Antibacterial agents - Silver Sulphadiazine,Povidone cream or Chloherxidine cream for those allergic to sulfur containing medication. ŌĆó Antibiotics if burns are infected depending on the sensivity tests of the centre. ŌĆó Haematinics to boost blood levels. ŌĆó ŌĆó Analgesia ŌĆó Others care
- 17. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 17 Complications ŌĆó 1. Early ŌĆó Airway obstruction ŌĆó Hypovolaemia ŌĆó 2. Intermediate ŌĆó Wound infection ŌĆó Septicemia ŌĆó Amputation ŌĆó 3. Late ŌĆó Contractures ŌĆó Hypertrophic scar or keloids
- 18. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 18 ŌĆó Marjolins ulcers (malignant) ŌĆó Nerve compression ŌĆó Psychological effects- cosmetic effect
- 19. 08/08/2024 DR KAPAMBWE CHRISPINE D 19 ASANTENI SAANA