Business Intelligence Presentation 1 (15th March'16)
- 2. Agenda ŌĆó What is business intelligence (BI)? ŌĆō Values, capabilities, potential ŌĆó BI evolution and trend -Chronological hierarchy, history, trend ŌĆó Why BI? -Benefits, Necessities, Application areas ŌĆó BI Technical Overview -Process, Components, servers ŌĆó BI process and system ŌĆō Components, technologies, and applications ŌĆó BI tools, products, industry, and market 2
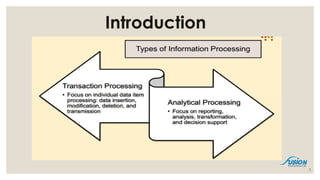
- 4. What is Business Intelligence? ’ü▒ Business Intelligence is an umbrella term for a set of - methods, - processes, - technologies, and - tools that help us to convert data into information, information into knowledge and knowledge into plans that guide the organizations for its very betterment, traditionally known as Decision Support System (DSS). 4
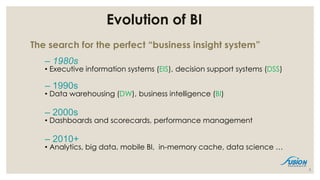
- 5. Evolution of BI The search for the perfect ŌĆ£business insight systemŌĆØ ŌĆō 1980s ŌĆó Executive information systems (EIS), decision support systems (DSS) ŌĆō 1990s ŌĆó Data warehousing (DW), business intelligence (BI) ŌĆō 2000s ŌĆó Dashboards and scorecards, performance management ŌĆō 2010+ ŌĆó Analytics, big data, mobile BI, in-memory cache, data science ŌĆ” 5
- 6. Why BI? BI is for answering following business related questions technically- 6 ŌĆó What happened? ŌĆó Why did it happen? ŌĆó What is happening? ŌĆó What will happen? ŌĆó What do I want to happen? Past Present Future
- 7. Benefits of Business Intelligence ŌĆó Improve Management Processes ŌĆō planning, controlling, measuring and/or changing results in increased revenues and reduced costs. ŌĆó Improve Operational Processes ŌĆō fraud detection, order processing, purchasing.. ŌĆó Better Adjustment settings ŌĆō Competitor analysis, adjustments settings to changing trends. ŌĆó Predict The Future ŌĆō Predictive analysis, Forecasting. 7
- 8. BI Application Areas BI can be applied in all ŌĆ£businessesŌĆØ both private and public sector ŌĆō Private ŌĆó Retail, manufacture, real-estate, sports, media, publication, etc. ŌĆō Public (non-profit) ŌĆó Education, government, healthcare, association, etc. 8
- 9. Sample BI Application Areas ŌĆó Business management 1. Strategic planning 2. Benchmarking ŌĆó IT management 1. Web analytics 2. Security management ŌĆó Logistics 1. Supplier & vendor management 2. Shipping and inventory control ŌĆó City planning 1. Traffic management 2. Urban Analytics ŌĆó Education 1. Learning analytics 2. Institutional effectiveness ŌĆó Internet and web 1. Social analytics 2. Sports and games analytics 9
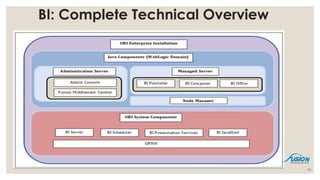
- 10. BI: Complete Technical Overview 10
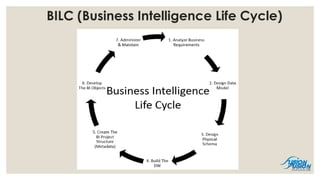
- 11. 11 BILC (Business Intelligence Life Cycle)
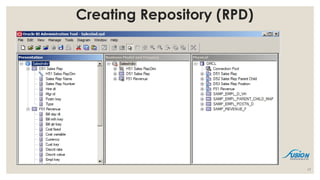
- 12. BILC (Business Intelligence Life Cycle) ŌŚ” Analyze Business Requirements - reviewing business requirements to determine the types of analysis user need to perform. ŌŚ” Design Data Model - Based on the business requirements, design the logical data model, which shows the information that users want to analyze and the relationships that exists within the data. ŌŚ” Design the Physical Schema - Using the data model design physical schema (creating dimension and fact table hence star schema) which defines the content and structure of the data warehouse. ŌŚ” Build the Data Warehouse - Build the data warehouse according to the schema design and load data into the warehouse (Developing RPD with 3 layers accordingly- Physical, Logical/BMM, Presentation layers) from source systems through ETL. ŌŚ” Create the Project Structure (Metadata) - Create the metadata and begin to connect and map the metadata to table in the data warehouse e.g. ŌŚ” Develop The BI Objects - Develop object, like reports, scorecards and dashboard. ŌŚ” Administer and Maintain the Project - Administer and maintain the project as it undergoes continued development and changes, monitor performance and make adjustments to improve it, manage security, and perform other ongoing administrative tasks. 12
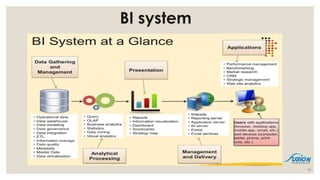
- 13. BI system 13
- 14. Data Management ŌŚ” A special database system called Data Warehouse or Data Mart (a subset of Data Warehouse) is often used to store enterprise data ŌĆō The purpose of a data warehouse is to organize lots of stable data for ease of analysis and retrieval. ŌŚ” Large databases that aggregate data collected from multiple sources ŌŚ” Enterprise level data are coming from multiple different sources, but finally combined into Data Warehouse ŌĆō Operational databases ŌĆō Spreadsheets ŌĆō Text, CSV ŌĆō PDF, Paper 14
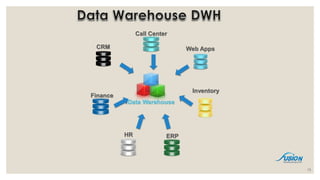
- 15. Data Warehouse CRM ERPHR Call Center Web Apps Finance Inventory 15
- 16. 16
- 18. BI - Analysis Tools ŌĆó Basic querying and reporting - ŌĆ£Tell me what happened.ŌĆØ ŌĆō Structured and fixed format reports Based on simple and direct queries ŌĆō Usually involves simple descriptive analysis and transformation of data, such as calculating, sorting, filtering, grouping, and formatting ŌĆó Ad hoc query and reporting - ŌĆ£Tell me what happened when they need.ŌĆØ ŌĆō Similar to operational reporting but on a need basis ŌĆó Business analysis(OLAP) - ŌĆ£Tell me what happened with why.ŌĆØ ŌĆō A multi-dimensional analysis and reporting application for aggregated data ŌĆō Great for discovering details from large quantities of data ŌĆō Business analytics (BA) is the practice of iterative, methodical exploration of an organizationŌĆÖs data with emphasis on statistical analysis. ŌĆó Data mining - ŌĆ£Tell me what might happenŌĆØ or ŌĆ£Tell me something interesting.ŌĆØ ŌĆō Data mining techniques are a blend of statistics and mathematics, and artificial intelligence and machine-learning. 18
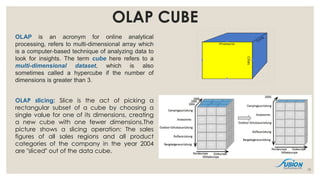
- 19. OLAP CUBE OLAP is an acronym for online analytical processing, refers to multi-dimensional array which is a computer-based technique of analyzing data to look for insights. The term cube here refers to a multi-dimensional dataset, which is also sometimes called a hypercube if the number of dimensions is greater than 3. OLAP slicing: Slice is the act of picking a rectangular subset of a cube by choosing a single value for one of its dimensions, creating a new cube with one fewer dimensions.The picture shows a slicing operation: The sales figures of all sales regions and all product categories of the company in the year 2004 are "sliced" out of the data cube. 19
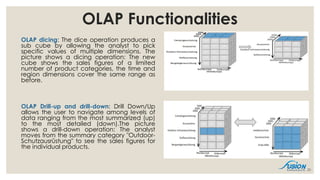
- 20. OLAP Functionalities OLAP dicing: The dice operation produces a sub cube by allowing the analyst to pick specific values of multiple dimensions. The picture shows a dicing operation: The new cube shows the sales figures of a limited number of product categories, the time and region dimensions cover the same range as before. OLAP Drill-up and drill-down: Drill Down/Up allows the user to navigate among levels of data ranging from the most summarized (up) to the most detailed (down).The picture shows a drill-down operation: The analyst moves from the summary category "Outdoor- Schutzausr├╝stung" to see the sales figures for the individual products. 20
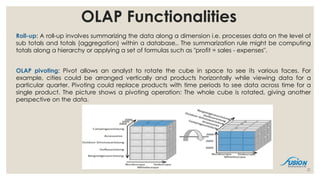
- 21. Roll-up: A roll-up involves summarizing the data along a dimension i.e. processes data on the level of sub totals and totals (aggregation) within a database,. The summarization rule might be computing totals along a hierarchy or applying a set of formulas such as "profit = sales - expenses". OLAP pivoting: Pivot allows an analyst to rotate the cube in space to see its various faces. For example, cities could be arranged vertically and products horizontally while viewing data for a particular quarter. Pivoting could replace products with time periods to see data across time for a single product. The picture shows a pivoting operation: The whole cube is rotated, giving another perspective on the data. 21 OLAP Functionalities
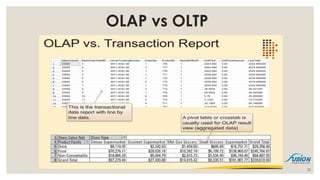
- 22. OLAP vs OLTP 22
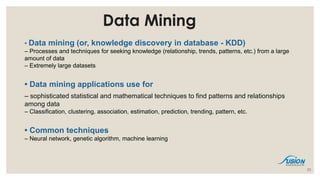
- 23. Data Mining ŌĆó Data mining (or, knowledge discovery in database - KDD) ŌĆō Processes and techniques for seeking knowledge (relationship, trends, patterns, etc.) from a large amount of data ŌĆō Extremely large datasets ŌĆó Data mining applications use for ŌĆō sophisticated statistical and mathematical techniques to find patterns and relationships among data ŌĆō Classification, clustering, association, estimation, prediction, trending, pattern, etc. ŌĆó Common techniques ŌĆō Neural network, genetic algorithm, machine learning 23
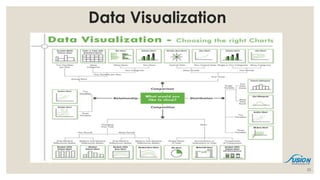
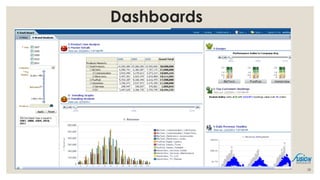
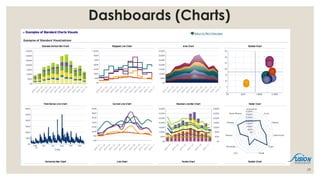
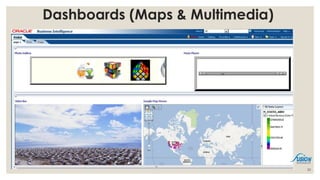
- 24. Presentation ŌĆó Reports ŌĆō A report is the presentation of data transformed into formatted and organized information according to specific business requirements. ŌĆō Based on simple and direct queries: usually involves simple analysis and transformation of data (sorting, calculating, filtering, filtering, grouping, formatting, etc.) ŌĆō Reports can be static or interactive. But most reports are ready for printing. ŌĆó Visualization ŌĆō An essential way for human understanding and sense making ŌĆō In the forms of table, charts, diagrams ŌĆō Visualization can also be part of the analysis process (visual analytics) ŌĆó Dashboard ŌĆō A dashboard is a visual display of the most important information needed to achieve one or more objectives; consolidated and arranged on a single screen so the information can be monitored at a glance. ŌĆōAbility to identify trends and Gain total visibility of all systems instantly at one place 24
- 27. Dashboards 27
- 28. 28 Dashboards
- 30. 30 Dashboards (Maps & Multimedia)
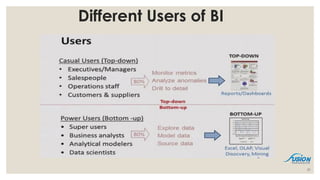
- 31. Different Users of BI 31
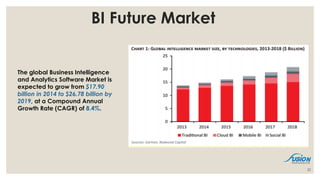
- 32. BI Future Market 32 The global Business Intelligence and Analytics Software Market is expected to grow from $17.90 billion in 2014 to $26.78 billion by 2019, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.4%.