Business Optimization via Causal Inference
- 1. Business Optimization via Causal Inference HayaData 2021 Outcome Action
- 2. Why Causal Inference? ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 2
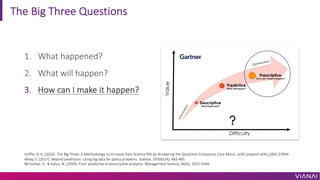
- 3. The Big Three Questions 1. What happened? 2. What will happen? 3. How can I make it happen? Griffin, D. K. (2020). The Big Three: A Methodology to Increase Data Science ROI by Answering the Questions Companies Care About. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.07069. Athey, S. (2017). Beyond prediction: Using big data for policy problems. Science, 355(6324), 483-485. Bertsimas, D., & Kallus, N. (2020). From predictive to prescriptive analytics. Management Science, 66(3), 1025-1044.
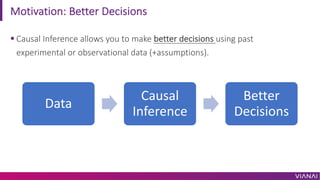
- 4. Motivation: Better Decisions ¡ì Causal Inference allows you to make better decisions using past experimental or observational data (+assumptions). Data Causal Inference Better Decisions
- 5. Nobel Prize in Economics, October 2021 ¡ì"for their methodological contributions to the analysis of causal relationships." ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 5 https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/economic-sciences/2021/summary/
- 6. https://www.linkedin.com/company/vianai/jobs/ ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 6
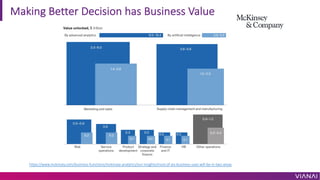
- 7. Making Better Decision has Business Value https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-analytics/our-insights/most-of-ais-business-uses-will-be-in-two-areas
- 8. ¡°Industry experts agree, the importance of causal data science for data-augmented business decisions will only grow in the future¡° ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 9 https://causalscience.org/blog/causal-data-science-in-large-us-firms
- 9. Causal Inference in the Industry ¡°We analyze marketing campaigns and the impact of app preloads using a fourth type of observational study format." ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 10 "Causal Inference helps us provide a better user experience for customers on the Uber platform" ¡°We rely on quasi-experiments and Causal Inference methods, especially to measure new marketing and advertising ideas."
- 10. Why not just use Prediction? Predicting churn and preventing churn are not the same thing ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 11 C A L L E V E R Y O N E P>80% Predicting Churn Then Target
- 11. Lost Causes Prescriptive is Better ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 12 Sure Things Persuadables Sleeping Dogs C A L L D O N ¡¯ T C A L L D O N ¡¯ T C A L L D O N ¡¯ T C A L L Preventing Churn Understanding the difference worth 300% better churn prevention "Retention futility: Targeting high-risk customers might be ineffective." Ascarza, Eva. Journal of Marketing Research 55.1 (2018): 80-98.
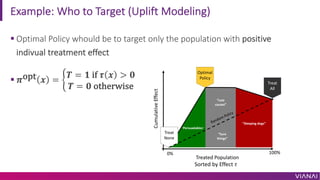
- 12. Example: Who to Target (Uplift Modeling) ¡°Persuadables¡± ¡°Lost causes¡± ¡°Sure things¡± ¡°Sleeping dogs¡± Treated Population Cumulative Effect Treat All Treat None Optimal Policy Random Policy 0% 100% ¡ì Optimal Policy whould be to target only the population with positive indivual treatment effect ¡ì ?opt ? = ' ? = ? if ? ? > ? ? = ? otherwise Sorted by Effect ?
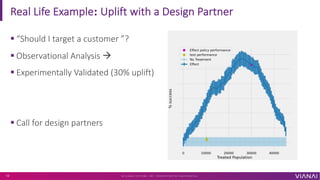
- 13. Real Life Example: Uplift with a Design Partner ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 14 ¡ì ¡°Should I target a customer ¡±? ¡ì Observational Analysis ¨¤ ¡ì Experimentally Validated (30% uplift) ¡ì Call for design partners
- 14. Resources for Prescription Controlled Experiments ? Stats Simulations ? RL Observational Study ? Causal
- 15. What is the Fundamental Problem? ¡ì Counterfactual is a missing data problem ¡ì Play make belief with potential outcomes https://www.bradyneal.com/causal-inference-course ? ? ? ?? ?? ? = ?? ? ?? 1 0 0 ? 0 ? 2 1 1 1 ? ? 3 1 0 0 ? ? 4 0 1 ? 1 ? 5 0 1 ? 1 ? treatment outcome potential outcomes Individual treatment effect
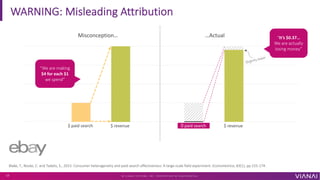
- 16. Blake, T., Nosko, C. and Tadelis, S., 2015. Consumer heterogeneity and paid search effectiveness: A large-scale field experiment. Econometrica, 83(1), pp.155-174. 0 paid search $ revenue $ paid search $ revenue Slightly lower WARNING: Misleading Attribution Misconception¡ ¡Actual ¡°We are making $4 for each $1 we spend¡± ¡°It¡¯s $0.37¡ We are actually losing money¡± ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 17
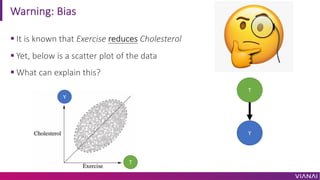
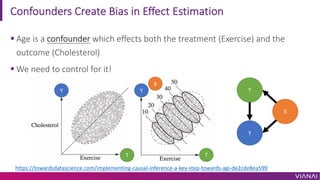
- 17. Warning: Bias ¡ì It is known that Exercise reduces Cholesterol ¡ì Yet, below is a scatter plot of the data ¡ì What can explain this? Y T Y T
- 18. Confounders Create Bias in Effect Estimation ¡ì Age is a confounder which effects both the treatment (Exercise) and the outcome (Cholesterol) ¡ì We need to control for it! https://towardsdatascience.com/implementing-causal-inference-a-key-step-towards-agi-de2cde8ea599 Y T X Y T X T Y
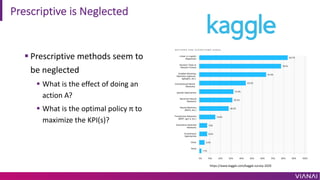
- 19. Prescriptive is Neglected ¡ì Prescriptive methods seem to be neglected ¡ì What is the effect of doing an action A? ¡ì What is the optimal policy ¦Ğ to maximize the KPI(s)? https://www.kaggle.com/kaggle-survey-2020
- 20. How? Causal Inference 101 ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 21
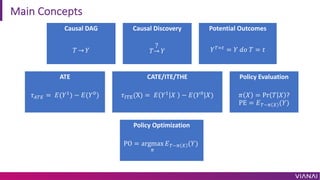
- 21. Main Concepts Causal DAG ? ¡ú ? Causal Discovery ?¡ú ? ? Potential Outcomes ?!"# = ? ?? ? = ? ATE ?$!% = ?(?& ) ? ?(?' ) CATE/ITE/THE ?()*(X) = ? ?& ? ? ?(?' |?) Policy Evaluation ? ? = Pr ? ? ? PE = ?!~, - (?) Policy Optimization PO = argmax , ?!~, - (?)
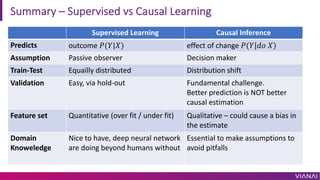
- 22. Summary ¨C Supervised vs Causal Learning Supervised Learning Causal Inference Predicts outcome ?(?|?) effect of change ?(?|?? ?) Assumption Passive observer Decision maker Train-Test Equailly distributed Distribution shift Validation Easy, via hold-out Fundamental challenge. Better prediction is NOT better causal estimation Feature set Quantitative (over fit / under fit) Qualitative ¨C could cause a bias in the estimate Domain Knoweledge Nice to have, deep neural network are doing beyond humans without Essential to make assumptions to avoid pitfalls
- 23. Typical Stages in a Causal Project 1. Causal Model 2. Identify 3. Estimate 4. *Evaluate & Optimize 5. Refute
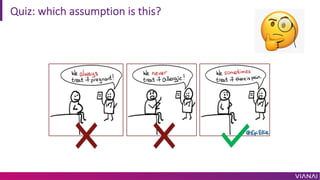
- 24. Identifiability ¡ìThe ability to estimate causal effect from observed data. ¡ìStable Unit Treatment Value Assumption (SUTVA) for ? ¡Ù ?: ?( ¡Í ?) and ?( ¡Í ?) ¡ìConsistency ? = ? ¡ú ? = ?. ?? ¡ìIgnorability ?', ?& ¡Í ?|? ¡ìPositivity ? ? = ? ? = ? > 0 ??, ? Paper accepted to CDSM21
- 25. Quiz: which assumption is this?
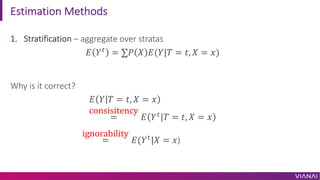
- 26. Estimation Methods 1. Stratification ¨C aggregate over stratas ? ?/ = ¡Æ? ? ?(?|? = ?, ? = ?) Why is it correct? ? ? ? = ?, ? = ? = consisitency ? ?/ ? = ?, ? = ? = ignorability ?(?/ |? = ?)
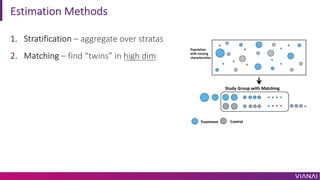
- 27. Estimation Methods 1. Stratification ¨C aggregate over stratas 2. Matching ¨C find ¡°twins¡± in high dim
- 28. Estimation Methods 1. Stratification ¨C aggregate over stratas 2. Matching ¨C find ¡°twins¡± in high dimension 3. Propensity Matching ¨C find twins in one dimension
- 29. Propensity Score ¡ì Define ? = 1 for treatment and ? = 0 for control, we will denote the propensity score for subject ? by ?0 = Pr(? = 1|?0) ¡ì propensity is a ¡°balancing score¡±: meaning if we control/match for it, we will get unbiased effect estimation ? ? ? ? = ?, ? = 1 = ? ? ? ? = ?, ? = 0
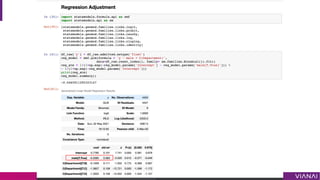
- 30. Estimation Methods 1. Stratification ¨C aggregate over stratas 2. Matching ¨C find ¡°twins¡± in high dimension 3. Propensity Matching ¨C find twins in one dimension 4. IPTW - Inverse Propensity Treatment Weighting Note: It can be shown that IPTW and standardization are equivalent (Technical Point 2.3, see Appendix)
- 31. Inverse Propensity Weighting ¡ì ?0 = Pr(?0|? = ?0) ¡ì ??? = ? ?1 ? ?2 = ¡Æ?0 3!45! 5! 145!
- 32. What? In Practice ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 33
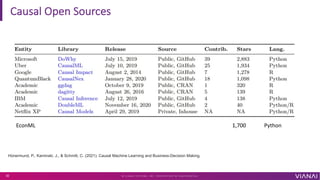
- 33. Causal Python Open Sources Microsoft/EconML
- 34. Causal Open Sources EconML 1,700 Python ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 35 H¨¹nermund, P., Kaminski, J., & Schmitt, C. (2021). Causal Machine Learning and Business-Decision Making.
- 35. Causal Inference is Hard but Worth it ¡ì Hard ¡ì High entrance barrier - you can easily do it wrong ¡ì Validation and evaluation is hard ¡ì Domain Knowledge is (sometimes) essential ¡ì Valuable ¡ì Can Optimize decision making (¡°increamentality¡±) ¡ì Detect real effects and attribution ¡ì Personaliztion
- 36. Code for Toy Problem ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 37
- 37. hanan@vian.ai office hours 15:00-15:30 ? V I A N A I S Y S T E M S , I N C . P R O P R I E T A R Y & C O N F I D E N T I A L 38
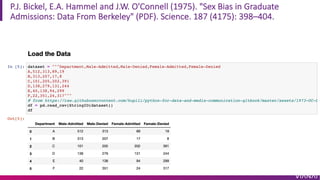
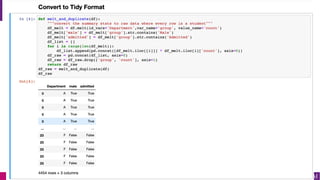
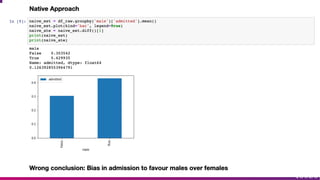
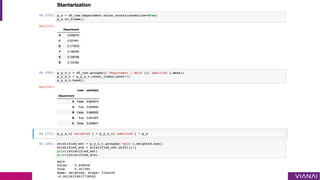
- 38. P.J. Bickel, E.A. Hammel and J.W. O'Connell (1975). "Sex Bias in Graduate Admissions: Data From Berkeley" (PDF). Science. 187 (4175): 398¨C404.
- 43. IPTW