C++ programming
- 1. DEV C++ Programming Baylon, Gerone Vianca Q. http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 2. Looping in Programming • Loops in programming are used to repeat a block of code. Being able to have your programming repeatedly execute a block of code is one of the most basic but useful tasks in programming -- many programming programs or programming websites that produce extremely complex output are really only executing a single task many times. A loop in programming lets you write a very simple statement to produce a significantly greater result simply by repetition. http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 3. For Loop For Loop is the most useful type in loop programming. The syntax for for loop is : for ( variable initialization; condition; variable update ) { Code to execute while the condition is true } The variable initialization in for loop allows you to either declare a variable and give it a value or give a value to an already existing variable. Second, the condition tells the programming that while the conditional expression in programming is true the loop should continue to repeat itself. The variable update section is the easiest way for a for loop to handle changing of the variable in programming . http://eglobiotraining.com.
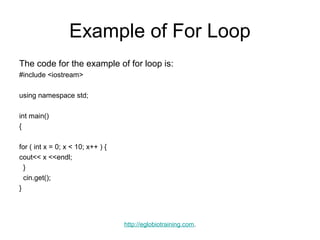
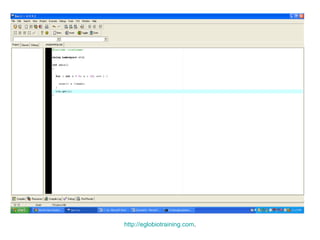
- 4. Example of For Loop The code for the example of for loop is: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { for ( int x = 0; x < 10; x++ ) { cout<< x <<endl; } cin.get(); } http://eglobiotraining.com.
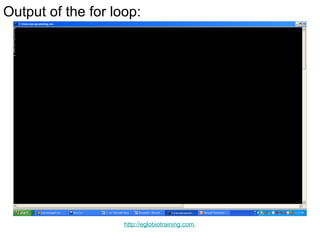
- 6. Output of the for loop: http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 7. Explanation of the for loop This programming is a simple example of a for loop. x is set to zero, while x is less than 10 it calls cout<< x <<endl; and it adds 1 to x until the condition in the programming is met. http://eglobiotraining.com.
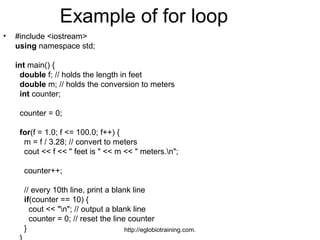
- 8. Example of for loop • #include <iostream> usingĚýnamespace std; intĚýmain() { doubleĚýf; // holds the length in feet doubleĚým; // holds the conversion to meters intĚýcounter; counter = 0; for(f = 1.0; f <= 100.0; f++) { m = f / 3.28; // convert to meters cout << f << " feet is " << m << " meters.n"; counter++; // every 10th line, print a blank line if(counter == 10) { cout << "n"; // output a blank line counter = 0; // reset the line counter } http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 9. Output of For Loop http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 10. Output of For Loop http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 11. Output of For Loop http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 12. Output of For Loop http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 13. Output of For Loop http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 14. Explanation of For Loop The output of the above example showed tha conversion table of length (feet to meters). http://eglobiotraining.com.
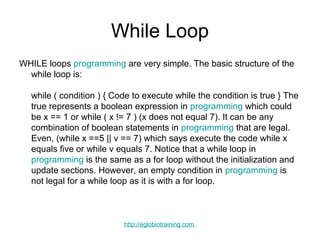
- 15. While Loop WHILE loops programming are very simple. The basic structure of the while loop is: while ( condition ) { Code to execute while the condition is true } The true represents a boolean expression in programming which could be x == 1 or while ( x != 7 ) (x does not equal 7). It can be any combination of boolean statements in programming that are legal. Even, (while x ==5 || v == 7) which says execute the code while x equals five or while v equals 7. Notice that a while loop in programming is the same as a for loop without the initialization and update sections. However, an empty condition in programming is not legal for a while loop as it is with a for loop. http://eglobiotraining.com.
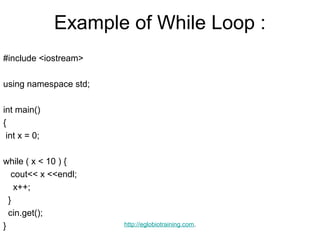
- 16. Example of While Loop : #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int x = 0; while ( x < 10 ) { cout<< x <<endl; x++; } cin.get(); } http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 18. Output of the While Loop http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 19. Expalanation for While : This While is simple, but it is longer than the above FOR loop programming. The easiest way to think of the loop programming is that when it reaches the brace at the end it jumps back up to the beginning of the loop programming, which checks the condition again and decides whether to repeat the block another time, or stop and move to the next statement after the block. http://eglobiotraining.com.
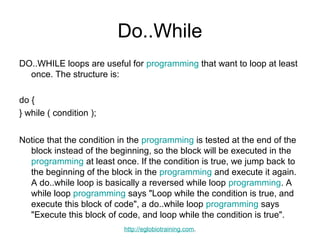
- 20. Do..While DO..WHILE loops are useful for programming that want to loop at least once. The structure is: do { } while ( condition ); Notice that the condition in the programming is tested at the end of the block instead of the beginning, so the block will be executed in the programming at least once. If the condition is true, we jump back to the beginning of the block in the programming and execute it again. A do..while loop is basically a reversed while loop programming. A while loop programming says "Loop while the condition is true, and execute this block of code", a do..while loop programming says "Execute this block of code, and loop while the condition is true". http://eglobiotraining.com.
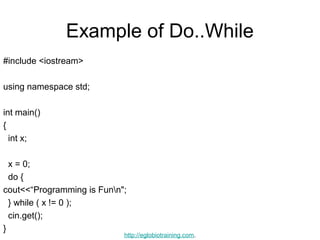
- 21. Example of Do..While #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int x; x = 0; do { cout<<“Programming is Funn"; } while ( x != 0 ); cin.get(); } http://eglobiotraining.com.
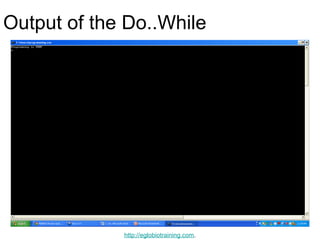
- 23. Output of the Do..While http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 24. Explanation of Do..While You must include a trailing semi-colon after the while in the above example. A common error is to forget that a do..while loop in C++ programming must be terminated with a semicolon (the other loops should not be terminated with a semicolon, adding to the confusion). Notice that this loop will execute once, because it automatically executes before checking the condition. http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 25. Infinite loop A loop becomes infinite loop in C++ programming if a condition never becomes false. The for loop is traditionally used for this purpose. Since none of the three expressions that form the for loop are required, you can make an endless loop by leaving the conditional expression empty. http://eglobiotraining.com.
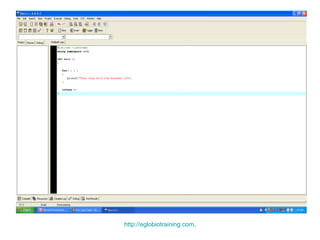
- 26. Example of Infinite Loop #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main () { for( ; ; ) { printf("This loop will run forever.n"); } return 0; } http://eglobiotraining.com.
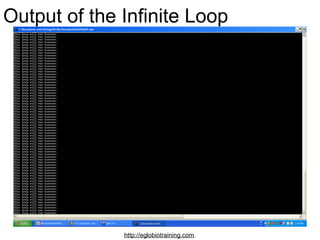
- 28. Output of the Infinite Loop http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 29. Switch Case programming The switch statement is used in C++ programming for testing if a variable is equal to one of a set of values. The variable must be an integer, i.e. integral or non-fractional. The programmer can specify the actions taken for each case of the possible values the variable can have. http://eglobiotraining.com.
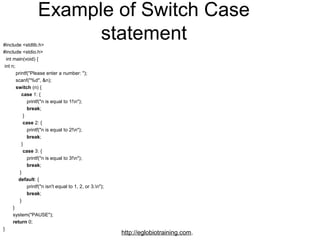
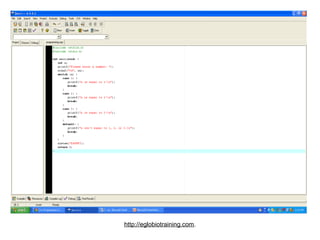
- 30. Example of Switch Case #include <stdlib.h> statement #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int n; printf("Please enter a number: "); scanf("%d", &n); ĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýswitch (n) { ĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýcase 1: { printf("n is equal to 1!n"); ĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýbreak; } ĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýcase 2: { printf("n is equal to 2!n"); ĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýbreak; } case 3: { printf("n is equal to 3!n"); ĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýbreak; } ĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýdefault: { printf("n isn't equal to 1, 2, or 3.n"); ĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýbreak; } } system("PAUSE"); ĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýĚýreturn 0; } http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 32. Output of Switch case using no.1 http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 33. Output of Switch case using no.2 http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 34. Output of Switch case using no.3 http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 35. Output of Switch case using other numbers http://eglobiotraining.com.
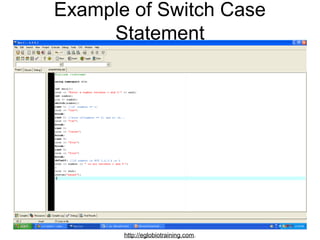
- 36. Example of Switch Case Statement http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 37. Output of the switch Case http://eglobiotraining.com.
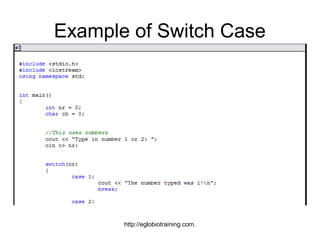
- 38. Example of Switch Case http://eglobiotraining.com.
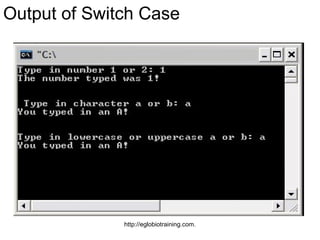
- 40. Output of Switch Case http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 41. Explanation • The Switch case program shown above will ask for a number and a letter an distinguish if it is available in the program. http://eglobiotraining.com.
- 42. DEV C++ PROGRAMMING Submitted By: Baylon, Gerone Vianca Q. http://www.slideshare.net/upload? from_source=loggedin_newsfeed Submitted To: Mr. Erwin Globio http://eglobiotraining.com/ http://eglobiotraining.com.