C:\Users\Shashank\Desktop\Job DocJob PPT.pptx
- 1. Presentation
- 2. Contents Self Introduction Educational background & Work Experiences Topic of Ineterest Research Experiences
- 3. Institution: ICFAI Location: Dehradun Name of Degree : B.Tech (CSE) Graduation Year: 2013 Institution: SRMU Location: Lucknow Name of Degree: M.Tech (CSE) Graduation Year: 2015 Institution: NIT Location: Raipur Name of Degree: Ph.D (S) (CSE) Graduation Year: 2024 Educational Background
- 4. Work Experience Job profile: Assistant professor Institution: BBDITM, Lucknow Date: 30/08/2021 to 22/10/2023 Job profile: Assistant professor Institution: DITU, Dehradun Date: 11/12/2023 to till date Job profile: Lecturer Institution: Cambridge group of Institution, Ranchi Date: 10-10-2017 to 08-08-2021 Job profile: Assistant professor Institution: SRMCEM, Lucknow Date: 08/11/2021 to 29/08/2022 Job profile: Assistant professor Institution: HITM, Lucknow Date: 03-08-2015 to 07-10-2017
- 5. Research experience Title of the research: Design a Framework for Routing Schemes in Wireless Sensor Networks using Metaheuristic Approach Area of Research: Wireless Sensor Networks
- 6. Research Publications 1. S. Singh and V. Anand, “Load balancing clustering and routing for IoT-enabled wireless sensor networks” International Journal of Network Management, e2244. https://doi.org/10.1002/nem.2244 [SCI] 2. S. Singh and V. Anand, “Trust-Based Clustering and Routing in WSNs Using DST-WOA” Peer-peer Networking and Applications Springer (Accepted) [SCI] 3. Shashank Singh, Veena Anand, Pallav Kumar Bera, “A Delay-Tolerant low-duty cycle scheme in wireless sensor networks for IoT applications”, International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering, Volume 4, 2023, Pages 194-204, ISSN 2666- 3074, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcce.2023.04.005. [SCOPUS] 4. Singh, S., Anand, V. (2023). “A Fuzzy C-Means Based Clustering Protocol to Improve QoS of Multi Sink WSNs”. In: Bhateja, V., Yang, XS., Lin, J.CW., Das, R. (eds) Evolution in Computational Intelligence. FICTA 2022. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 326. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7513-4_12 [SCOPUS] 5. S. Singh and V. Anand, "Comparative Study of Different Routing Protocol for Opportunistic IoT Applications" 2019 International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON), NCR New Delhi, India, 2019, pp. 385-389. [SCOPUS]
- 7. Courses /Topic of Interest 1. Computer networks: Reference Model (OSI) 2. Operating Systems: (Deadlock avoidance algorithm: Banker’s)
- 8. Computer Networks â—Ź Understanding the OSI Model
- 9. Seven layers of the OSI model
- 10. The interaction between layers in the OSI model
- 15. Operating Systems Deadlock avoidance algorithm: Banker’s
- 16. Deadlock â—Ź A deadlock is a situation where a set of processes are blocked because each process is holding a resource and waiting for another resource acquired by some other process.
- 17. Deadlock Avoidance ● The system knows the complete sequence of requests and releases for each process. ● The system decides for each request whether or not the process should wait in order to avoid a deadlock. ● Each process declare the maximum number of resources of each type that it may need. ○ The system should always be at a safe state. ○ Safe state → no deadlock
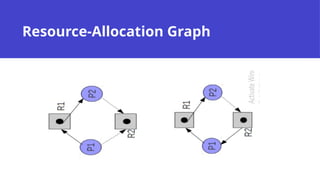
- 19. Banker's Algorithm Applicable to resources with multiple instances. ● Less efficient than the resource-allocation graph scheme. ● Each process declares its needs (number of resources) ● When a process requests a set of resources: ● Will the system be at a safe state after the allocation? – Yes → Grant the resources to the process. – No → Block the process until the resources are released by some other process
- 20. Banker's Algorithm • n: integer # of processes • m: integer # of resource-types • available[1..m] available[i] is # of avail resources of type i • max[1..n,1..m] max demand of each Pi for each Ri • allocation[1..n,1..m] current allocation of resource Rj to Pi • need[1..n,1..m] max # resource Rj that Pi may still request
- 21. Banker’s Algorithm: Example This is a safe state: safe sequence <P1, P3, P4, P2, P0> ● Suppose that P1 requests (1,0,2) • Add it to P1’s allocation and subtract it from Available.
- 22. References 1. Data Communications and networking (2021). New York: McGraw-Hill. 2. SILBERSCHATZ, A. (2021). Operating system concepts. JOHN WILEY.
- 23. 23 Thank You
Editor's Notes
- A-126, 128, 192, 224,240






![Research Publications
1. S. Singh and V. Anand, “Load balancing clustering and routing for IoT-enabled wireless sensor networks” International Journal
of Network Management, e2244. https://doi.org/10.1002/nem.2244 [SCI]
2. S. Singh and V. Anand, “Trust-Based Clustering and Routing in WSNs Using DST-WOA” Peer-peer Networking and
Applications Springer (Accepted) [SCI]
3. Shashank Singh, Veena Anand, Pallav Kumar Bera, “A Delay-Tolerant low-duty cycle scheme in wireless sensor networks for
IoT applications”, International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering, Volume 4, 2023, Pages 194-204, ISSN 2666-
3074, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcce.2023.04.005. [SCOPUS]
4. Singh, S., Anand, V. (2023). “A Fuzzy C-Means Based Clustering Protocol to Improve QoS of Multi Sink WSNs”. In: Bhateja,
V., Yang, XS., Lin, J.CW., Das, R. (eds) Evolution in Computational Intelligence. FICTA 2022. Smart Innovation, Systems and
Technologies, vol 326. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7513-4_12 [SCOPUS]
5. S. Singh and V. Anand, "Comparative Study of Different Routing Protocol for Opportunistic IoT Applications" 2019
International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON), NCR New Delhi, India, 2019,
pp. 385-389. [SCOPUS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jobppt-240811101624-3bf75680/85/C-Users-Shashank-Desktop-Job-DocJob-PPT-pptx-6-320.jpg)












![Banker's Algorithm
• n: integer # of processes
• m: integer # of resource-types
• available[1..m] available[i] is # of avail resources of
type i
• max[1..n,1..m] max demand of each Pi for each Ri
• allocation[1..n,1..m] current allocation of resource Rj to Pi
• need[1..n,1..m] max # resource Rj that Pi may still
request](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jobppt-240811101624-3bf75680/85/C-Users-Shashank-Desktop-Job-DocJob-PPT-pptx-20-320.jpg)


