How to create a camera2
- 1. How to create camera 2 Heaton
- 2. How to create a camera2 ? Step1:To enumerate, query, and open available camera devices, obtain a CameraManager instance. CameraManager manager = (CameraManager) activity.getSystemService(Context.CAMERA_SERVICE); String cameraId = manager.getCameraIdList()[0];
- 3. Initialize CameraDevice Ąņ Step2:Individual CameraDevices provide a set of static property information that describes the hardware device and the available settings and output parameters for the device. // To get a list of available sizes of camera preview, we retrieve an instance of // StreamConfigurationMap from CameraCharacteristics CameraCharacteristics characteristics = manager.getCameraCharacteristics(cameraId); StreamConfigurationMap map = characteristics .get(CameraCharacteristics.SCALER_STREAM_CONFIGURATION_MAP); (Camera.Size) mPreviewSize = map.getOutputSizes(SurfaceTexture.class)[0]; (SurfaceTexture) mTextureView.setAspectRatio(mPreviewSize.getWidth(), // We are opening the camera with a listener. When it is ready, onOpened of // (CameraDevice.StateListener)mStateListener is called. manager.openCamera(cameraId, mStateListener, null);
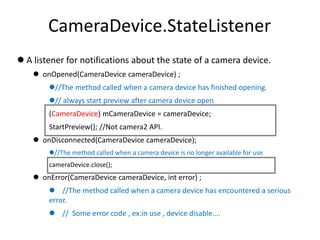
- 4. CameraDevice.StateListener ? A listener for notifications about the state of a camera device. ? onOpened(CameraDevice cameraDevice) ; ?//The method called when a camera device has finished opening. ?// always start preview after camera device open (CameraDevice) mCameraDevice = cameraDevice; StartPreview(); //Not camera2 API. ? onDisconnected(CameraDevice cameraDevice); ?//The method called when a camera device is no longer available for use. cameraDevice.close(); ? onError(CameraDevice cameraDevice, int error) ; ? //The method called when a camera device has encountered a serious error. ? // Some error code , ex:in use , device disable....
- 5. CameraDevice ?The CameraDevice class is a representation of a single camera connected to an Android device, allowing for fine-grain control of image capture and post- processing at high frame rates. ?Device is modeled as a pipeline ? Input : CaptureRequest for a single Frame ? Output: CaptureResult Metadata packet + output image buffers for the request. These buffers can go to one or multiple output targets ?SurfaceView ?SurfaceTexture ?MediaCodec ?MediaRecorder ?Renderscript Allocation et al ?ImageReader ? Requests are processed in order, multiple requests are in flight to maintain full frame rate ( generally means 30 frames per second )
- 6. Start preview ?Step3:To capture or stream images from a camera device, the application must first create a camera capture session with a set of output Surfaces for use with the camera device SurfaceTexture texture = mTextureView.getSurfaceTexture(); // We configure the size of default buffer to be the size of camera preview we want. texture.setDefaultBufferSize(mPreviewSize.getWidth(), mPreviewSize.getHeight()); // This is the output Surface we need to start preview. Surface surface = new Surface(texture); // We set up a CaptureRequest.Builder with the output Surface. mPreviewBuilder = mCameraDevice.createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_PREVIEW); mPreviewBuilder.addTarget(surface); // Here, we create a CameraCaptureSession for camera preview. mCameraDevice.createCaptureSession(Arrays.asList(surface), new CameraCaptureSession.StateListener(){.....}
- 7. CaptureRequest.Builder ?A builder for capture requests. ?To obtain a builder instance, use the createCaptureRequest(int) method, which initializes the request fields to one of the templates defined in CameraDevice. ?Method ? addTarget(Surface outputTarget) ?Add a surface to the list of targets for this request ? set(Key<T> key, T value) ?Set a capture request field to a value.
- 8. CaptureRequest ?An immutable package of settings and outputs needed to capture a single image from the camera device. ?Contains the configuration for the capture hardware (sensor, lens, flash), the processing pipeline, the control algorithms, and the output buffers. Also contains the list of target Surfaces to send image data to for this capture. ?CaptureRequests can be created by using a CaptureRequest.Builder instance, obtained by calling createCaptureRequest(int) ?Method ? (<T> T) get(Key<T> key) ?Get a capture request field value. ? (List<Key<?>>) getKeys() ?Returns a list of the keys contained in this map.
- 9. CameraCaptureSession.StateListener ?A listener for tracking the state of a camera capture session. ? onConfigured(CameraCaptureSession session) ?This method is called when the camera device has finished configuring itself, and the session can start processing capture requests. ?//In here, we set this session to update preview public void onConfigured(CameraCaptureSession cameraCaptureSession) { // When the session is ready, we start displaying the preview. mPreviewSession = cameraCaptureSession; // In this sample, we just let the camera device pick the automatic settings. mPreviewBuilder.set(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_MODE , CameraMetadata.CONTROL_MODE_AUTO); HandlerThread thread = new HandlerThread("CameraPreview"); thread.start(); Handler backgroundHandler = new Handler(thread.getLooper()); // Finally, we start displaying the camera preview. mPreviewSession.setRepeatingRequest(mPreviewBuilder.build(), null, backgroundHandler); }
- 10. CameraCaptureSession ?A configured capture session for a CameraDevice, used for capturing images from the camera. ?A CameraCaptureSession is created by providing a set of target output surfaces to createCaptureSession. Once created, the session is active until a new session is created by the camera device, or the camera device is closed. ?Method ? capture(CaptureRequest request, CameraCaptureSession.CaptureListener listener, Handler handler) ?Submit a request for an image to be captured by the camera device. ? captureBurst(List<CaptureRequest> requests, CameraCaptureSession.CaptureListener listener, Handler handler) ?Submit a list of requests to be captured in sequence as a burst. ? setRepeatingBurst(List<CaptureRequest> requests, CameraCaptureSession.CaptureListener listener, Handler handler) ?Request endlessly repeating capture of a sequence of images by this capture session. ? setRepeatingRequest(CaptureRequest request, CameraCaptureSession.CaptureListener listener, Handler handler) ?Request endlessly repeating capture of images by this capture session.
- 11. Take picture ?Step4: Capture of JPEG images or RAW buffers forDngCreator can be done with ImageReader with the {android.graphics.ImageFormat#JPEG} and {android.graphics.ImageFormat#RAW_SENSOR} formats. CameraManager manager = (CameraManager) activity.getSystemService(Context.CAMERA_SERVICE); // Pick the best JPEG size that can be captured with this CameraDevice. CameraCharacteristics characteristics = manager.getCameraCharacteristics(mCameraDevice.getId()); Size[] jpegSizes = null; if (characteristics != null) { jpegSizes = characteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.SCALER_STREAM_CONFIGURATION_MAP) .getOutputSizes(ImageFor mat.JPEG); } int width = 640; int height = 480; if (jpegSizes != null && 0 < jpegSizes.length) { width = jpegSizes[0].getWidth(); height = jpegSizes[0].getHeight(); }
- 12. Take picture ?Step5:Use ImageReader to get output data. // We use an ImageReader to get a JPEG from CameraDevice. // Here, we create a new ImageReader and prepare its Surface as an output from camera. ImageReader reader = ImageReader.newInstance(width, height, ImageFormat.JPEG, 1); List<Surface> outputSurfaces = new ArrayList<Surface>(2); outputSurfaces.add(reader.getSurface()); outputSurfaces.add(new Surface(mTextureView.getSurfaceTexture())); // This is the CaptureRequest.Builder that we use to take a picture. final CaptureRequest.Builder captureBuilder = mCameraDevice.createCaptureRequest(CameraDevice.TEMPLATE_STILL_CAPTURE); captureBuilder.addTarget(reader.getSurface()); // In this sample, we just let the camera device pick the automatic settings. captureBuilder.set(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_MODE,CameraMetadata.CONTROL_MODE_AUTO);
- 13. ImageReader ?The ImageReader class allows direct application access to image data rendered into a Surface ? Method ?static (ImageReader) newInstance(int width, int height, int format, int maxImages) ?Create a new reader for images of the desired size and format. ?(Image) acquireLatestImage() ?Acquire the latest Image from the ImageReader's queue, dropping older images. ?(Image) acquireNextImage() ?Acquire the next Image from the ImageReader's queue.
- 14. Take picture ?Step5:Set output data parameters. // In this sample, we just let the camera device pick the automatic settings. capturebuilder.set(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_MODE, CameraMetadata.CONTROL_MODE_AUTO); // Orientation int rotation = activity.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getRotation(); captureBuilder.set(CaptureRequest.JPEG_ORIENTATION, ORIENTATIONS.get(rotation)); // Output file final File file = new File(activity.getExternalFilesDir(null), "pic.jpg"); // This listener is called when a image is ready in ImageReader ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener readerListener = new ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener() {Ą.}
- 15. ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener ?Callback interface for being notified that a new image is available. ? onImageAvailable(ImageReader reader) { image = reader.acquireLatestImage(); ByteBuffer buffer = image.getPlanes()[0].getBuffer(); byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.capacity()]; buffer.get(bytes); save(bytes); Ą..//Use output stream to write out to file. ĄĄ Image.close();
- 16. Take picture ?Step6:Set output data parameters. And start camera capture picture thread. // In this sample, we just let the camera device pick the automatic settings. capturebuilder.set(CaptureRequest.CONTROL_MODE, CameraMetadata.CONTROL_MODE_AUTO); // Orientation int rotation = activity.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getRotation(); captureBuilder.set(CaptureRequest.JPEG_ORIENTATION, ORIENTATIONS.get(rotation)); // Output file final File file = new File(activity.getExternalFilesDir(null), "pic.jpg"); // This listener is called when a image is ready in ImageReader ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener readerListener = new ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener() {Ą.} // We create a Handler since we want to handle the result JPEG in a background thread HandlerThread thread = new HandlerThread("CameraPicture"); thread.start(); final Handler backgroundHandler = new Handler(thread.getLooper()); reader.setOnImageAvailableListener(readerListener, backgroundHandler);
- 17. Take picture ?Step7:Restart preview thread after capture complete. // This listener is called when the capture is completed. // Note that the JPEG data is not available in this listener, but in the // ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener we created above. final CameraCaptureSession.CaptureListener captureListener = new CameraCaptureSession.CaptureListener() { public void onCaptureCompleted(CameraCaptureSession session, CaptureRequest request, TotalCaptureResult result) { // We restart the preview when the capture is completed startPreview(); } }; // Finally, we can start a new CameraCaptureSession to take a picture. mCameraDevice.createCaptureSession(outputSurfaces, new CameraCaptureSession.StateListener() { public void onConfigured(CameraCaptureSession session) { try { session.capture(captureBuilder.build(), captureListener, backgroundHandler); } catch (CameraAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, backgroundHandler );
- 18. Q&A
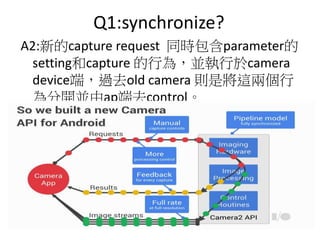
- 19. Q1:synchronize? A2:ÐÂĩÄcapture request ÍŽr°üšŽparameterĩÄ settingšÍcapture ĩÄÐÐéĢŽKĖÐÐėķcamera deviceķËĢŽß^ČĨold camera tĘĮĒß@ÉÐÐ é·Öé_KÓÉapķËČĨcontrolĄĢ
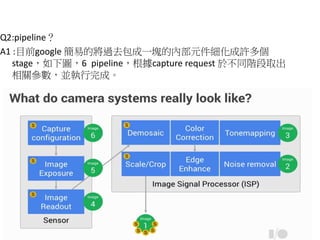
- 20. Q2:pipelineĢŋ A1 :ÄŋĮ°google šŌŨĩÄĒß^ČĨ°üģÉŌŧKĩÄČēŋÔŠžþžŧŊģÉÔSķā stageĢŽČįÏÂDĢŽ6 pipelineĢŽļųþcapture request ėķēŧÍŽëAķÎČĄģö ÏāęP ĒĩĢŽKĖÐÐÍęģÉĄĢ
- 21. Q3 Q:éšÎéšÎ captureSession rĢŽþ·ÅČë outputSurface(Surface[]) ķāsurface ķøK·Į ÖļķĻÎŌŧsurface? A:ÔŲ―ĻCameraCaptureSession ÍĻģĢþ·ÅČëÎī íŋÉÄÜþÓÃĩ―ĩÄtarget surfaces ĢŽKēŧþÖŧ ·ÅČëÎŌŧĩÄtarget surface ĢŽķøÎŌŧÖļķĻ surface ĩÄÐčĮóČëcapture requestŅeĄĢ
- 22. Q4 Q:ImageReader ĘđÓ÷―·ĻĢŋ A:Use ImageReader.getSurface() to get a Surface that can be used to produce Images for this ImageReader. Q3-1:what is surface? A3-1: 1.Handle onto a raw buffer that is being managed by the screen compositor. 2. surface ĩÄcanvasģÉTŋÉŌÔÓÃíĖáđĐĀLDĩÄöËųĢŽ raw buffer ÓÃíąĢīædata ĢŽČĄĩÃsurface ĩČÍŽČĄĩà canvas šÍ raw bufferĩÄČČÝĄĢ summary: ėķcamera ap ŅetĘĮĩČÍŽĖáđĐcaptureÝģö


![How to create a camera2
? Step1:To enumerate, query, and open available camera devices,
obtain a CameraManager instance.
CameraManager manager = (CameraManager)
activity.getSystemService(Context.CAMERA_SERVICE);
String cameraId = manager.getCameraIdList()[0];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camera2howtocreate-150329125634-conversion-gate01/85/How-to-create-a-camera2-2-320.jpg)
![Initialize CameraDevice
Ąņ Step2:Individual CameraDevices provide a set of static property
information that describes the hardware device and the available
settings and output parameters for the device.
// To get a list of available sizes of camera preview, we retrieve an instance of
// StreamConfigurationMap from CameraCharacteristics
CameraCharacteristics characteristics = manager.getCameraCharacteristics(cameraId);
StreamConfigurationMap map = characteristics
.get(CameraCharacteristics.SCALER_STREAM_CONFIGURATION_MAP);
(Camera.Size) mPreviewSize = map.getOutputSizes(SurfaceTexture.class)[0];
(SurfaceTexture) mTextureView.setAspectRatio(mPreviewSize.getWidth(),
// We are opening the camera with a listener. When it is ready, onOpened of
// (CameraDevice.StateListener)mStateListener is called.
manager.openCamera(cameraId, mStateListener, null);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camera2howtocreate-150329125634-conversion-gate01/85/How-to-create-a-camera2-3-320.jpg)






![Take picture
?Step4: Capture of JPEG images or RAW buffers forDngCreator can be done
with ImageReader with the {android.graphics.ImageFormat#JPEG} and
{android.graphics.ImageFormat#RAW_SENSOR} formats.
CameraManager manager =
(CameraManager) activity.getSystemService(Context.CAMERA_SERVICE);
// Pick the best JPEG size that can be captured with this CameraDevice.
CameraCharacteristics characteristics =
manager.getCameraCharacteristics(mCameraDevice.getId());
Size[] jpegSizes = null;
if (characteristics != null) {
jpegSizes =
characteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.SCALER_STREAM_CONFIGURATION_MAP) .getOutputSizes(ImageFor
mat.JPEG);
}
int width = 640; int height = 480;
if (jpegSizes != null && 0 < jpegSizes.length) {
width = jpegSizes[0].getWidth();
height = jpegSizes[0].getHeight();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camera2howtocreate-150329125634-conversion-gate01/85/How-to-create-a-camera2-11-320.jpg)



![ImageReader.OnImageAvailableListener
?Callback interface for being notified that a new image is available.
? onImageAvailable(ImageReader reader) {
image = reader.acquireLatestImage();
ByteBuffer buffer = image.getPlanes()[0].getBuffer();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.capacity()];
buffer.get(bytes);
save(bytes);
Ą..//Use output stream to write out to file.
ĄĄ
Image.close();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camera2howtocreate-150329125634-conversion-gate01/85/How-to-create-a-camera2-15-320.jpg)



![Q3
Q:éšÎéšÎ captureSession rĢŽþ·ÅČë
outputSurface(Surface[]) ķāsurface ķøK·Į
ÖļķĻÎŌŧsurface?
A:ÔŲ―ĻCameraCaptureSession ÍĻģĢþ·ÅČëÎī
íŋÉÄÜþÓÃĩ―ĩÄtarget surfaces ĢŽKēŧþÖŧ
·ÅČëÎŌŧĩÄtarget surface ĢŽķøÎŌŧÖļķĻ
surface ĩÄÐčĮóČëcapture requestŅeĄĢ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/camera2howtocreate-150329125634-conversion-gate01/85/How-to-create-a-camera2-21-320.jpg)
