CAN Bus
- 1. CAN BUS (Controller Area Network) Presented by: AnoopMathew For: ECE
- 2. Contents • Overview • Data Information • Frame Format • Protocol • Error Detection • Implementations • Basic CAN • Full CAN • FIFO • Enhanced Full CAN • Manufacturers • Diagrams
- 3. Overview • CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial bus system used to communicate between several embedded 8-bit and 16-bit microcontrollers. • It was originally designed for use in the automotive industry but is used today in many other systems (e.g. home appliances and industrial machines).
- 4. Overview (con’t) • Highest Baud Rate is 1Mbit. • CAN uses a message oriented transmission protocol. • There are no defined addresses, just defined messages.
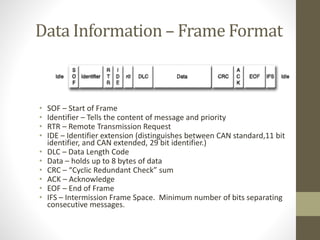
- 5. Data Information – Frame Format • SOF – Start of Frame • Identifier – Tells the content of message and priority • RTR – Remote Transmission Request • IDE – Identifier extension (distinguishes between CAN standard,11 bit identifier, and CAN extended, 29 bit identifier.) • DLC – Data Length Code • Data – holds up to 8 bytes of data • CRC – “Cyclic Redundant Check” sum • ACK – Acknowledge • EOF – End of Frame • IFS – Intermission Frame Space. Minimum number of bits separating consecutive messages.
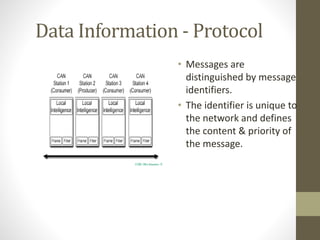
- 6. Data Information - Protocol • Messages are distinguished by message identifiers. • The identifier is unique to the network and defines the content & priority of the message.
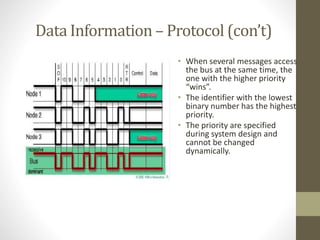
- 7. Data Information – Protocol (con’t) • When several messages access the bus at the same time, the one with the higher priority “wins”. • The identifier with the lowest binary number has the highest priority. • The priority are specified during system design and cannot be changed dynamically.
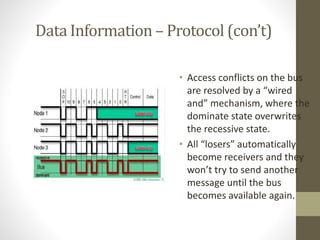
- 8. Data Information – Protocol (con’t) • Access conflicts on the bus are resolved by a “wired and” mechanism, where the dominate state overwrites the recessive state. • All “losers” automatically become receivers and they won’t try to send another message until the bus becomes available again.
- 9. Data Information – Error detection • If one or more errors are detected, the transmission is aborted. This prevents all other stations or nodes from accepting the message. • Re-transmission is automatic. If errors continue, then the station or node may switch itself off to prevent the bus from being tied up. • Error detection is done on two levels: • Message level • Bit level
- 10. Data Information – Error detection (con’t) • Message Level • CRC = Cyclic Redundant Check sum • Frame Check = compares message to fixed format and frame size • ACK errors = if transmitter does not receive an ACK signal from the receivers • Bit level • Monitoring = The transmitter monitors the bus signal as it sends the message and compares the bit sent to the bit received. • Bit Stuffing = After five consecutive equal bits, the transmitter inserts a stuff bit with a compliment value into the bit stream. The receivers remove this stuff bit.
- 11. Implementations • Basic CAN • Limited number of receive buffers and filters • Can get bogged down quickly with multiple consecutive messages.
- 12. Implementation (con’t) • Full CAN • Has several message objects (usually 15) • Can loose data if message objects are setup for multiple filters • Can still get bogged down if too many messages are sent consecutively
- 13. Implementation (con’t) • FIFO • “First In First Out” receive buffer • Fixes problem with multiple consecutive messages • Cannot allow a high priority message to move to front. It has to wait its turn
- 14. Implementation (con’t) • Enhanced Full Can • Dedicated FIFO for each individual message object • Very complicated to use • Less common
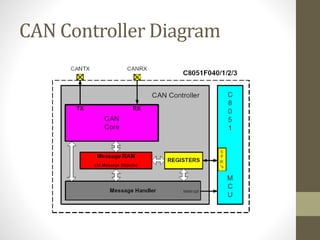
- 15. Manufacturers • Over 20 different chip manufacturers produce microcontrollers with on-chip CAN interfaces. • Some more notable ones are: • Cygnal • Intel • Motorola • NEC • Phillips • Toshiba
- 16. Cygnal C8051F040/042 Block Diagram
- 18. Useful Links • Manufacturer and Product List • http://www.can-cia.org/products/can/chips/ • CAN Information • http://www.canbus.us/ • http://www.can-cia.org/can/
- 19. Summary • CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial bus system used to communicate between several embedded 8-bit and 16-bit microcontrollers • Data Information • Frame Format • Protocol – message oriented • Error Detection • Message level (CRC, frame check, ACK errors) • Bit level (monitoring, bit stuffing) • Implementations • Basic CAN • Full CAN • FIFO • Enhanced Full CAN • Over 20 different chip manufacturers produce microcontrollers with on-chip CAN interfaces including Cygnal, Intel, and Motorala.