Cara i'rab bhs arb
- 1. . - in nouns - Modification/change reaching the end of nouns because of the change of the active element (denoting the end of the noun changes according to the position of the word in the sentence). [ - non-modification/change reaching the end of nouns because of the change of the active element (denoting the end of the) word assumes one eternal/unchangeable form. [ In respect to nouns, all are ) ( ( ( ŲĄ ] except the following: ( ( ] ) ) ) ) / /
- 2. . - i.e. taking their normal form as dictated by Arabic Grammar: i.e. not taking their normal form as dictated by specific rules in Arabic Grammar: - - () ( ) - ( ) ( ) / / / / / / / ( ) ŲĒ / / / / /
- 3. . ( ŲĢ ) / /
- 4. . - The in three areas within which are not present/clear, but are therefore assumed/hypothetical. [ ] An where the last letter is an ( ), i.e. : ] . [. : ( ) - An where the last letter is a and the letter before it is , i.e. . ] [. ( ) Note the condition of the without the ,( â ): ( ) : - ŲĪ / /
- 5. . - An where the of the last letter is the , and the letter before it is ( . ) ( ( ( ) ( ( ) ( ŲĨ / /
- 7. . ( ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ( ) () ( ( ( ) Ų§ / /
- 8. . ( ( ) ( ( ) ( ) ( ( ( ( ŲĻ / / ( ) )
- 9. . - Any which follows completely the of what has just preceded it. Of this there are types: / / / ŲĐ / /
- 12. . ( ) ( ) ŲĄŲĒ / /
- 13. . - in verbs. and and are both then it becomes . i.e. is / (from ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ŲĄŲĢ / / unless it has ). ( )
- 14. . ( ) ( ) ( ( ) ) ( ) ( ( ) ) - - ŲĄŲĪ For i.e. not taking their normal form as dictated by specific rules in Arabic Grammar: there are ; taking their normal form as dictated by Arabic Grammar: / /
- 15. . ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) - The ( ) here is not present/clear, but is therefore assumed/hypothetical. ( ( ) ŲĄŲĨ / / )
- 16. . ( ( ) ) ( ) ( ) - following in It is being written ( In , the - If the i.e. ŲĄŲĶ despite the transformation of is a ) formats in substitute of the He is writing . It was written He wrote ) is always dropped and the is / ( takes itâs place and becomes to . This is because is with necessary harakah changes. . , apply same (harakah changes) rules as above, and simply change the < / / , to itâs equivalent ,
- 20. . ( ( ( ) ) ) - ( ) Expresses the place/time the action of the verb is committed. ) : / / ( ( ( / / ) ( ( ( / ) ) / ( ( ) ( ( ( / / / / ( ) ) ) ) ) ( ( ) ( ŲĒŲ / / ( ( ( The plural form is ) / / / ) (
- 21. . ( ) ( ) ( - describes the instrument with which the action of the verb is carried out. ( ( ) ( ) ) ( ( - ) formed by adding ( ) ) ( ) ( ) to a noun. Denotes that a person/thing governed is related/connected with the original noun. If a noun has ending, this must be dropped before adding If a noun ends in ( / ) ( } ( ŲĒŲĄ . â , this is changed to before ending. { ) { ( ) ) / / ) }
- 22. . () ( ( ) ) ( ) ( ) - either/or. Four conditions of usage. Note, the second ( ) of the pair is always preceded by : ( ) ( ) () ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) () ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) () ( ) ( ) ( ŲĒŲĒ ) / /
- 23. . ( ) ( ) ( ) () ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) - definition indicating a precise noun â ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ( - in-definition indicates an indefinite noun - ŲĒŲĢ / / ) ( â ) ) ( )
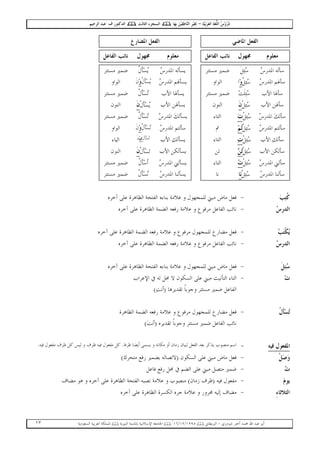
- 24. . ( ) ( ) [ =( + / ) ] - both (of), the two - . / - That is. Used for only / / there he is ! here I am ! - starts with an - constituted by ( ( ŲĒŲĪ ) ( ) < . { } >{ } { / / }
- 25. . - starts with a / - constituted by . ( ( ( ) ) / ( ) ) - derived noun indicating action of verb or itâs behaviour - â [(he is) writing] - derived noun indicating element undergoing action of verb - [written] - ( ( ) ( ) ) ( { } { } : ( : ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ( ( ) ( ) ( . ŲĒŲĨ ( ) ( ) ( ) ) : ) ( ) ) ( ( - ( / /
- 27. . If you have in a , then the st is a and the nd is a . If positions change then the changes: ( ) ( ) - if, whether, when, whenever. Also used with embodying a condition. Used mostly with . It is permissible for the answer to the condition ( must be prefixed by ( { , transforming in meaning to the future. ) to be . ) in the following situations: } ( ( (( )) ( (defective) } { ŲĒŲ§ } / / ( ) ( ( ) { ( ( ) (
- 28. . ( will not be if preceded by . However, the ) ( ( ) ( for it will be . ( ( ( } { ) ) ( ) ( ( ( ) â( ) ) ( ) ( ) ( ŲĒŲĻ ( } { The ) ) / / )
- 29. . ( ) ( ) ( (! ) ) ( / ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) .( ) ( ) ( ) ŲĒŲĐ / / â
- 30. . . not; - he did not eat; he has not eaten ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) when, at the time when, as â ( ) ( ) ( ) . . . ( ) ( ) ( ) ŲĢŲ / / ( )
- 31. . . no! donât! - donât eat! ( ( ) ) . ( ( ) ( ) ) ( ( ) ) until, till, up to, as far as, to ( ) ( ) ( so that, in order that, that, in order to, to, as, with a view, for ( ) ( ŲĢŲĄ ) ( ) ( ) ( ) / / ) ( )
- 32. . - calling to one who is mourned or to a cause of pain (...) - one who is mourned, stricken to death. ( - to distress, afflict, pain, agonise, torment, make suffer ) - the cause of pain, the place where disease and suffering are located. â pain, ache, suffering, agony, anguish (...) ( ( ( ) show him your notebook - to show, present, bring out. ( . ( â ) show me your book ) . . .( . ) .( ) ( . ( ) ( ) ŲĢŲĒ ) / / ). ).
- 33. . - It is permissable to for the following conjugations, so long as it is not followed by sukoon ( ): () ( ) perhaps, maybe to hope (for), wish, to look forward to fear, fright, worry, anxiety, concern, care ( ) ( ) < ŲĢŲĢ < . / /
- 34. . ( ) ( ) .( ( ). .( ( ) ) ) ( ) .( ) ) â( ( ) ( ) ) ( ) ( ( ) ) ( { â ) / } ) ( ) / ( ) ( ) . ) ( ) â( ( ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ( ( ŲĢŲĪ / / ) )
- 35. . ( ( : ){ ( ) }: ( ) ( ( ) . ( ) ( ) ( ) ) ( ( ) ( ) ( ) ŲĢŲĨ / / ( ) :( ) ) . : . )
- 36. . . . : ( ) .( . . ( ) ) ( ) ( ) . : : ( ) ) ( ) . ( ) ( . : . . ŲĢŲĶ .( / / ): .

![.
-
in nouns
-
Modification/change reaching the end of nouns because of the change of the active element (denoting the end of
the noun changes according to the position of the word in the sentence). [
-
non-modification/change reaching the end of nouns because of the change of the active element (denoting the
end of the) word assumes one eternal/unchangeable form. [
In respect to nouns, all are
)
(
(
(
ŲĄ
]
except the following:
(
(
]
)
)
)
)
/ /](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carairabbhsarb-131129224845-phpapp01/85/Cara-i-rab-bhs-arb-1-320.jpg)


![.
-
The
in three areas within
which are not present/clear, but are therefore assumed/hypothetical. [
]
An
where the last letter is an (
), i.e.
:
]
.
[.
:
( )
-
An
where the last letter is a
and the letter before it is
, i.e.
.
]
[.
( )
Note the condition of the
without the
,(
â
):
( )
:
-
ŲĪ
/ /](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carairabbhsarb-131129224845-phpapp01/85/Cara-i-rab-bhs-arb-4-320.jpg)


















![.
(
)
( )
[
=( +
/
)
]
- both (of), the two -
.
/
- That is. Used for
only
/
/
there he is !
here I am !
- starts with an
- constituted by
(
(
ŲĒŲĪ
)
( )
<
.
{
} >{
}
{
/ /
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carairabbhsarb-131129224845-phpapp01/85/Cara-i-rab-bhs-arb-24-320.jpg)
![.
- starts with a
/
- constituted by
.
(
(
(
)
)
/
(
)
)
- derived noun indicating action of verb or itâs behaviour -
â [(he is) writing]
- derived noun indicating element undergoing action of verb -
[written] -
(
(
)
(
)
)
(
{
}
{
}
:
(
:
(
)
( )
( )
(
(
( )
(
)
(
.
ŲĒŲĨ
( )
( )
( )
)
:
)
( )
)
(
(
-
(
/ /](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carairabbhsarb-131129224845-phpapp01/85/Cara-i-rab-bhs-arb-25-320.jpg)











