Carbohydrates
- 1. B.Sc BIOTECHNOLOGY – Semester II SRI HARSHINI DEGREE & PG COLLEGE. ONGOLE-523001. Dr Vemu Anil kumar M.Sc, Ph.D.nanobiotechanil@gmail.com
- 2. Definition • Optically active Polyhydroxy Aldehydes or Ketones, or substance that yield one of these compounds on hydrolysis. • Hydrates of Carbon. • Also known as Saccharides. • Contain Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen. • Contains Carbonyl group : Aldo (–CHO) or Keto (=O). At least Two Hydroxyl group (– OH). • Simplest carbohydrate. • Aldo form : Glyceraldehyde. • Keto form : Dihydroxy acetone.(Now its not considered )
- 3. Classification Sugars (Saccharide) Mono saccharides Aldoses Aldo triose Aldo tetrose Aldo pentose Aldo hexose Ketoses Keto triose Keto tetrose Keto pentose Keto hexose Oligo saccharides Di Tetra Tri Penta Non sugars (PolySaccharide) Homo Hetero Neutral sugars Muco polysaccharides
- 4. MONOSACCHARIDES • Simple sugars with a free Aldehyde or Ketone, and two or more Hydroxyl groups. • Sweet in taste, Soluble in water, Optical activity – mutarotation, • Crystalline. • Contain 3 to 10 carbon atoms. • General formula - (CH2O)n. • Also called as Reducing agents or sugars. • Contain one or more asymmetric Carbon atoms. C attached to 4 different groups. • Based on number of C atoms – Triose, Tetrose, Pentose, Hexose….. • Based on Carbonyl group – Aldehyde : Aldoses. Ketone : Ketoses.
- 5. • Aldoses have suffix – ose. • Ketoses have suffix – ulose.
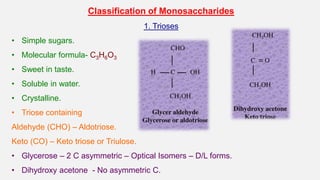
- 6. Classification of Monosaccharides 1. Trioses • Simple sugars. • Molecular formula- C3H6O3 • Sweet in taste. • Soluble in water. • Crystalline. • Triose containing Aldehyde (CHO) – Aldotriose. Keto (CO) – Keto triose or Triulose. • Glycerose – 2 C asymmetric – Optical Isomers – D/L forms. • Dihydroxy acetone - No asymmetric C.
- 7. 2. Tetroses • Simple sugars. • Molecular formula- C4H8O4 • Sweet in taste. • Soluble in water. • Crystalline. • Tetrose containing Aldehyde (CHO) – Aldotetrose. Keto (CO) – Keto triose. • Erythrose – 2 and 3 C asymmetric – Optical Isomers – D/L forms. • Erythrulose - 3 C asymmetric.
- 9. 3. Pentoses • Simple sugars. • Molecular formula- C5H10O5 • Sweet in taste. • Soluble in water. • Crystalline. • Tetrose containing Aldehyde (CHO) – Aldopentose – 3 asymmetric Carbons. Keto (CO) – Ketopentose / pentulose – 2 asymmetric Carbons. • Ribose, Ribulose, Xylose, Xylulose…
- 11. 4. Hexoses • Simple sugars. • Molecular formula- C6H12O6. • Sweet in taste. • Soluble in water. • Crystalline. • Tetrose containing Aldehyde (CHO) – Aldohexose – 4 asymmetric Carbons. Keto (CO) – Ketohexose / Hexulose – 3 asymmetric Carbons. • Glucose, Galactose, Mannose, Fructose…
- 13. 9700702939