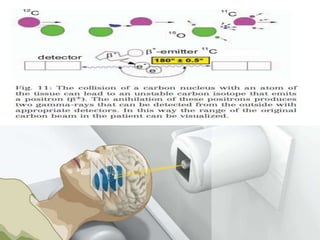
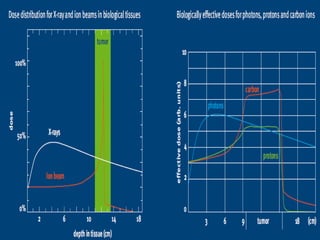
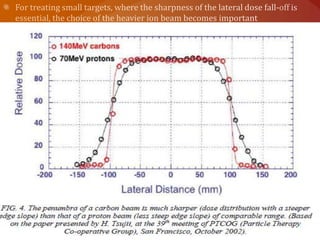
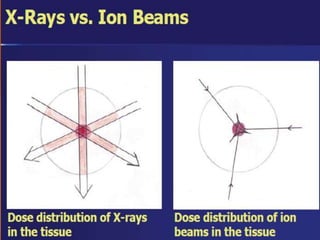
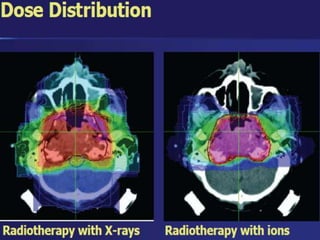
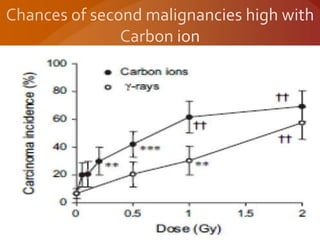
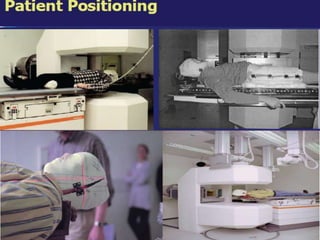
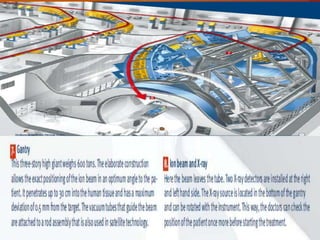
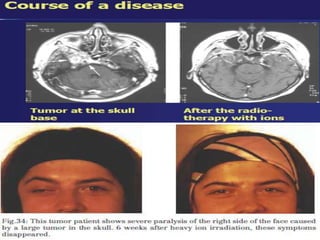
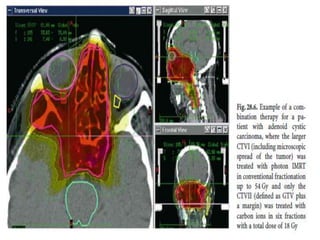
Carbon ion therapy
- 2. Heavy ion therapy ions heavier than helium ions
- 4. the NIRS (National Institute of Radiological Sciences) in Chiba, Japan using the HIMAC (Heavyâion Medical Accelerator in Chiba) synchrotron, the GSI (Helmholtzzentrum fÞr Schwerionenforschung GmbH) in Darmstadt, Germany followed ; Hyogo Ion Beam Medical Center, Japan and the Institute of Modern Physics, China started carbon-ion therapy in 2002 and 2006, respectively. The Heidelberg Ion Beam Therapy Center (HIT) in Germany started proton/carbon ion therapy in 2010 while the following four synchrotrons are currently under construction
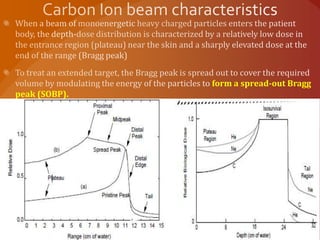
- 5. form a spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP).
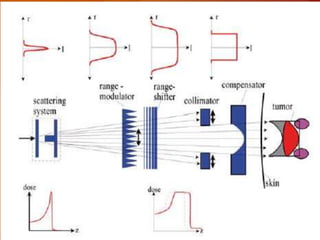
- 24. Principle of the passive dose delivery system used for proton and ion beams. Shown is the incoming broadened beam that is modulated in depth. The variable range shifter has to shift the modulated dose to the desired depth, whereas collimator and compensator are patient specific devices. The lines in the body represent the distal dose fall-off that can be shifted in depth with the range shifter Principle of the active raster scan system used at GSI for carbon ions. A small pencil beam is scanned in vertical and horizontal direction, using two pairs of scanner magnets. By switching the energy of the synchrotron, the position of the Bragg peak can be chosen so that each scanned area is adapted to the extent of the target in depth