Carpentry
- 1. WORKSHOP MANUFACTURING PRACTICES SEMESTER ĻC II CARPENTRY BY MANOJ KUMAR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SCE SAHARSA DATE 07-04-2020
- 2. CARPENTRY ? What is carpentry? Carpentry is a skilled trade and a craft in which the primary work performed is the cutting, shaping and installation of building materials during the construction of buildings, ships, timber bridges, concrete formwork, etc. Strictly speaking, carpentry deals with all works of a carpentry such as roofs, floors, partitions, etc. of a building. Another terms joinery deals with the making of doors, windows, stairs and all interior fitments for a building. carpentry shop deals with the timber, various types of tools and the art of joinery. ? Timber and wood Timber is the basic material used for any class of wood working. The term timber is applied to the trees which provide us with wood. 2
- 3. ?Hard and soft wood ? Exogenous types are also known as outward growing trees which produce timber for commercial use. ? Endogenous trees are also known as inward growing. 3
- 4. ? Seasoning of wood (a) Natural seasoning (b) Artificial seasoning Advantages: ? Lighter in weight ? More resilient ? Less liable to twist, warp and split ? Strength, hardness and stiffness increases 4
- 5. 1. Marking and measuring tool 2. Cutting tool 3. Planning tool 4. Boring tool 5. Striking tool 6. Holding and miscellaneous tool ? CARPENTRY TOOL ? Defects in timber knot 5
- 6. 1. Marking and measuring tools (a) Rules (0-60 cm) Steel rule Foldable rule Flexible steel rule 6
- 7. (b) Try square (used for marking and testing angles of 90) Stock Blade (150 to 300 mm) (c) Mitre square ? Used to measure an angle of 45 ? Maximum blade length 300 mm 7
- 8. (d) Combination square Square head Protractor head Centre head Rule/blade 8
- 9. 9
- 10. 2. Cutting tool (b) Rip saw: used for cutting along the grain in thick wood ? used for cutting along the grain in thick wood ? Made of high grade tool steel ? About 700 mm long ? 3 to 5 points or teeth per 25 mm (a) Adze ? used for rough cutting, squaring, to chop inside curves and to produce concave surfaces ? Its outer face is convex, inner face concave and edge is bevelled to form a cutting edge ? It is made of carbon steel. 10
- 11. (c) cross-cut saw (hand saw) ? Used for cutting across the grain in thick wood ? 600 to 650 mm long ? 8 to 10 teeth per 25 mm (d) Panel saw ? 500 mm long ? 10 to 12 teeth per 25 mm ? It has finer blade & mostly used for fine work 11
- 12. (e) Tenon or back saw ? Used for cross cutting when finer and more accurate finish is required ? 250 to 400 mm long ? 13 teeth per 25 mm equilateral triangle shaped teeth sometimes called Ą°pegĄą teeth (f) Dovetail saw ? A smaller version of Tenon ? Used where high accuracy needed ? 200 to 350 mm long ? 12 to 18 teeth per 25 mm 12
- 13. (g) Bow saw ? Narrow blade used ? The blade is held in tension by twisting the string with a smaller wooden lever ? Used for cutting quick curve 13
- 14. (h) Coping saw ? Similar blade as bow saw ? The blade is tensioned by screwing the handle ? Used for cut small radius curve (i) Compass saw ? Narrow tapering blade ? 250to 400 mm long ? Used for sawing small curve in confined space (j) Pad or keyhole saw ? Smallest saw ? 250 mm long ? Used for interior cuts or cutting key holes 14
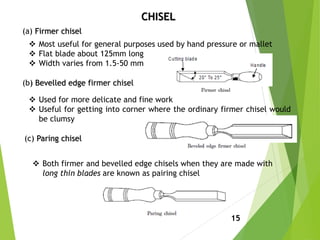
- 15. CHISEL (a) Firmer chisel ? Most useful for general purposes used by hand pressure or mallet ? Flat blade about 125mm long ? Width varies from 1.5-50 mm (b) Bevelled edge firmer chisel ? Used for more delicate and fine work ? Useful for getting into corner where the ordinary firmer chisel would be clumsy (c) Paring chisel ? Both firmer and bevelled edge chisels when they are made with long thin blades are known as pairing chisel 15
- 16. (d) Mortise chisel ? Used for chopping out mortices ? Very nearly square in cross section ? Withstand heavy blows from a mallet (e) Gouges ? Chisel with curved section ? Inside or outside grounded ? Inside grounded gouges are called scribing gauges ? Outside ground gouges are called firmer gouges 16
- 17. 3.Planning tool Jack planes Smoothing plane Trying plane Rabbet plane 17
- 19. 19 Spokeshave plane ? Spokeshave a wood shaving tool used for fine finishing. Its small bearing surface makes it perfect for shaping edged work and fine tuning curves.
- 20. 20 ? Router plane is a plane used for smoothing out sunken panels, and more generally for all depressions below the general surface of the pattern. It planes the bottoms of recesses to a uniform depth and can work into corners that otherwise can only be reached with a chisel.
- 21. 4. Boring tool Used to make round holes in wood. ? Types of bits ? Gimlet ? Bradawl ? Auger Bradawl and Gimlet 21
- 23. 5. Striking tool (a) Mallet ? Wooden-headed hammer of round or rectangular cross-section ? Used for giving light blows to the cutting tool like chisels and gouges (b) Warrington hammer ? The face of hammer is hardened, tempered and ground slightly convex ? The handle is made of wood and is oval in cross-section to have a comfortable grip ? The head is forged from tool steel and is obtainable in various weights. (c) Claw hammer 23
- 24. 6. Holding & supporting tool (a) Work bench 24
- 25. (b) Carpenter vice Jaw Trigger for quick opening 25
- 26. (c) Bar clamp ? Clamps are commonly used in pairs in gluing up operations at the final assembly of wood joinery work ? Both jaws of the sash clamp are generally made of malleable cast iron which is tougher and less brittle than ordinary cast iron 26
- 27. (d) G or C clamp 27
- 28. 6. Miscellaneous tools (a) Raps and files : used for cleaning up some curved surface 28
- 29. (b) Scraper and Glass-paper (c) Pincer 29
- 30. CARPENTRY PROCESSES ? Marking ? Sawing ? Planning ? Chiselling ? Boring ? Grooving ? Rebating ? Moulding 30
- 31. COMMOM WOOD JOINTS (a) (b) (c) (d) 31