Case presentation on AUTOIMMUNE HEP final.pptx
- 1. MORNING MEETING Dr.Hadia nasir Unit 3
- 2. Presenting complain ’üĄ 11-year-old female child, vaccinated, weighing 20 kg resident of Larkana admitted with c/o : Abdominal distention ŌĆō 1 year blood in stoolŌĆō 2 episodes
- 3. HOPC
- 4. ’üĄ BIRTH HISTORY : Non significant. ’üĄ IMMUNIZATION HISTORY :Completely vaccinated according to EPI schedule. ’üĄ NUTRITION HISTORY : Consumes up to 1200 kcal per day including dairy, vegetables and meat. No history of fava bean consumption in diet. ’üĄ DEVELOPMENTAL HISTORY : Developmentally normal
- 5. ’üĄ PAST MEDICAL HISTORY : No significant history of hospital admissions and IV medications before this illness. ’üĄ PAST SURGICAL HISTORY : Non significant. ’üĄ FAMILY HISTORY : 6th product of consanguineous marriage. All elder siblings are alive and healthy. Mother had history of hepB which was treated before her birth. ’üĄ DRUG AND TRANSFUSION HISTORY : No history of blood transfusions. No significant history of prolonged use of painkillers , anti epileptics or any other drug.
- 6. ’üĄ PERSONAL HISTORY : sleep and eating habits were normal before this illness. Normal bowel and bladder habits. Drinks unboiled tap water. ’üĄ SOCIOECONOMIC HISTORY : belongs to middle class family, lives in well ventilated house.
- 7. GENERAL PHYSICALEXAMINATION ’üĄ Young girl lying on bed well oriented with following vitals: ’ü▒ HR = 84b/m ’ü▒ RR= 24b/m ’ü▒ BP = 100/60mmhg ( 50th centile) ’ü▒ SO2= 96% at room air Patient has A+, CL+, E+ at the time of admission while No signs of J-,CY-, LN-,D- ’āś Weight = 30kg (-1.23 SDS) ’āś Height =130cm ( -2.22 SDS)
- 8. HEADTO TOE EXAMINATION ’üĄ Clubbing positive ’üĄ Nail & palmer crease pale ’üĄ Purplish discoloration of skin at both right lumber regions ’üĄ No cervical lymphadenopathy. ’üĄ No gum bleeding or oral ulcer. ’üĄ No jaundice ,Palmar erythema, Asterixis, koilonychias, leukonychia, Spider navi, Caput medusa ,Telangiectasia ’üĄ BCG scar present. ’üĄ All joints normal with no tenderness & swelling ’üĄ No bruising or bleeding seen With no spider nevi seen
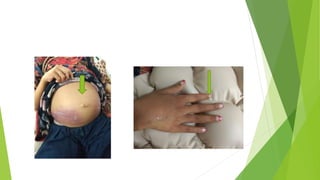
- 10. ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION ’üĄ on inspection abdomen is grossly distended with slit like centrally placed everted umbilicus ,abdomen is moving with respiration. Purplish discoloration of both sides of lower abdomen is present extending to back , cough reflex is -ve ’üĄ on palpation abdomen is soft distended mildly tender and abdominal grith is 40cm ’üĄ visceromegaly not appreciated due to massive ascites ’üĄ on percussion : fluid thrill and shifting dullness is positive ’üĄ on auscultation gut sounds audible with no abdominal bruits ’üĄ perineum and genital exam is unremarkable with no pubic hair
- 11. . ’üĄ CNSEXAMINATION ’üĄ CVSEXAMINATION ’üĄ CHESTEXAMINATION 6/4/2023 11 UNREMARKABLE
- 12. DIFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS : ’üĄ CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE SEC TO : ’üČ METABOLIC LIVER DISEASE ( WILSON ) ’üČ AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS ’üČ CHRONIC VIRAL HEPATITIS ( HEP B OR HEP C)
- 13. INVESTIGATIONS
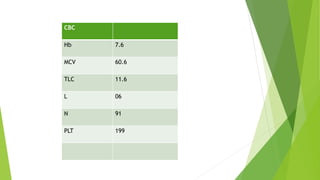
- 14. CBC Hb 7.6 MCV 60.6 TLC 11.6 L 06 N 91 PLT 199
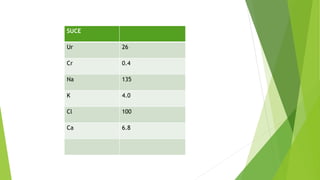
- 15. SUCE Ur 26 Cr 0.4 Na 135 K 4.0 Cl 100 Ca 6.8
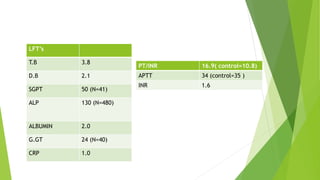
- 16. LFTŌĆÖs T.B 3.8 D.B 2.1 SGPT 50 (N=41) ALP 130 (N=480) ALBUMIN 2.0 G.GT 24 (N=40) CRP 1.0 PT/INR 16.9( control=10.8) APTT 34 (control=35 ) INR 1.6
- 17. Ultrasound abdomen ’üĄ Liver small in size with heterogenous texture and irregular margins ’üĄ Portal veins dilated but patent ’üĄ Multiple abnormal vascular channels seen in epigastric , peripancreatic and peri splenic area. ’üĄ Massive ascites.
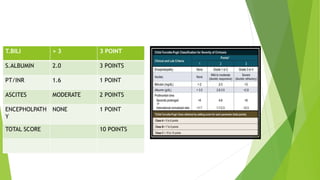
- 18. T.BILI > 3 3 POINT S.ALBUMIN 2.0 3 POINTS PT/INR 1.6 1 POINT ASCITES MODERATE 2 POINTS ENCEPHOLPATH Y NONE 1 POINT TOTAL SCORE 10 POINTS
- 19. Workup for Wilson disease : ’üĄ Serum ceruloplasmin : 0.29 age 4-12yrs ( 0.25-0.45 ) ’üĄ Urinary copper : 19.08 ug/Day normal : (less than 60ug/day )
- 20. Viral markers ’üĄ Anti HCV = non reactive ’üĄ HbsAg = non reactive
- 21. ANA PROFILE : ’üĄ ANA = POSITIVE ’üĄ ASMA = POSITIVE
- 22. COOMBŌĆÖS TEST Direct coombs test : positive.
- 23. IMMUNOGLOBULIN : SERUM IgG : 24.7 (6.5-15 g/dl )
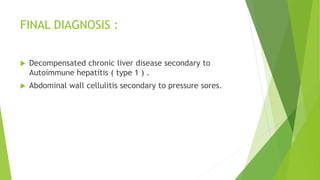
- 24. FINAL DIAGNOSIS : ’üĄ Decompensated chronic liver disease secondary to Autoimmune hepatitis ( type 1 ) . ’üĄ Abdominal wall cellulitis secondary to pressure sores.
- 25. GASTRO OPINION ’üĄ Gastroenterology was taken on board , they advised to continue conservative management . ’üĄ Add tablet rifaximine and tab Aldactone. ’üĄ Liver biopsy in plan.
- 26. MANAGEMENT IN WARD ’üĄ Admit in unit 3 ’üĄ IV line maintained ’üĄ IV fluids started ’üĄ IV antibiotics started ’üĄ Inj vit K and omeprazole started. ’üĄ Syp duphalac 30ml HS ’üĄ Tab Aldactone 25mg 1+1+1 ’üĄ Tab rifixamine 500mg 1 OD
- 27. ’üĄ Findings are likely of cirrhosis of liver with portal hypertension without portal venous thrombosis.
- 29. AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS ’üĄ Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disease of unknown cause, characterized by continuing hepatocellular inflammation and necrosis and has a tendency to progress to cirrhosis. ’üČ Autoimmune hepatitis may present as acute or chronic hepatitis or as well-established cirrhosis, although in rare cases it presents as fulminant hepatic failure. ’üČ Autoimmune hepatitis can present at any age and in all ethnic groups, but it occurs predominantly in women. For type 1 autoimmune hepatitis, the female to male ratio is 4:1, but for type 2 autoimmune hepatitis, the ratio is 10:1
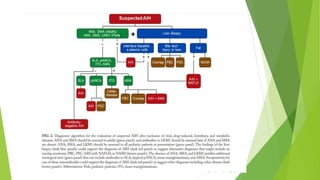
- 30. TYPES OF AIH :
- 32. DIAGNOSIS : ’üĄ Evidence for Autoimmune hepatitis include: ’üĄ Elevation in transaminases. ’üĄ Association with hypergammaglobulinemia and the presence of a rheumatoid factor ’üĄ Circulating autoantibodies (ie, nuclear, smooth muscle, thyroid, liver-kidney microsomal, soluble liver antigen, hepatic lectin) ’üĄ Hepatic histopathologic lesions composed predominantly of cytotoxic T cells and plasma cells ’üĄ Association with other autoimmune diseases ’üĄ Response to steroid and/or immunosuppressive therapy
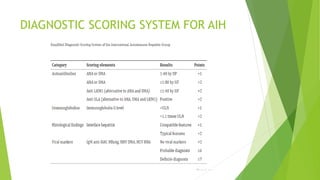
- 34. DIAGNOSTIC SCORING SYSTEM FOR AIH
- 35. NON INVASIVE FIBROSIS ASSESMENT : ’üĄ FibroTest (APRI) : AST/Platelet ratio index ’üĄ Fibroscan (VCTE ) ’üĄ MRE
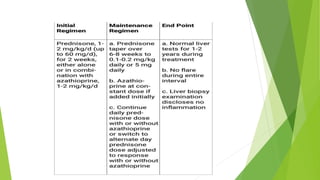
- 39. TREATMENT END-POINTS : Patient may achieve 1 of 4 end points ’üĄ Remission: Remission is indicated by the absence of symptoms, normalization of aminotransferases, and histologic improvement to normal or minimal inflammatory activity on liver biopsy. ’üĄ Treatment failure: Treatment failure is defined as deterioration in a patient's clinical condition, laboratory tests, or histologic features during therapy. ’üĄ Incomplete response: Incomplete response is defined as an improvement that is insufficient to satisfy remission criteria. It is estimated to occur in 13% of patients. ’üĄ Drug toxicity: Drug toxicity may occur. Patients must be tapered off from the culprit medication. Some patients successfully achieve treatment goals on alternative medications.
- 40. ’üĄ RELAPSE Relapse occurs in 50% of patients within 6 months of treatment withdrawal and in 80% of patients within 3 years of treatment. Reinstitution of the original treatment regimen usually induces another remission; however, relapse commonly recurs after a second attempt at terminating therapy. The major consequence of relapse and re-treatment is the development of drug-related complications, which occurs in 70% of patients
- 41. PROGNOSIS : ’üĄ Without treatment, approximately 40% to 50% of the individuals with severe disease will die within 6 months to 5 years. Treatment with steroids has dramatically changed the course of the disease. Most patients respond to therapy and the 10-year survival rate is approximately 83.8% to 94%. ’üĄ The long-term outlook after liver transplantation is excellent, with 10-year survival rates reported as greater than 70%.Positive autoantibodies and hypergammaglobulinemia tend to disappear within 2 years of transplantation. ’üĄ Treatment failure, Relapse and need for long term Maintenance is common in type 2 AIH. So, compared to type 1 AIH itŌĆÖs prognosis is poor.